Buy Solar Stocks on the Dip
Now that the stock market appears destined to soon enter correction territory, I have started searching for industries and companies that I want to buy at the bottom. The solar industry is at the top of that list.
Solar has a been a long time in coming. For decades, it was a niche energy source with very narrow following among scientists, the military, and Greenpeace activists. The problem was that it was just too expensive. It made sense only to those with unlimited budgets (the army), pursuing a political agenda (environmentalists), or when there was no other alternative power source (outer space).
Ironically, what really got the solar bandwagon moving was oil, which saw prices soar to $150 a barrel in 2008. That dramatically raised the breakeven cost of solar. Projects that only existed on paper suddenly made economic sense.
Then, Barack Obama was elected president. One of his first moves was to make available over $100 billion in subsidies for alternative energy projects of every description. All of a sudden, it was off to the races for solar.
This led to the first solar stock market boom in 2009. Some highflyers, like First Solar (FSLR) rose tenfold (it was a favorite ?BUY? recommendation of mine at the time). They were aided by states like sun-drenched California that mandated 20% of power consumption comes from alternative sources, to rise to 30% in the 2020?s.
This created an enormous solar and wind infrastructure throughout the west to meet the state?s voracious needs. Some 29 other states have passed similar laws with varying targets.
I inspected the centerpiece of the state?s solar strategy, flying over the gigantic Ivanpah facility in a wheezing, rented Cessna 172 in the barren, baking, but beautiful Mojave Desert. I brought plenty of extra water bottles and a compass in case I crash-landed and had to walk home.
It all looks like a film set from a science fiction movie, with 347,000 concave mirrors placed in enormous circles focusing light on hot water boilers atop three 460-foot towers. The plant opened in February, 2014 and is generating 377 megawatts of electricity, enough to power 140,000 homes in the Los Angeles area.
Planned a decade ago, the technology is now so primitive that it is unlikely to be ever used again. Far more advanced than film, solar is now taking over the world.
Then China came in and spoiled the party. Overproduction by poorly managed and weakly financed Chinese solar firms using inferior technologies quickly glutted the global market, and solar prices crashed by 80% or more. Many companies did not survive, such as the San Francisco Bay Area?s Solyndra, which defaulted on some $536 million in federal government loans (the feds got $143 million back).
This triggered a Darwinian clearing out of the industry, where only the strongest, the most innovative, and the most desperate survived. Technologies and efficiencies improved. The administration extended a helping hand by slapping hefty anti dumping tariffs on Chinese imports. The industry is lobbying for further restrictions. This all set the stage for a solar renaissance.
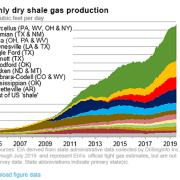
For the first time in history, solar is now cost competitive with conventional sources of power on a standalone, unsubsidized basis. As a result, the industry is exploding. In 2013, solar accounted for 29% of new power generation capacity in the US, after quasi-green natural gas, at 46%.
The advent of cheap solar roof panels and ?smart? electric meters in 43 states has enabled individuals to get in on the act. Such devices are now a standard feature on most new high-end homes. They genuinely do save money, especially when considering that utilities will bill you up to 50 cents per kilowatt hour for prime time consumption, compared to their average rate of 11 cents. There have been over 200,000 such installations in the past two years, half in the Golden State.
The Department of Energy wants to see solar grow from 1% of total generation today to 27% by 2050. This is creating the basis for a gigantic industry in the future. Hence, my interest as a long-term equity investor.
All of this will require a complete rethinking of the electric utility industry (XLU), which still uses a volume based business model that has remained unchanged for 120 years. The more they sold the more money they made.
The utility industry has mixed feeling about the new solar revolution. They are going to have to evolve from distributors of power for a single, large, capital-intensive source to an intermediary operation that buys and sells power between millions of users and producers. This is easier said than done, as this is the most conservative of American industries. People run to utilities in a bear market for a reason.
Only the other hand, moving towards solar and other alternatives gets them out of the carbon burning business, either through using coal or oil as fuel. There is not a utility in the country that isn?t swamped by lawsuits from well represented consumers claiming that the byproducts from burning these traditional fuels gave them asthma, lung cancer, or worse.
In the end, it won?t be a desire to save the environment, or the expediency to appear politically correct that will convert utilities to solar. It will be hard-nosed business sense.
The buy on the dip list is fairly short. The front-runner in this industry is the aforementioned First Solar (FSLR), which has been an industry leader for two decades. Not only is their US business booming, they have a gigantic project in western China that promises to spin off profits for years to come.
SunPower Corp (SPWR) has the attraction of a $1 billion order backlog. Or you can go generic and buy the Guggenheim Solar ETF (TAN), which tacked on and impressive 270% last year.
I am less enamored with Solar City (SCTY). It is in the business of installing roof panels on homes. It takes advantage of generous government subsidies and the current ultra low cost of financing to keep prices low.
As much as I applaud the long-term vision of founder, Elon Musk, his association with the company has given it a cult like status. That is good for the share prices, but bad for valuations, which are through the roof. A greater dependence on subsidies could hurt them in the future.
Some formidable challenges lie ahead. In 2017 the government?s investment tax credit for solar drops from 30% to 10%. Other state subsidies are expiring as well. If this coincides with a recession that triggers a collapse in the price of oil, we could be in for another great clearing out.
Hopefully, by then, steadily advancing technology will further cut costs by half, making it possible for more firms to survive.
Until then, let the sun shine in!