If Bonds Can’t Go Down, Stocks Can’t Either
The U.S. Treasury bond market has suddenly ground to a halt, puzzling traders, investors, and hedge fund managers alike.
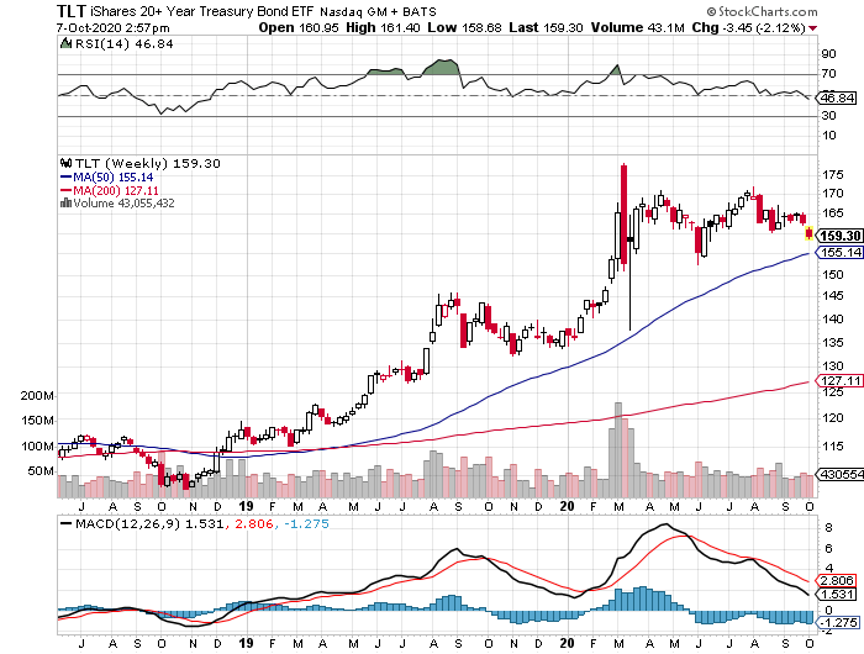
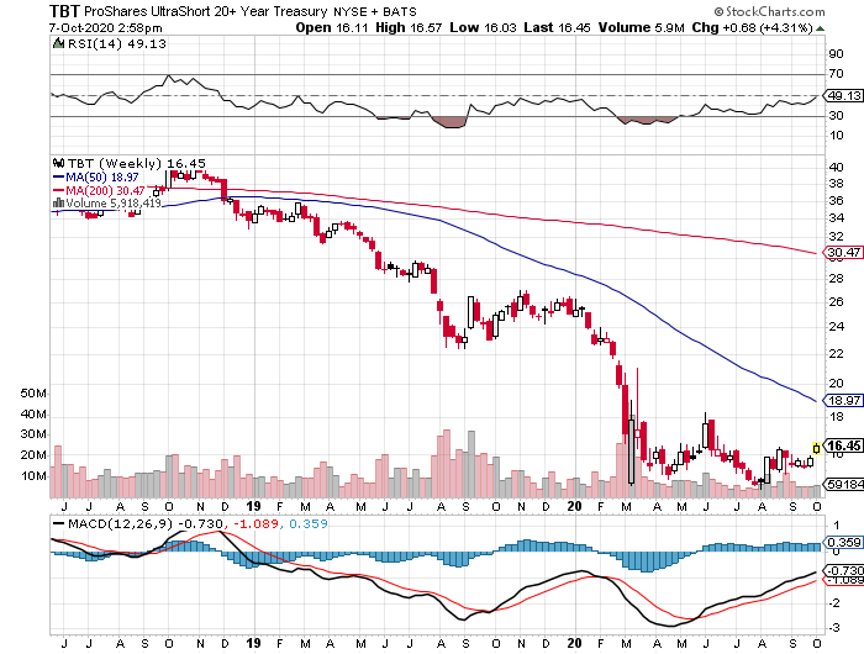
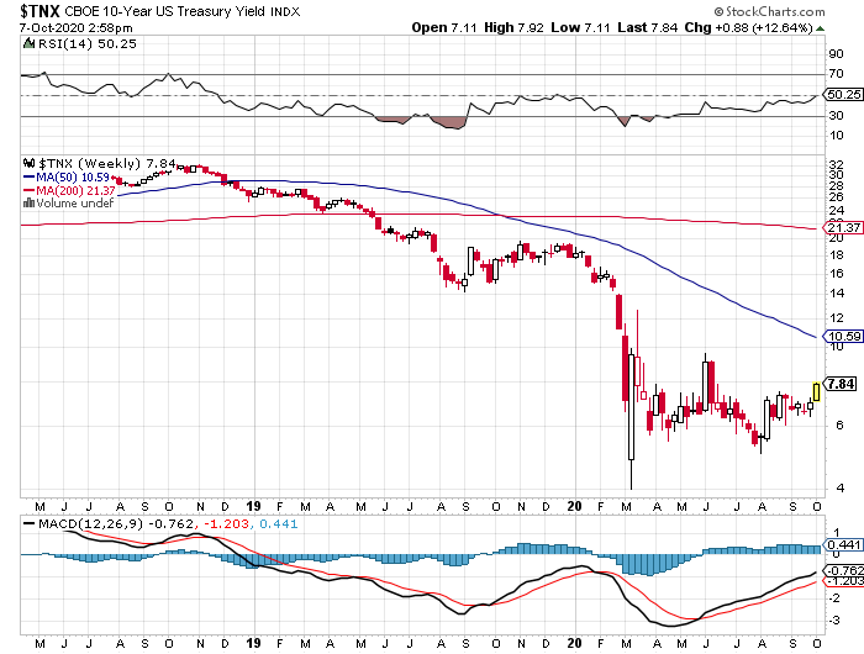
Today, the yield on the 10-year Treasury bond (TLT), (TBT) traded as low as 0.77%.
This is despite the U.S. economy delivering a horrific negative GDP growth during Q2. Growth is expected to rebound to 2-5% in Q3, depending on if there is another stimulus package from Washington, or not. 2021 could bring economic growth as high as an astronomical 10%.
If I blindfolded any professional money manager, told him the above and asked him where the 10-year Treasury yield should be, most would come in at around the 5% level.
So what gives?
I have put a great deal of thought into this and the answer can be distilled down to two letters: QE.
Global quantitative easing has created about $30 trillion in new money over the past 10 years. It has not been spent, it hasn’t disappeared, nor has it gone to money heaven. It is still around.
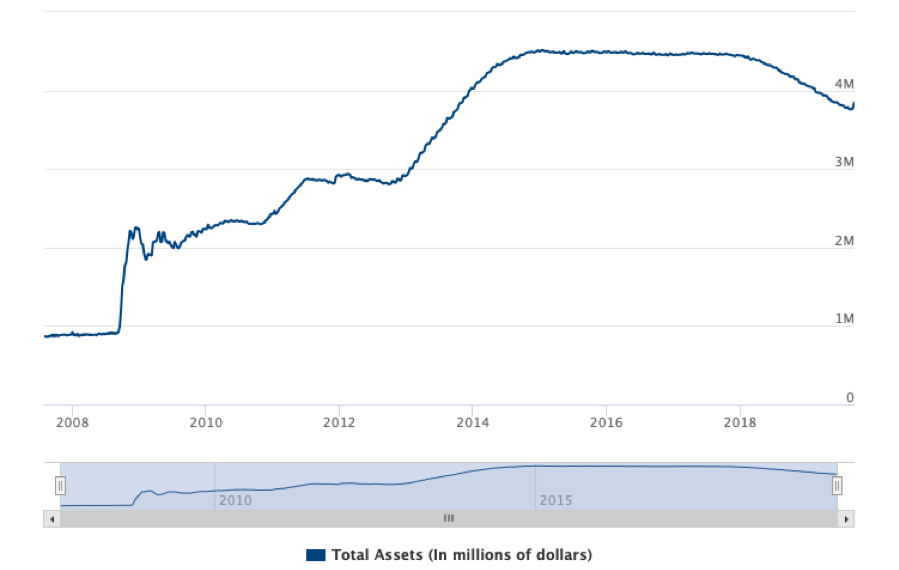
The U.S. Federal Reserve, the first to start QE in November 2008 during the Great Recession, ended it in October 2014. From start to finish, it created $4.5 trillion in new money. Over the past five years was wound down to $3.8 trillion by letting debt on its balance sheet mature.
Enter the pandemic. The expectation is that the new round of QE could exceed another $10 trillion or more.
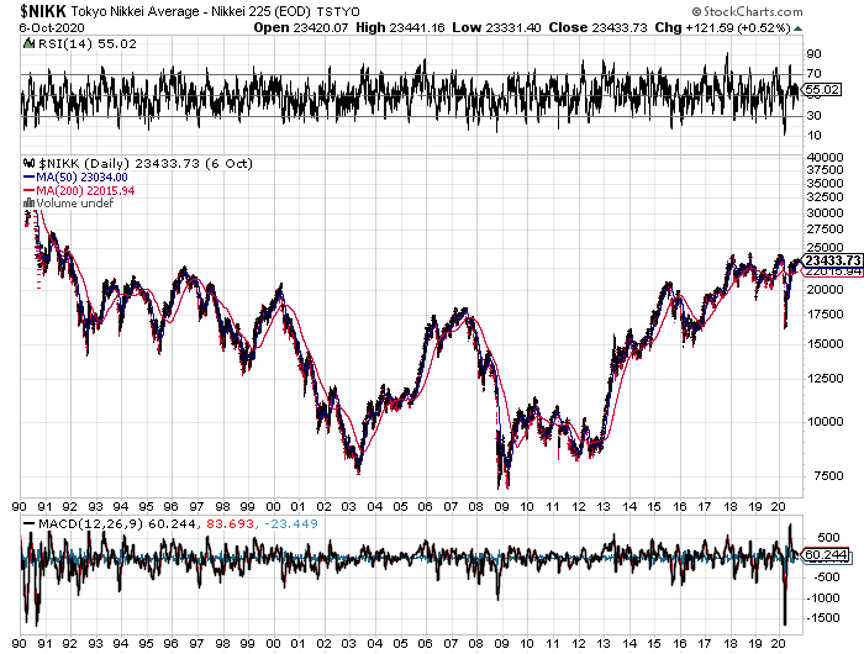
Japan actually began its QE program in 2001, long before anyone else, to deal with the aftermath of the 1990 Japanese stock market crash and a massive demographic headwind (they’re not making Japanese anymore).
Some 20 years later, the Japanese government now owns virtually all of the debt in the country. When you hear about Japan’s prodigious 240% debt to GDP ratio, it’s all nonsense. Net out government holdings and there is no national debt in Japan at all. That’s why the Japanese yen is consistently strong.
After the 2008 crash, the Japanese government expended its QE to include equities as well. As a result, the government is now the largest single buyer of stocks in the Land of the Rising Sun. The Nikkei Average has risen by 234% since the 2009 bottom despite a miserable economic performance, and the yield on 10-year JGBs stand at a lowly 0.03%.
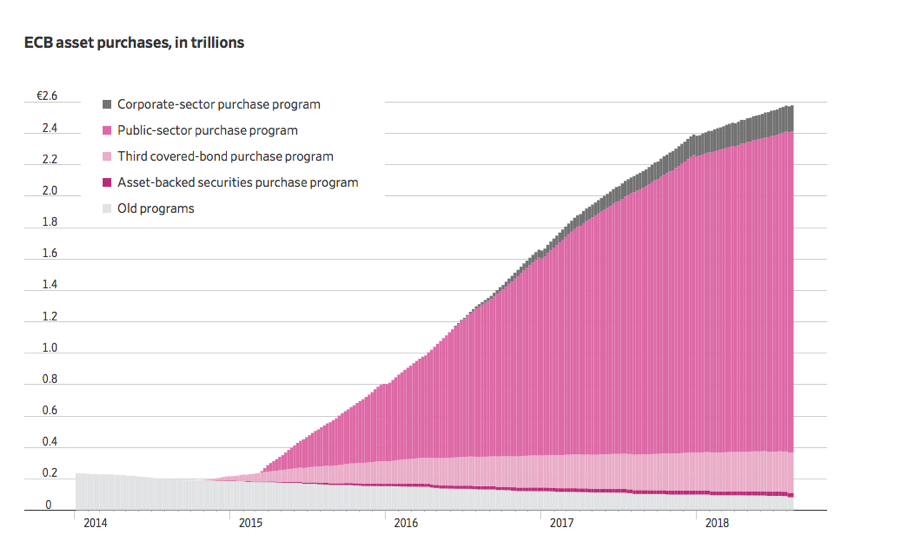
The European Central Bank got into the QE game very late, not until 2015, and its program continues anew, although at half its peak rate. The ECB has just renewed its plan to print a ton of new money.
Part of the problem is that the ECB is running out of bonds to buy, as it already owns most of the paper issued by European entities. That’s why 10-year German bunds are yielding a paltry -0.50%.
As a result, there is excess liquidity everywhere and this has broad implications for your investment or retirement portfolio. It could take as long as a decade before all of this artificial cash is removed from the global financial system.
For a start, bonds may not fall much from here, even if the Fed continues its near-zero interest rate policy for three more years, as promised.
Stocks can’t fall either with this much cash underpinning the market, at least not for a while and not by much. While company share buybacks have virtually disappeared this year, foreign investors have stepped in to pick up the slack.
It also means you can’t have a global contagion leading to a financial crisis. There is ample money available to refinance your way out of any problem when 70% of the world’s debt is still yielding close to zero.
The bottom line here is that global excess liquidity can cover up a multitude of sins. It means the price of everything has to go up, or at least stay level until that liquidity runs out. That includes stocks, bonds, your home, classic cars, and even that rare coin collection of yours gathering dust in a safe deposit box somewhere.
Yes, when the excess free cash runs out in a decade, there will be hell to pay. Until then, make hay while the sun shines.