How Free Energy Will Power the Coming Roaring Twenties
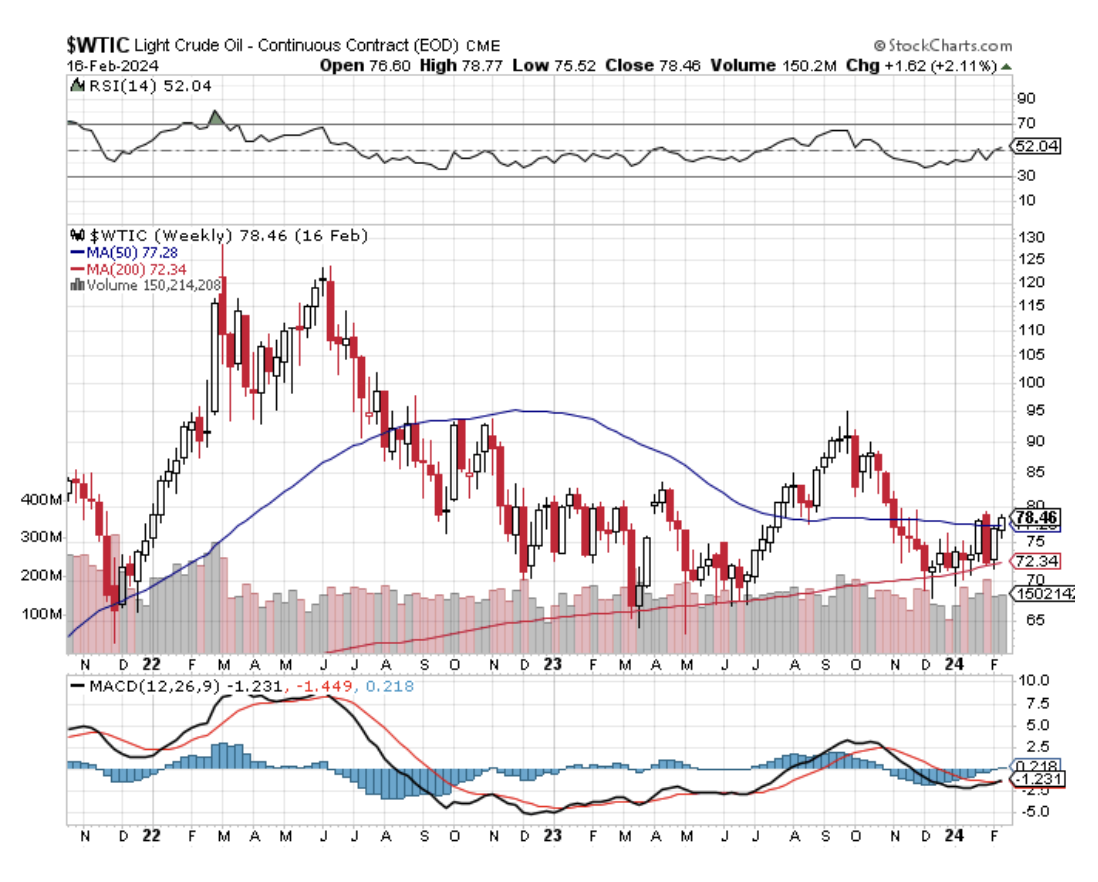
With the price of Texas tea barely scratching $78 a barrel today it is time to revisit the doomed future of this ancient energy source.
With energy stocks now trading like they’re having a going out of business sale, you have to wonder if the sector will ever come back. The short answer is short-term yes, long term no.
A key part of my argument for a new Golden Age to take place during the current Roaring Twenties is that the price of energy is effectively going to zero.
It may not actually make it to zero. I’ll settle for down 90%-95%, which is good enough for me.
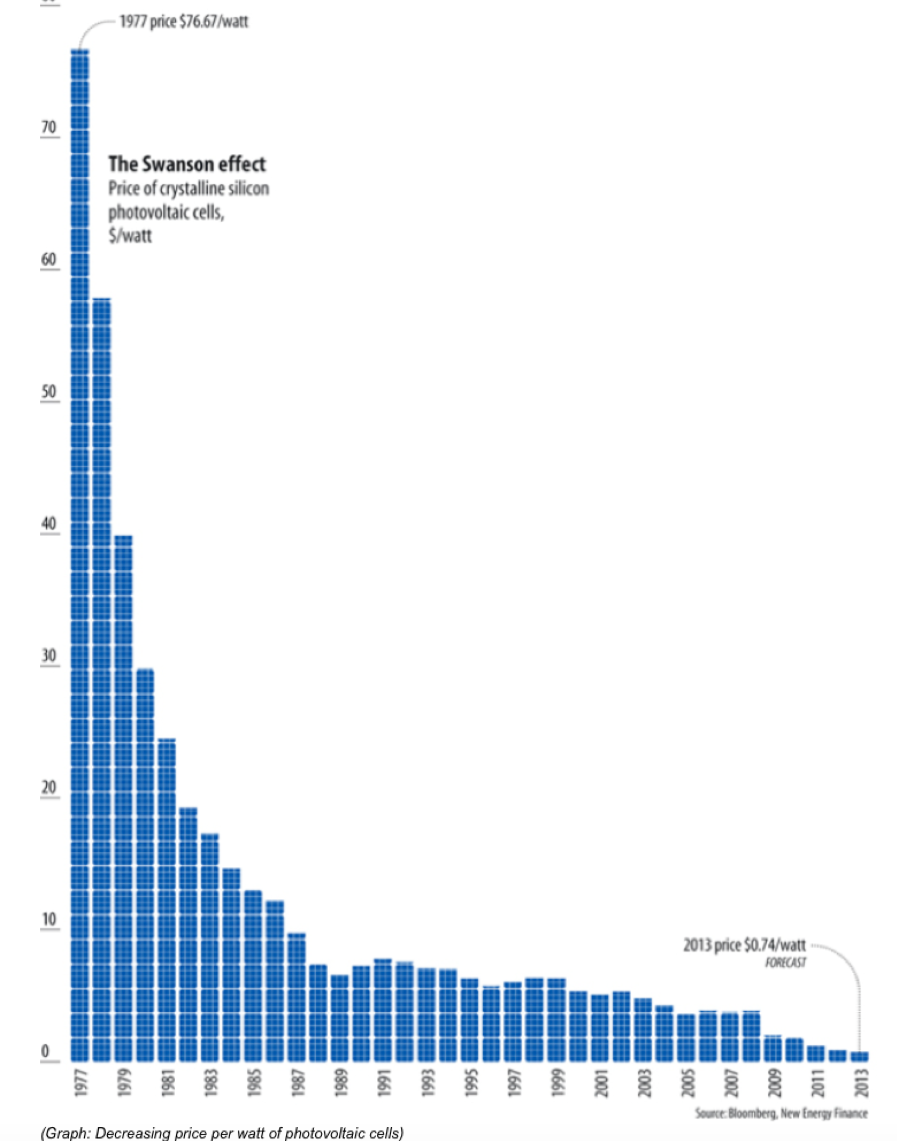
Take a look at the charts below.
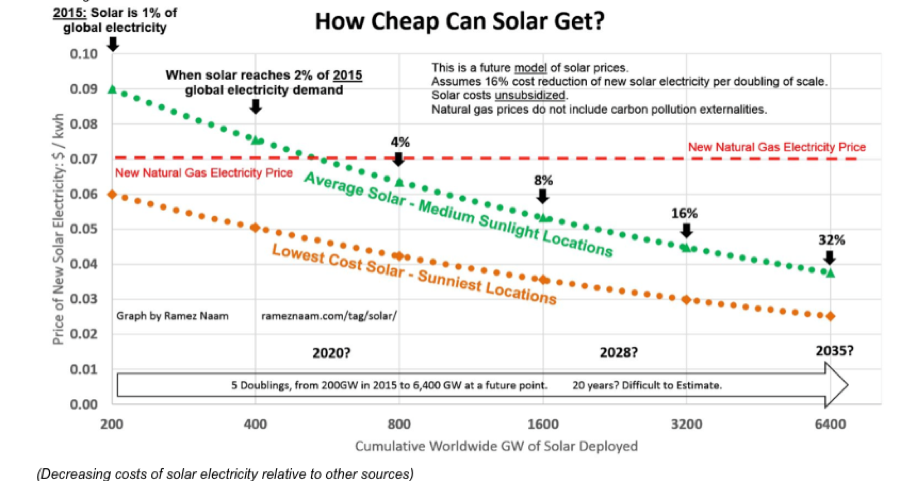
The first one shows how the price of a watt of solar generated electricity has plunged by 99.03% since 1977, from $76.67 to $0.74.
Just in the past six years, retail prices for completed solar panels dropped by a staggering 80%. That is cheaper than electricity supplies generated by new natural gas plants
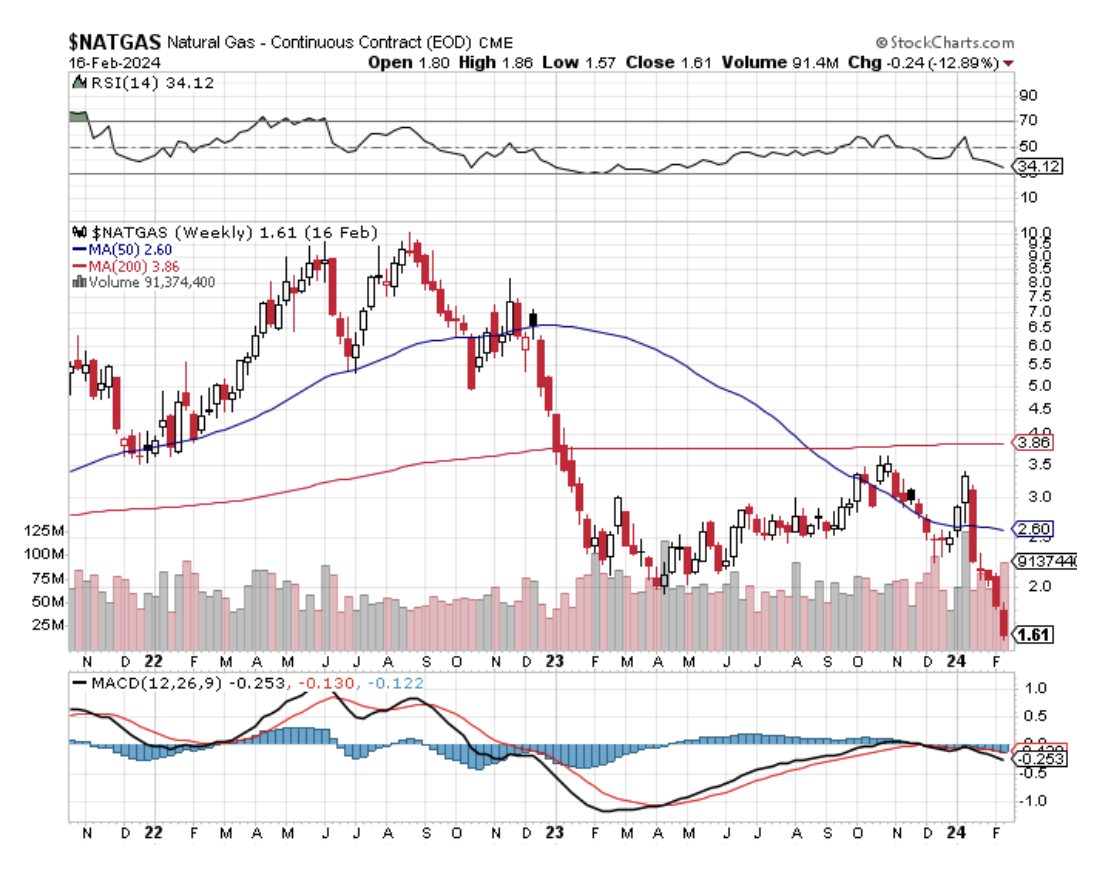
The potential price declines for natural gas from here are near zero. After all, it’s hard to improve on the near 100% burn rates you get with gas, and many producers are already losing money at current price levels of $1.61 per MM BTU.
Squeezing efficiencies out of our existing solar technology through improved software, production methods, chemistry, and design are nearly unlimited, are expected to drive solar costs by half down to 3 cents per kwh by 2035.
And here is the great shortcoming of all these wonderful predictions. Technology NEVER stays the same.
My own SunPower (SPWR) SPR A420 panels with their Maxeon solar cell technology deliver an efficiency of 20.1%, the best on the market available four years ago.
This means that they convert 22.5% of the solar energy they receive into electricity.
SunPower is now producing 25.1% efficiency panels in the lab. Another research lab in Germany, Fraunhofer, is getting 44.7%.
And my friends at the Defense Department tell me they have functioning solar cells delivering 70% efficiencies which they use in space. Whether they are economic and scalable is anyone’s guess.
(Warning: most cheap Chinese made solar cells have only lowly 15% efficiencies, so don’t be tricked by any great “deals”).
And this is how most long-term predictions fall short.
When I bought the system, I was warned the electricity production would fall 1% a year thanks to the natural degradation of the solar cells.
Instead, output has risen by 1% annually. Global warming is the only possibly explanation.
Not only do they assume that technology doesn’t change, they fail to account for dramatic improvements in other related fields.
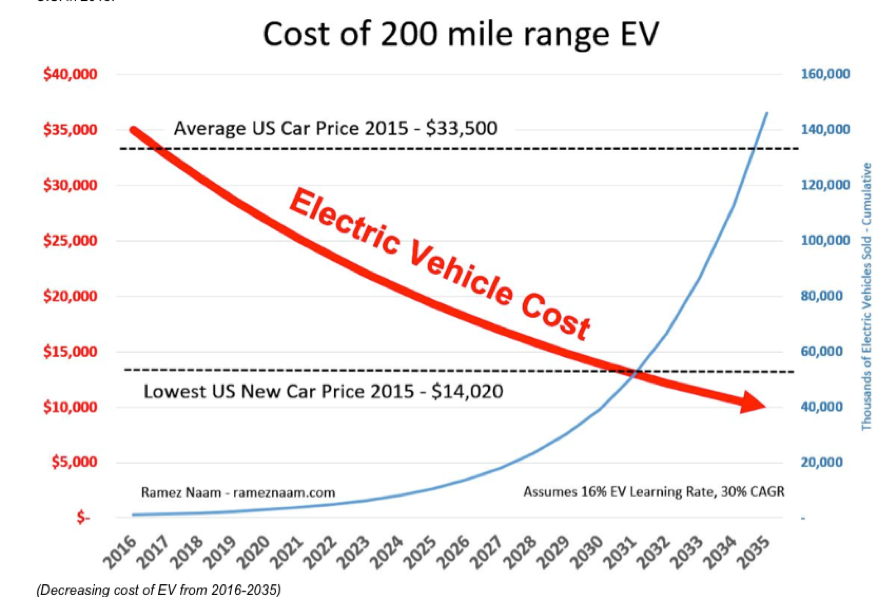
EV technology is a classic example. Battery costs are currently falling off a cliff.
When I bought the first Nissan Leaf offered for sale in California in 2010, the battery cost $833 per kilowatt. In 2012, I purchased a high-performance Tesla (TSLA) P85 Model S-1 at $353 per kilowatt.
When the Tesla 3 became available in 2017, the 60-watt battery will ran at $250 per kilowatt. Efficiencies gained through the economies of scale from the Sparks, Nevada Gigafactory took that under $100.
However, that is not the end of the story.
The car industry will start to move towards carbon fiber in five years, which has ten times the strength of steel at one-tenth the weight. The only issue now is mass production cost.
Some 67% of the weight of a Tesla S-1 is in the body, with the four motors at 13%, and the 1,200-pound lithium ion battery at 20%.
What happens when the body weight falls by 90%, to only 6.7% of total weight? The battery weight, and cost declines by two thirds. That cuts the effective cost of the battery to $66/kilowatt.
Add up all of this, and it is easy to see how energy costs can plunge by 90% or more. And it will happen must faster than you expect.
This has been the experience with memory costs, processor speeds, and hundreds of other digital technologies over the past 70 years. The cost of cotton yarn fell by 1,000 times during the 17th and 18th century, wiping out hundreds of existing industries but creating thousands more.
I could go on and on.
This is why the State of California has mandated to get 50% of its energy from alternative sources by 2030, and to ban the new sale internal combustion engines by 2035.
Some researchers believe a 100% target could be achieved. And it is doing this while closing its last remaining nuclear power plants at Diablo Canyon by 2030.
It already hit that target on several days this year when winter filled up all the dams, producing excess hydroelectric power.
As a result, the wholesale price of electricity fell to zero on those days. The grid was producing more power than could be consumed.
To say that free energy would be a game changer is a huge understatement.
The elimination of energy as a cost has enormous consequences for all companies. You can start with the energy intensive ones in transportation, steel, and aluminum, and work your way down the list.
My bet is that you won’t recognize the car industry in 10 years.
At a $66/kilowatt effective battery cost it will make absolutely no sense to build internal combustion engines in new cars.
Too bad Detroit is a decade behind in this technology.
Lose transportation, and you lose 50% of US oil consumption, or about 10 million barrels a day. Guess what that does to oil prices?
Goodbye Middle East. Go blow yourself up.
The profitability and efficiency of the entire economy will take a great leap forward, much like we saw with the mass industrialization that was first made possible by electricity during the 1920’s.
Share prices of all kinds will go ballistic.
Since energy costs will eventually fall effectively to near zero, that wipes out the present business model of the entire electric power, coal, oil, and gas industries, about 10% of US GDP.
Their business models will be reduced to trying to sell something that is free, like air.
Dow 250,000 anyone?
Goodbye Electric Power Bills
Getting Ready for the 2020’s