Crypto Keys 101
Cryptography transcends use cases from intelligence agencies — military writing — decoding confidential text messages.
Public and private keys are an important part of Bitcoin (BTC) and other cryptocurrencies.
They allow you to send and receive cryptocurrency without requiring a third party to verify the transactions.
The basic concept behind the two-key system is the following:
- the public key allows you to receive transactions, while the private key is necessary to send transactions.
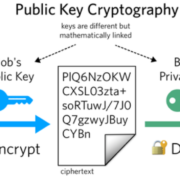
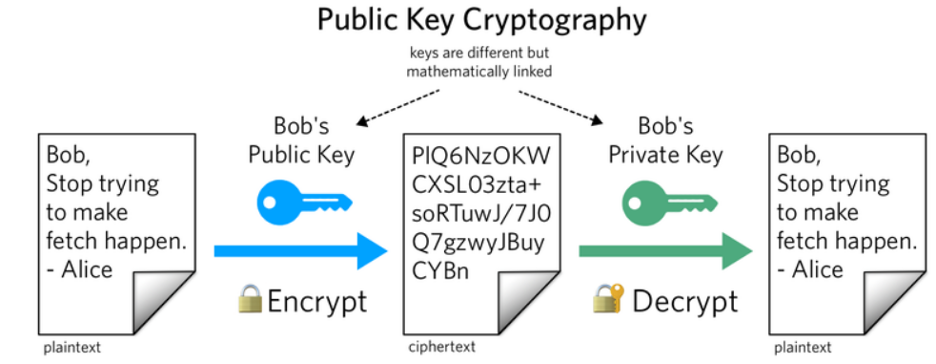
- Using two different keys (a public and a private key) is called asymmetric cryptography.
What Is a Public Key?
A public key allows you to receive cryptocurrency transactions.
It’s a cryptographic code that’s connected to a private key.
While anyone can send transactions to the public key, one needs the private key to “unlock” it and prove ownership of the cryptocurrency received in the transaction.
Therefore, freely sharing a public key is without risk.
While anyone can send the public key safely, someone would need the private key to unlock and access these sent funds.
What Is a Private Key?
A private key offers the ability to prove ownership or spend the funds associated with a public address. A private key is unique and can take many forms:
- 256 character long binary code
- 64-digit hexadecimal code
- QR code
- Mnemonic phrase
What Does It Mean to “Digitally Sign” a Transaction?
For a transaction on the blockchain to be complete, it needs to be signed. The steps for someone to send a transaction are:
- A transaction is encrypted using a public key. The transaction can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key.
- The transaction is signed using the private key confirming the transaction hasn’t been modified.
- The digital signature is generated by combining the private key with the data being sent in the transaction.
- Lastly, the transaction is verified as authentic using the accompanying public key.
Digitally signing a transaction means to prove the owner of the sent funds. Nodes check and authenticate transactions automatically. Any unauthenticated transactions get rejected by the network.
Where Are My “Private Keys?”
Private keys are in a cryptocurrency wallet, which is usually on a smartphone, desktop software, or a specialized hardware device.
Private keys are not on the cryptocurrency blockchain network.
If crypto assets are held on an exchange, then the exchange is the custodian of these private keys.
How public and private keys work together is essential to understanding how cryptocurrency transacts.
Buying crypto is effectively owning a private key that proves ownership of that cryptocurrency.
Since the record is stored on the blockchain, anyone can verify the individual as the owner with a specific public key.
Just remember that deferring to crypto exchange to hold a private key means a crypt holder trusts them with the security of protecting their crypto assets.
There is always the choice of taking custody of one’s own crypto in a hot or cold wallet.
Depending on the degree of comfort, philosophy, risk-tolerance, and amount, readers can make that decision for themselves.
Private keys are something that should never be shared.
And if one eschews their own private wallet for a custodial solution like an exchange, seek out a time-honored, trusted, dealing in large volume, and highly functional exchange instead of a marginal, half-baked exchange.