How Autonomous Driving Will Change the World
The car insurance industry will grapple with a massive existential crisis of epic proportions unless they evolve.
The looming threat is caused by technology and autonomous driving.
This is why parents usher their children into industries that won’t be blown up by technological disruption.
Removing the driver from the automobile industry could be the single most societal shift in our lifetimes.
This technology is getting ramped up as we speak and Waymo is the clear leader that is already collecting money for commercial rides in the state of Arizona.
Car insurers must wonder if they will be able to charge the same amount if there are no drivers?
The answer is that the liability will head from the driver to the manufacturer with companies like General Motors (GM) Tesla (TSLA) likely footing the bill while the passenger is likely to pay minimally.
We are headed towards another data war with insurers incentivized to dismiss the relevance of data in self-driving cars and devaluing it will cause the car companies’ bills to go higher.
Car insurance companies are also heavily investing in data analytics teams to see which part of the pie and how big of it they can get from self-driving technology.
This is uncharted territory.
Consensus has it that by 2035, 23 million autonomous vehicles or around 10 percent of today’s total will grace our roads and highways.
But I believe this number is understating the underlying series of generational factors at play.
It’s no secret that the majority of Millennials and Generation Z want to live in coastal urban cores participating in the heart of downtown activities mainly because of the chance to find a high-paying job.
This has exacerbated the migration from rural to metro areas around the country and sapping the need to drive or buy a car when Uber can become an almost perfect substitute.
And don’t forget that according to the latest data, cars are stationary 92% of the time signaling consumers’ intentions to stop purchasing and instead rent cars by the minute, hour, and day.
That is the beauty of the sharing economy and how self-driving cars will fit in.
This avant-garde model will emerge between 2035 and 2050 effectively reducing the value of owning a car, the self-driving car that will be bought, probably by the self-driving tech company itself, could constitute 50% of all vehicles sold globally.
The sum of the parts could mushroom into a $3 trillion addressable market, not only made up of the physical cars but the assortment of ancillary technology needed to fuel these cutting-edge machines.
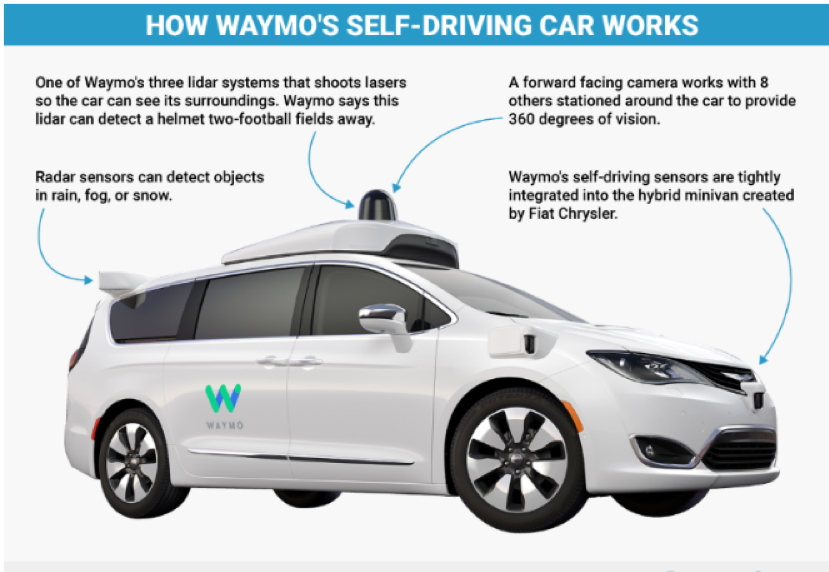
Alphabet’s (GOOGL) self-driving unit named Waymo run an onboard computer that processes images in real time using its machine learnings algorithm built by the industries’ best machine learning engineers.
However, not only do these firms need an army of artificial intelligence engineers to build the algorithms that are at the fulcrum of what they do, they also need other parts that fit into the puzzle such as lidar radar technology.
Lidar is an acronym for light detection and ranging, and the physical manifestation of this technology has so far been a cone-shaped object on top of the car's roof emitting laser pulses that bounce off objects allowing the car to recreate a 3D image of its surroundings.
The advancement of this technology and the potential production of scale will cut the cost of manufacturing this technology to less than $10 per sensor.
A full-blown lidar unit costs $75,000 at current market prices, but luckily the phenomenon of deflationary technology always drives the prices down to bare bones.
Cameras, sensors, cooling systems, and GPU chips are other products that must be heavily developed to accommodate self-driving technology.
GM is another prominent player in this field, and they have already outfitted close to 200 cars for testing.
The firm transformed its Orion Assembly plant in Michigan to accommodate cameras, lidar, and other sensors to its Chevrolet Bolt.
Whoever masters the lidar technology the quickest will have an inside edge to grab market share once this industry explodes and a lower insurance bill.
Waymo won’t be the only player usurping market share even though they are the brightest name out there, and there is room for others to crash the party.
GM invested $500 million into Lyft which could act as a gateway path into outfitting Lyft cars with GM’s proprietary technology.
Whoever specializes in the art of licensing self-driving technology to companies will ring in the register as well and the opportunities abroad are endless because emerging economies aren’t players in this industry.
GM’s Cruise AV has opened eyes with GM removing pedals or a steering wheel for this electric car.
It’s under testing in select cities and GM plans to integrate it into its ride-sharing program.
Investors are still waiting for companies to telegraph meaningful revenue to the top line, and this teething phase could cause the impatient to bolt for greener pastures.
Waymo has claimed it will be able to deliver up to 1 million trips per day by 2022 signaling that real top line revenue appears a few years off at the earliest.
This trade isn’t for the smash-and-grab type, but this is the future and it will be a slow crawl to broad-based adoption and material revenue.
The death of the car insurance industry is still years away and insurers still have time to save their bacon.
Data at the Association for Safe International Road Travel (ASIRT) shows that nearly 1.25 million people die in road crashes each year, on average 3,287 deaths a day and another 20-50 million are injured or disabled.
Technology is on the move and will try to correct this awful trend in road safety and human fatalities.
These years could be the high-water mark for car insurance and as self-driving technology continues to seep deeper into the public consciousness, it could snatch revenue from the coffers of the insurance companies.
But if these legacy companies become nimble and embrace the changes, they could potentially be at the vanguard of a highly lucrative industry charging the likes of GM and Tesla to ferry around humans.