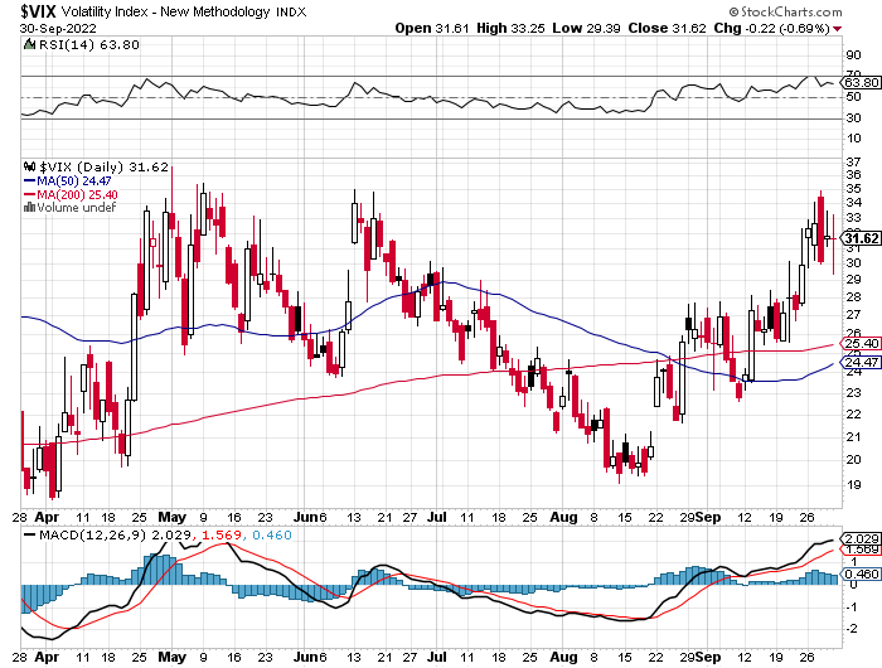
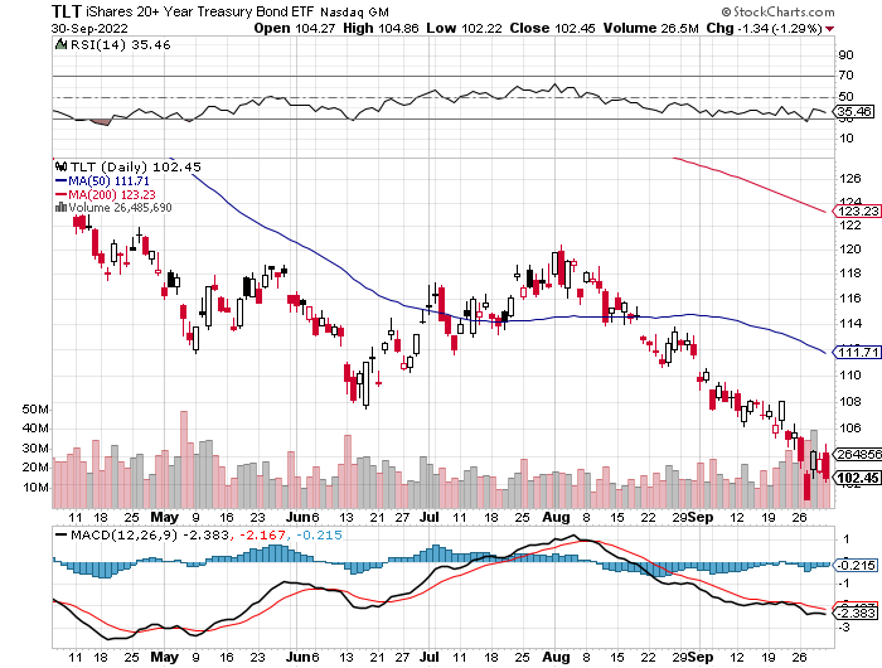
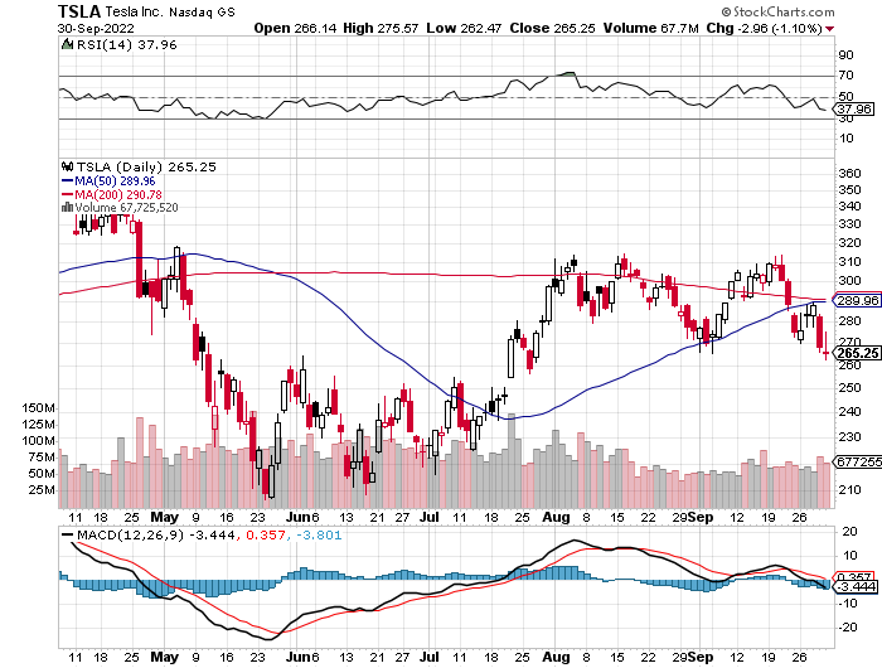
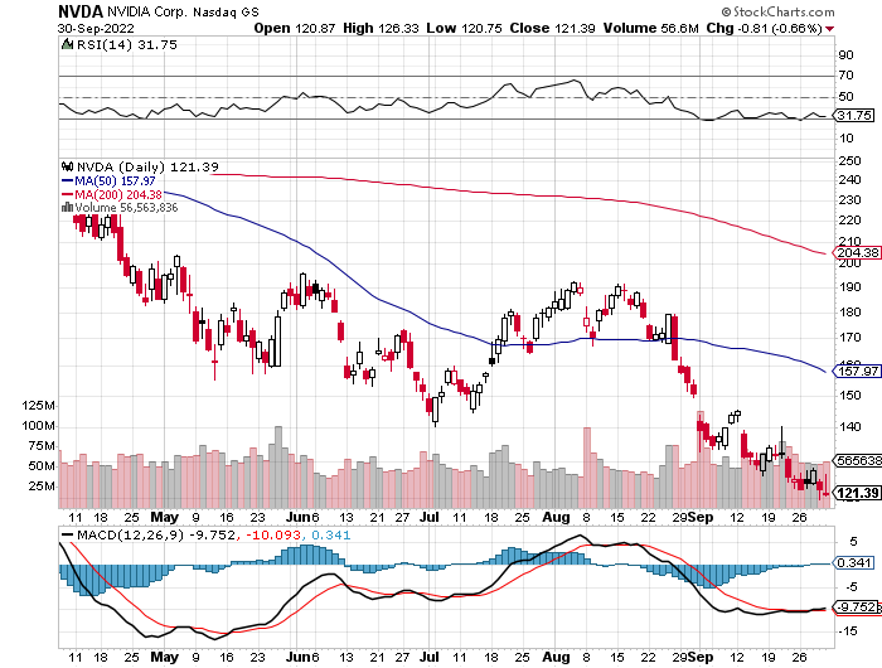
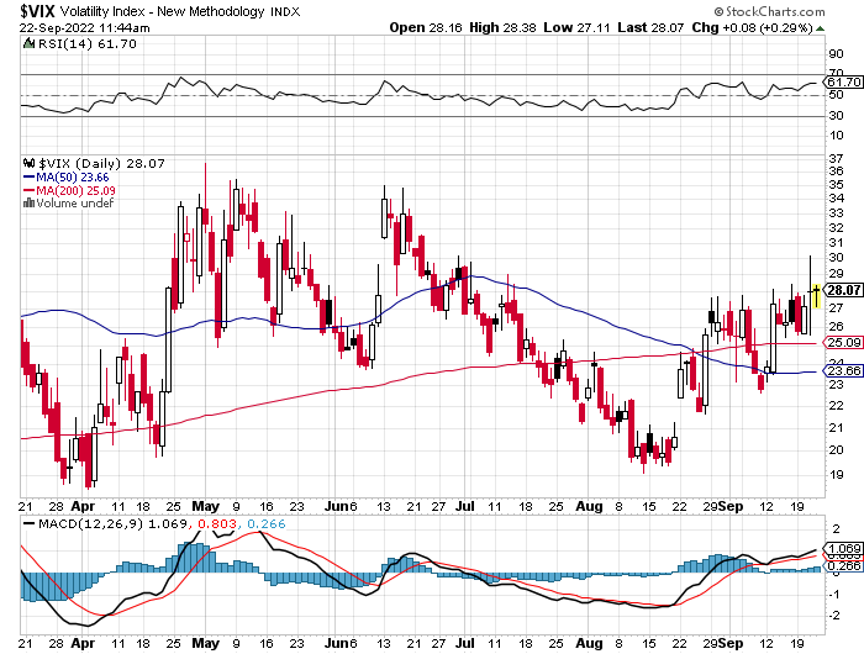
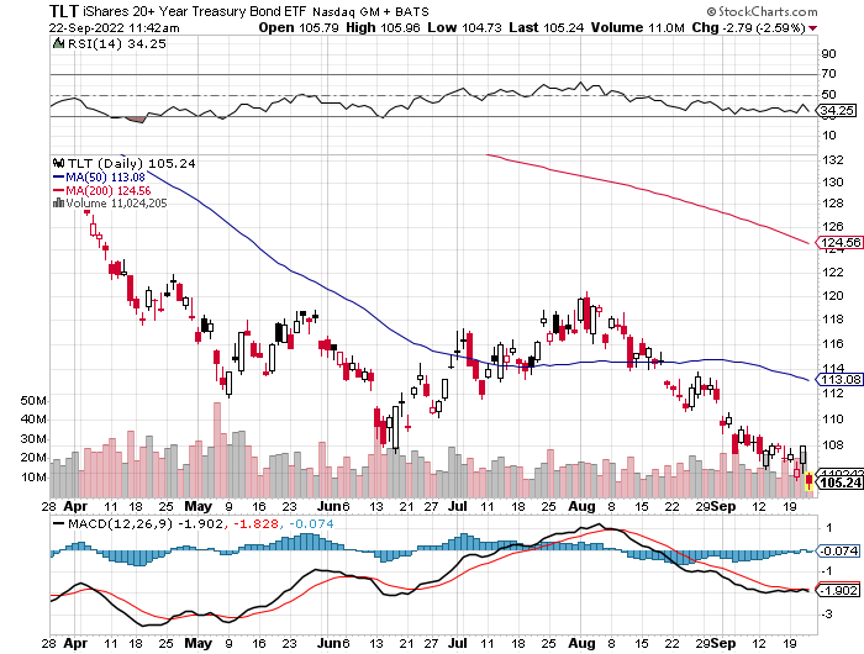
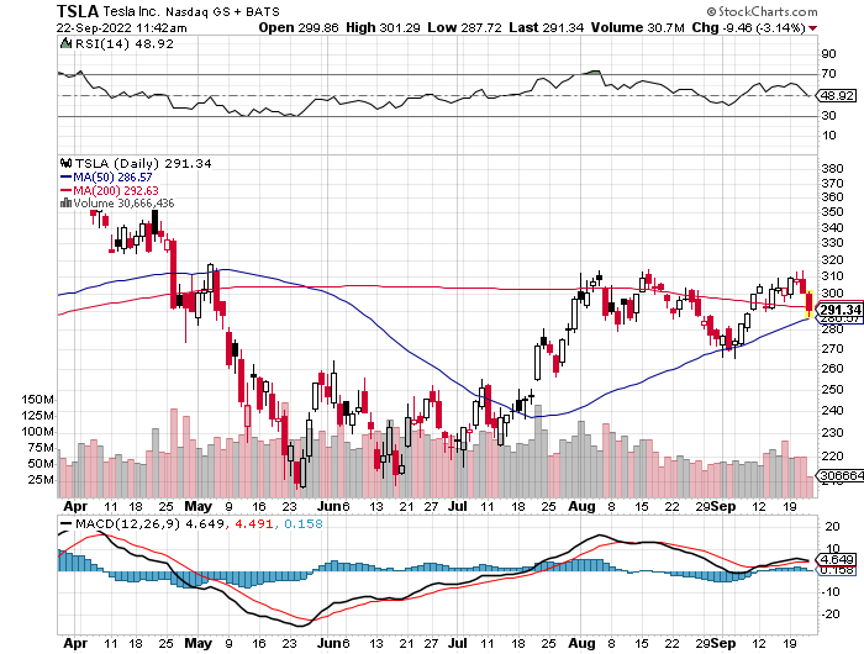
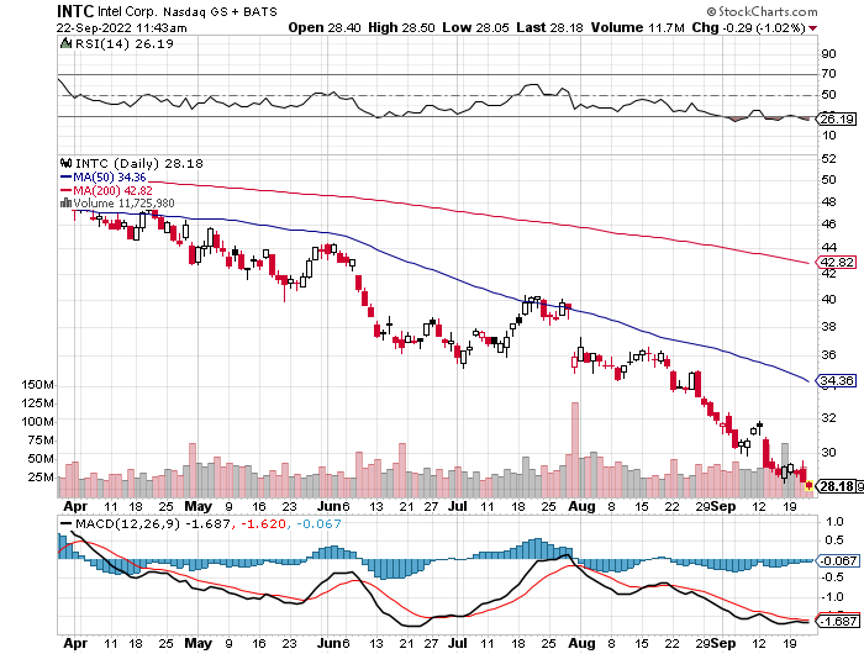
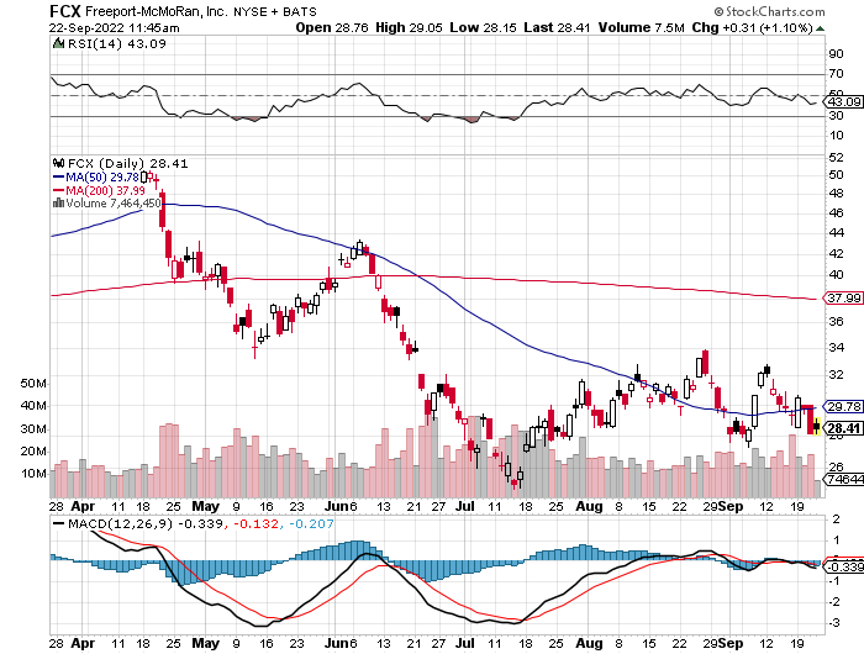
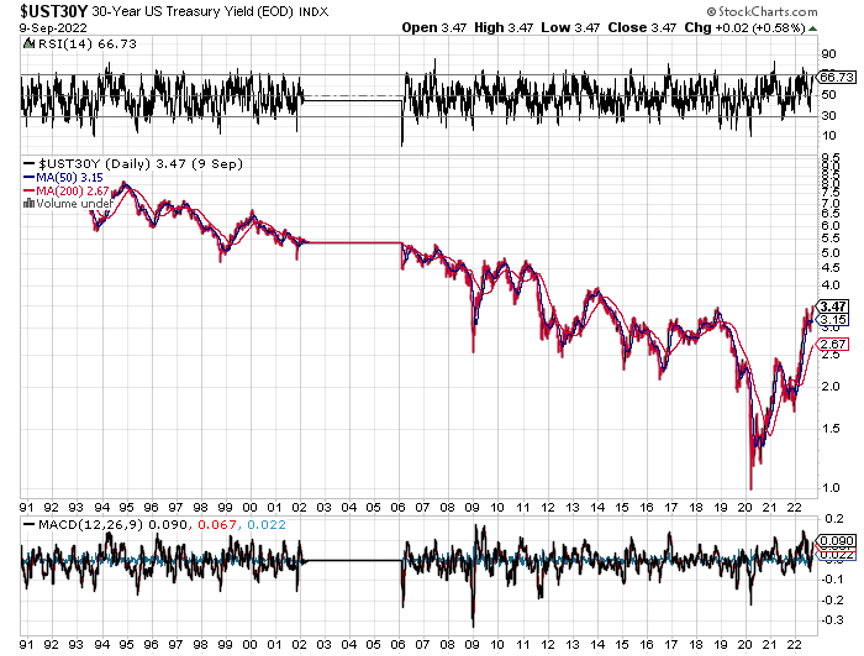
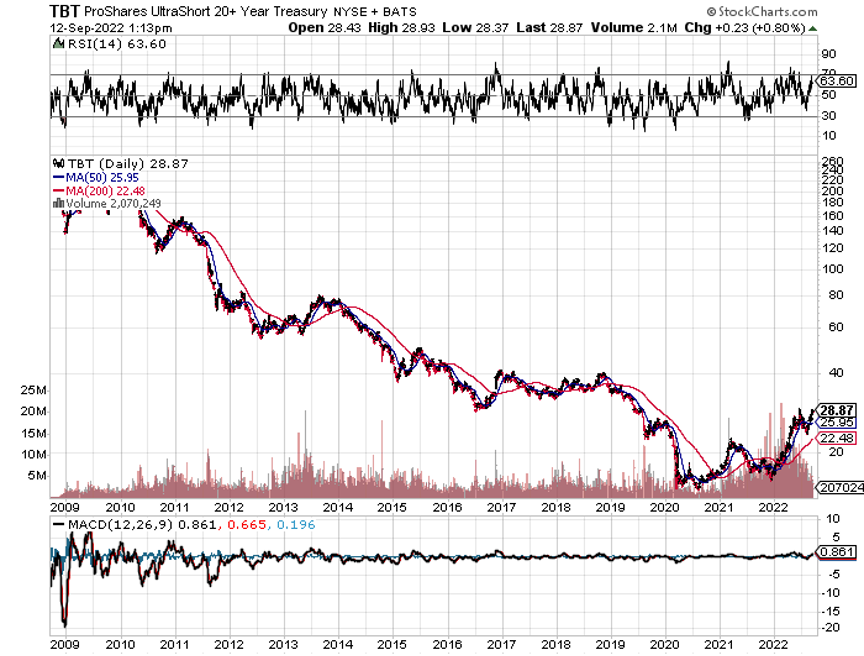
The year 2022 has been driven by rising interest rates, a strong dollar, a weak economy, a bear market in stocks.
A massive reversal is about to take place. 2023 will gain the benefit of gale force macroeconomic tailwinds for the right stocks.
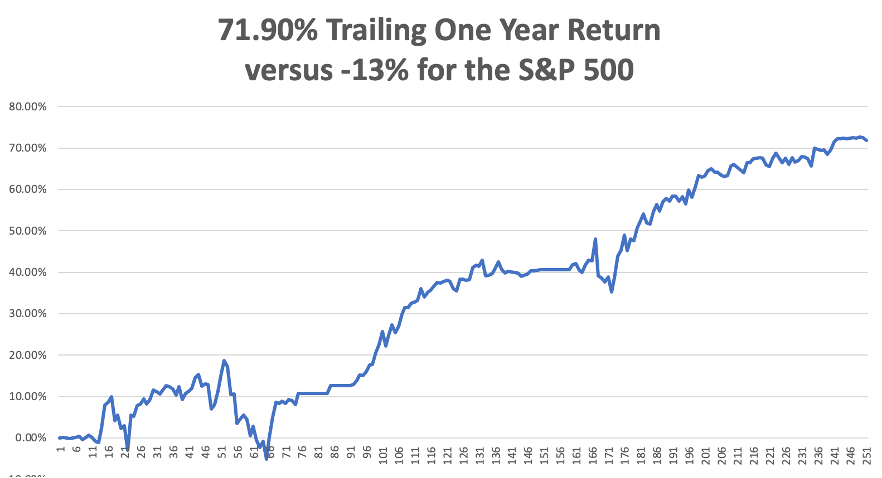
So far this year, Mad Hedge earned an astounding 77.20% profit cashing in on this year’s trends. We could earn the same return taking advantage of next year’s trends.
If you want to ride along on my coattails next year, that is fine with me. But it requires you to take a leap of faith.
I refer you to the motto of Britain’s Special Air Service: “Qui audet adipiscitur,” or “Who dares wins.”
For it only makes sense that the worst stocks of 2022 will be the best performers of 2023.
I have no doubt that tech stocks will bottom out sometime in 2023. Those who get in early will build some of the largest fortunes of this century. Those who miss the boat will spend their retirement years working at Taco Bell.
The reasons are very simple.
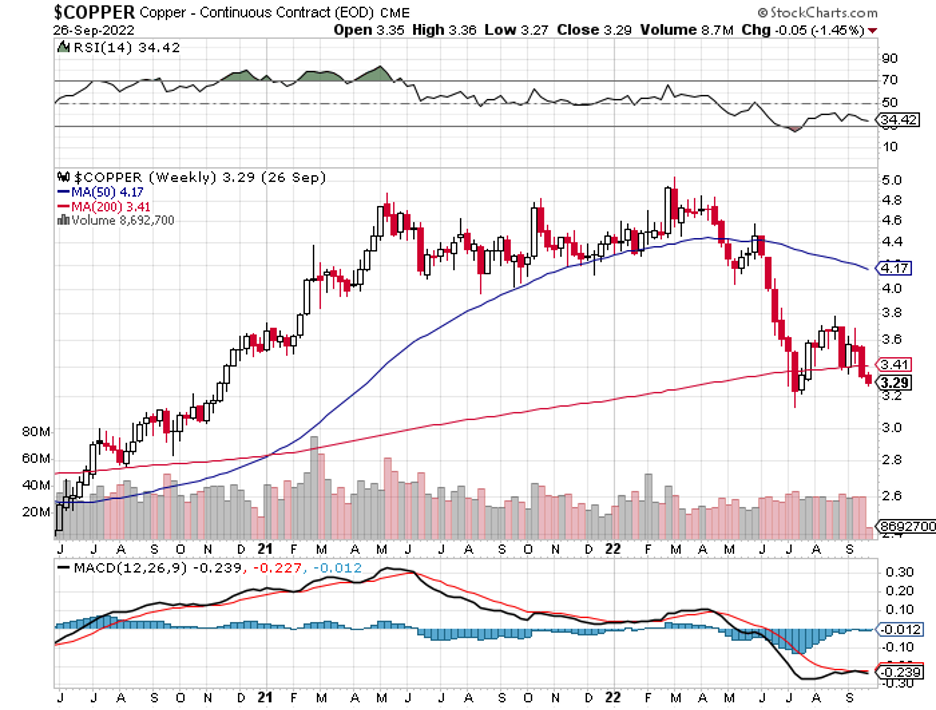
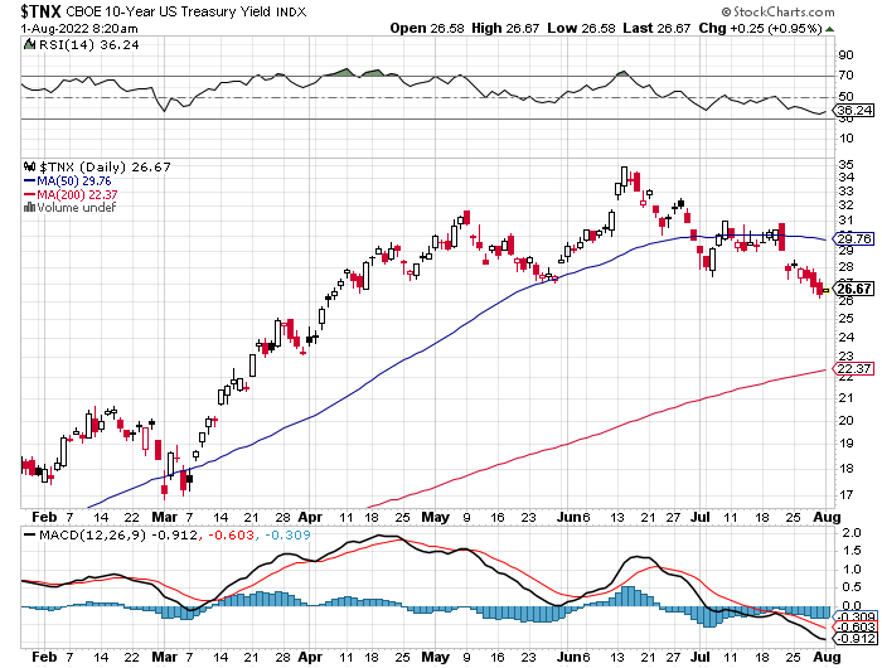
*Ultra-high interest rates will force a mild recession in early 2023. Then suddenly, inflation will plummet. We know this has already started because the largest element in the inflation calculation is housing costs, which are in free fall.
*The Fed will panic and deliver 2023 the sharpest DECLINE in interest rates in American history.
*Plunging interest rates will bring a crash in the US dollar.
*Foreign currencies like the Euro (FXE), the Japanese Yen (FXY), and the Australian dollar (FXA) will soar.
*And guess who gets the bulk of their earnings from abroad, sometimes up to two-thirds? The technology industry.
Kaching!
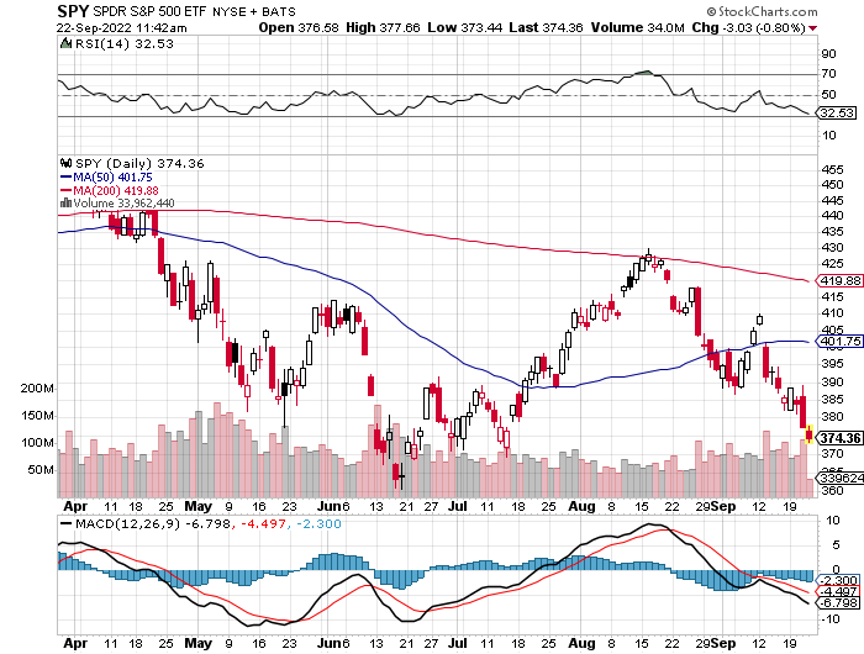
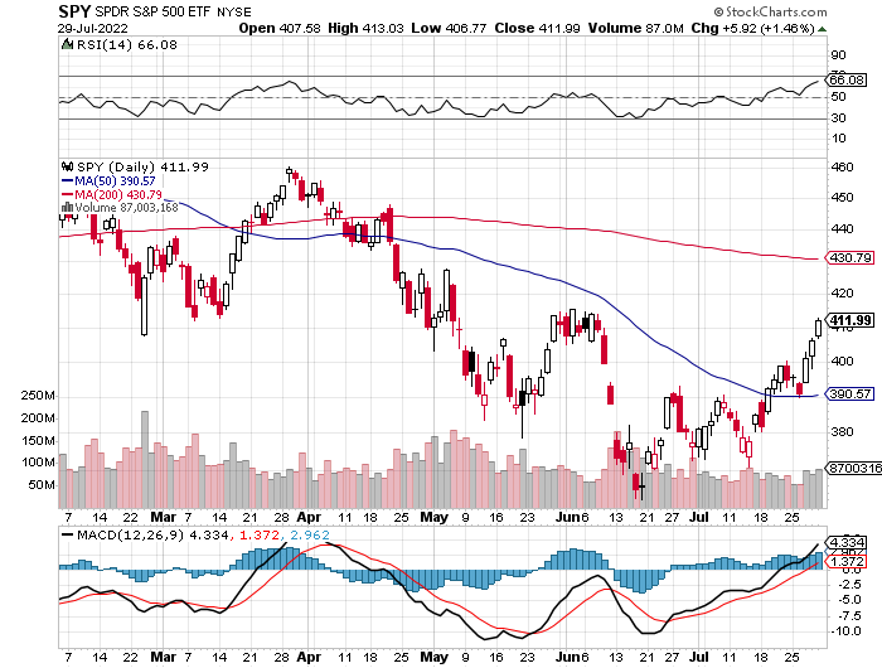
If you think I’m out of my mind, just look at the top performers of the historic stock market rally last week.
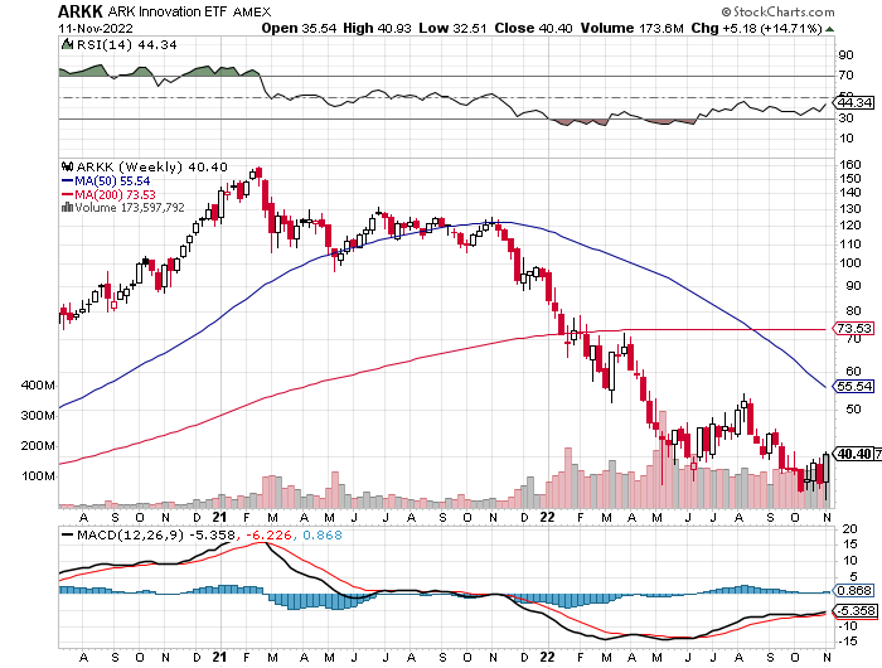
All the interest rate-sensitive sectors caught on fire. Technology stocks took off like a scalded cat, with Cathie Woods’ Ark Innovation Fund (ARKK) up an astounding 14% in a single day.
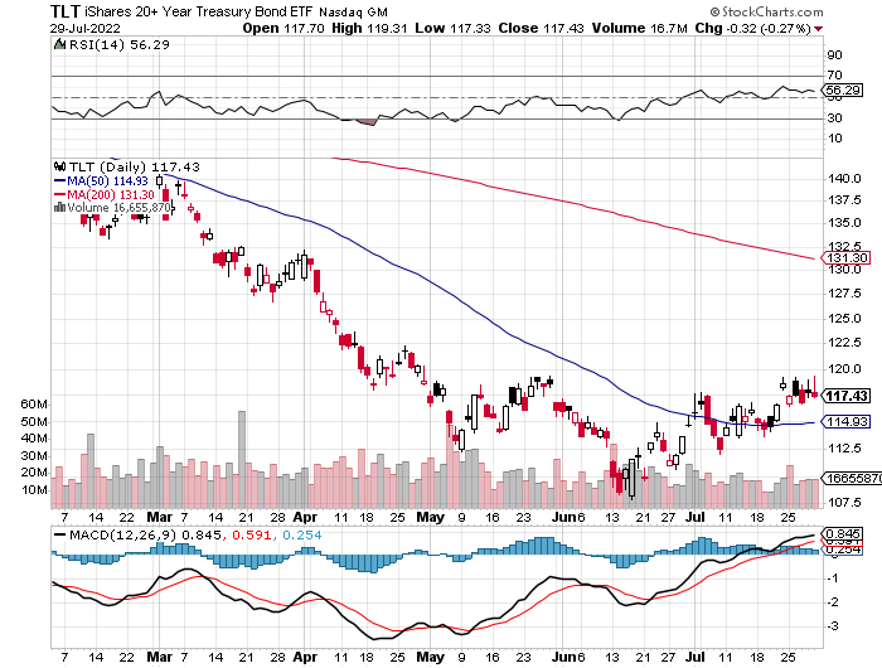
Bank shares soared. Homebuilders (LEN), (KBH), (DHI) caught a strong bid for the first time in ages. Junk bonds went bid only. US Treasury Bonds had their best day in 20 years (TLT), while the greenback (UUP) had its worst.
The bottom line here is so clear that I’ll write it on a wall for you. Falling interest rates will be the primary driver of stock prices for 2023 and 2024.
Of course, there is a better way to play this than buying the first technology index you stumble across.
So, let me boil this strategy down to just five names, close your eyes, and buy them.
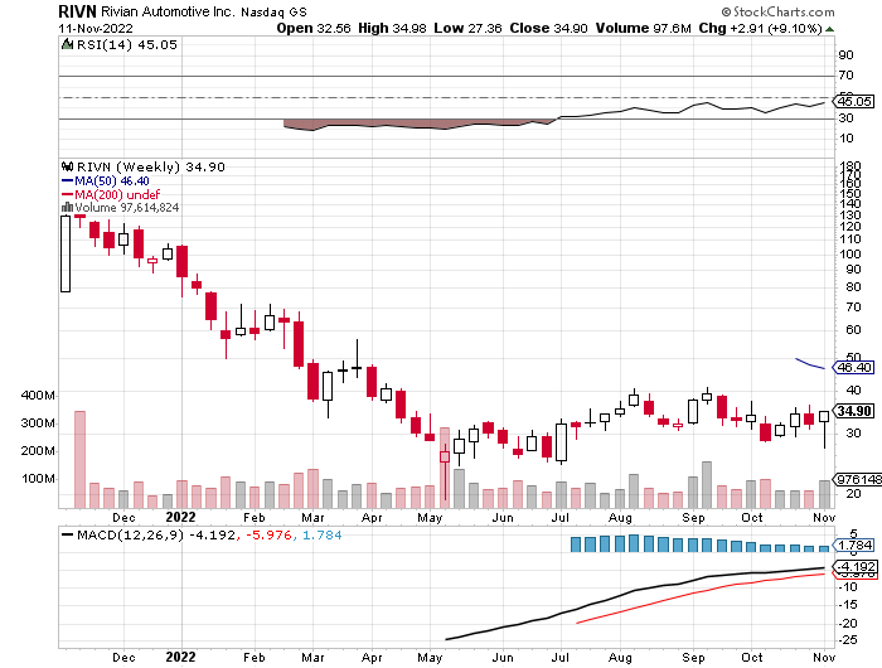
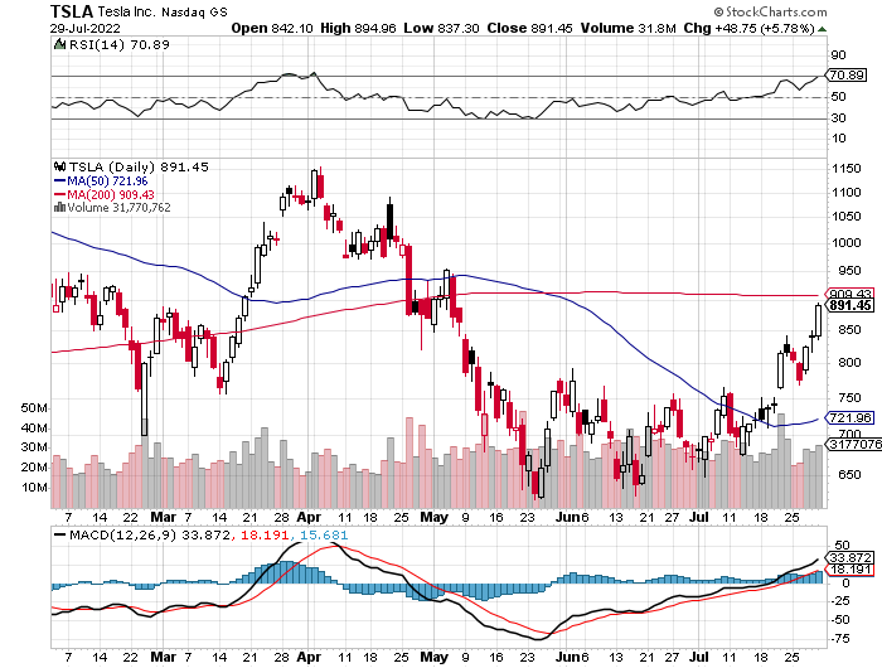
Rivian (RIVN) – ($34) - Rivian is widely believed to be the next Tesla (TSLA). Some 25% owned by its largest customer, Amazon (AMZN), Rivian produces three types of EVs: the R1T pickup truck, the R1S SUV, and Amazon's EDV (electric delivery van). Its R1 vehicles start at under $70,000 and can travel more than 300 miles on a single charge. To learn more about Rivian, please click here.
To say that Rivian is the hot car of the day would be a vast understatement. New cars are trading for double list on the grey market. Owners complain of getting mobbed with gawkers whenever they hit the beach or the ski slopes. The buzz has led to an outstanding order book of an impressive 98,000, or four years of current production. The obvious cool factor allows enormous pricing power.
And here is the key to buying Rivian at this time. At 25,000, it is right at the mass production point where Tesla shares went ballistic all those years ago. And it already has an 80% decline in the price, in the rear-view mirror.
In 2024, Rivian plans to open its second plant in Georgia. After it fully expands its Illinois plant, it expects its annual production capacity to reach 600,000 vehicles.
Inflation Reduction Act passed this summer greatly accelerated rollout of the entire EV industry, which created a $7,500 per vehicle tax credit on top of state benefits.
Yes, this company offers venture capital-type risks. But it offers venture capital-type returns as well, up 10X-50X from here.
Ark Innovation Fund (ARKK) – ($40) – Cathie Woods’ high-tech fund was the proverbial red-headed stepchild of this bear market. It fell a gut-punching 80% from the 2021 top until last week. Just to get back to its old high, likely over the next five years, it has to rise by 400%. Its largest holdings are a real rollcall of the severely abused, Tesla (TSLA), Roku (ROKU), Exact Sciences (EXAS), Intellia (INTL), and Teladoc Health (TDOC), which Woods actively trades. But they are also a valuable insight into the future, EVs, CRISPR technology, robotic surgery, and molecular diagnostics. To learn more about the Ark Innovation Fund, please click here.
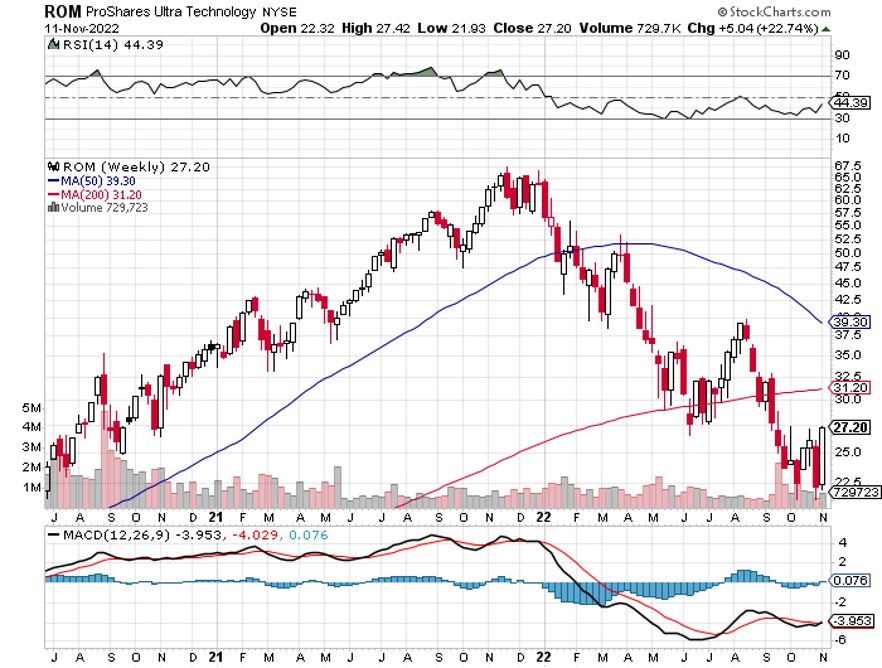
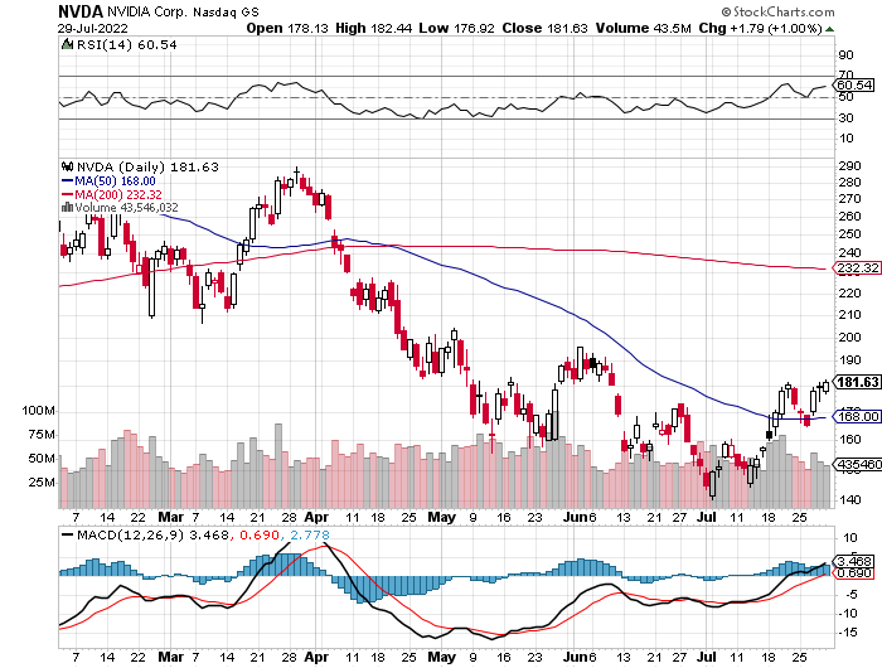
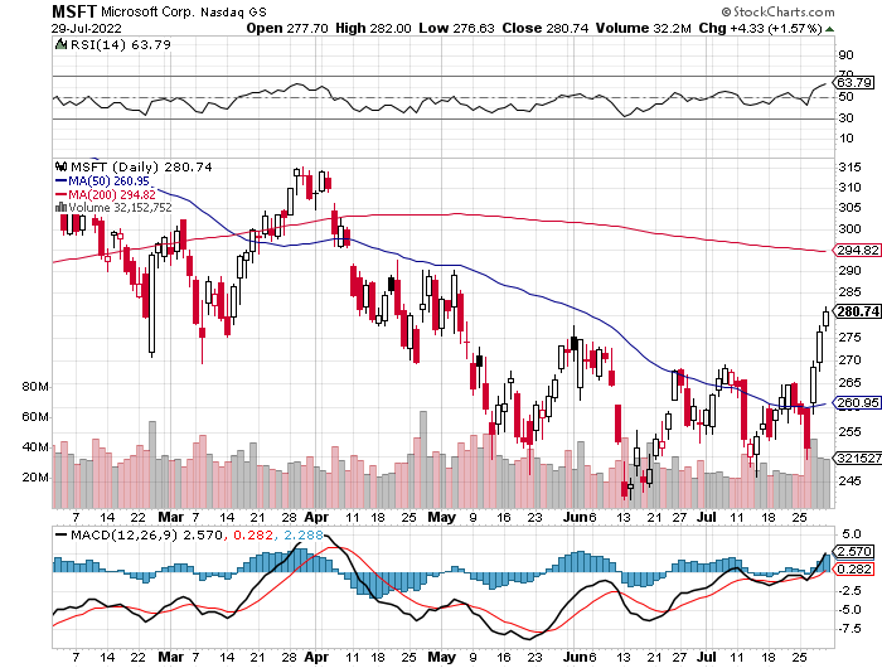
ProShares Ultra Technology ETF (ROM) – ($27) – This is a 2X long technology ETF that gives you an extremely aggressive position across the tech sector. It has 19% of its holdings in Apple (AAPL), 16% in Microsoft (MSFT), 10% in Alphabet (GOOGL) and Google (GOOG), at 3.5% in NVIDIA (NVDA), and 120 other smaller names. (ROM) shares are down a breathtaking 67% just in the past year. To learn more about the (ROM), please click here.
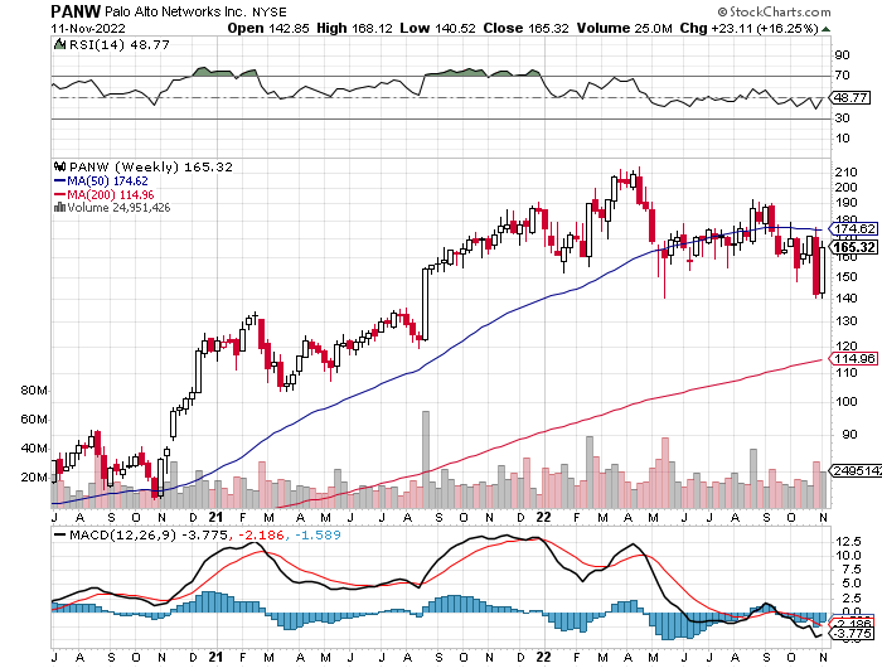
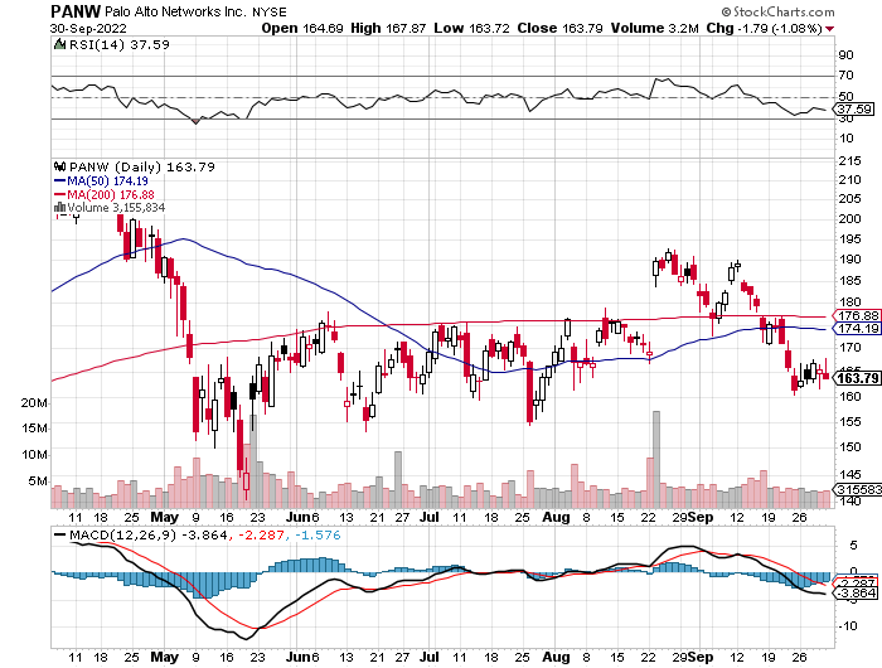
Palo Alto Networks (PANW) - $165 – Hacking is one of the fastest-growing sectors in technology, it is recession-proof and immune to the economic cycle. As a result, spending on the defense against hacking is absolutely exploding. Palo Alto Networks, Inc. is an American multinational cybersecurity company with headquarters in Santa Clara, California. Its core products are a platform that includes advanced firewalls and cloud-based offerings that extend those firewalls to cover other aspects of security. I have already earned a tenfold return over the past decade and expect to make another 10X in the coming years. You won’t find any dips in this stock as too many people are trying to get into it. To learn more about the Palo Alto Networks, please click here.
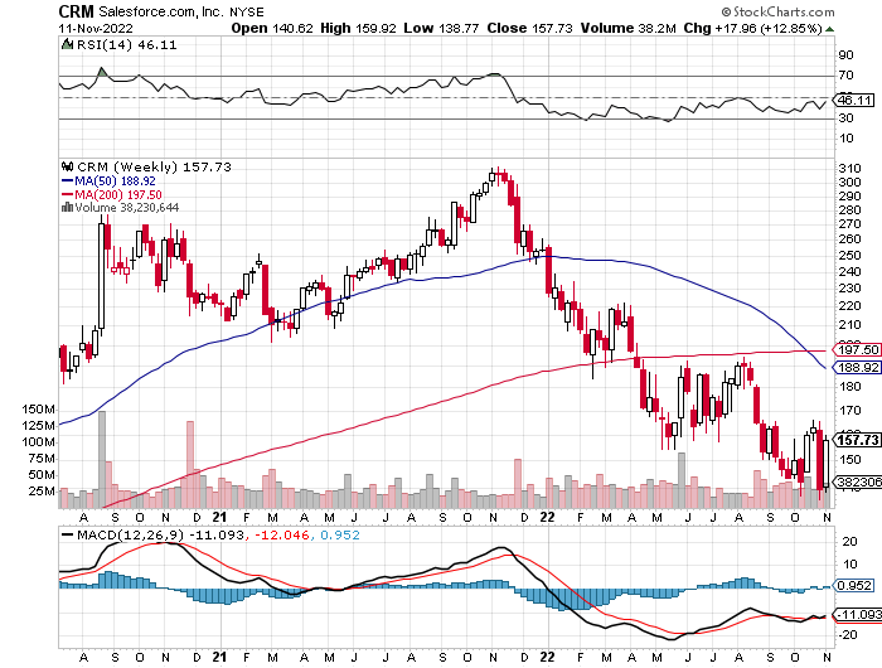
Salesforce (CRM) - $157 – The baby of tech genius Mark Benioff, this company is the dominant player in customer relationship management. If you want to do any business in the cloud, and almost all big companies do, you are up to your eyeballs in customer relationship management. Salesforce is the largest San Francisco-based cloud-oriented software company with virtually all of the Fortune 500 as its customer list. It provides customer relationship management software and applications focused on sales, customer service, marketing automation, analytics, and application development. Salesforce shares have been the target of a haymaker, down 55% in a year. To learn more about Salesforce, please click here.
You know what? I can do better than this.
I can create customized options LEAPS for you that will deliver a tenfold return on whatever performance these ultra-high beta stocks deliver. If the shares of one of my picks rise by 100%, you will make 1,000%.
This is an investment strategy that will enable you to retire early, real early. Tired of punching a time clock or logging into the next Zoom meeting on time?
Those will become a distant memory if you pursue my Mad Hedge Investment strategy for 2023.
As a result, my November month-to-date performance went off to the races, already achieving a hot +2.20%.
That leaves me with a very rare 100% cash position. With midterm election results out on Wednesday and the next report on the Consumer Price Index on Thursday, that sounds like a prudent place to be.
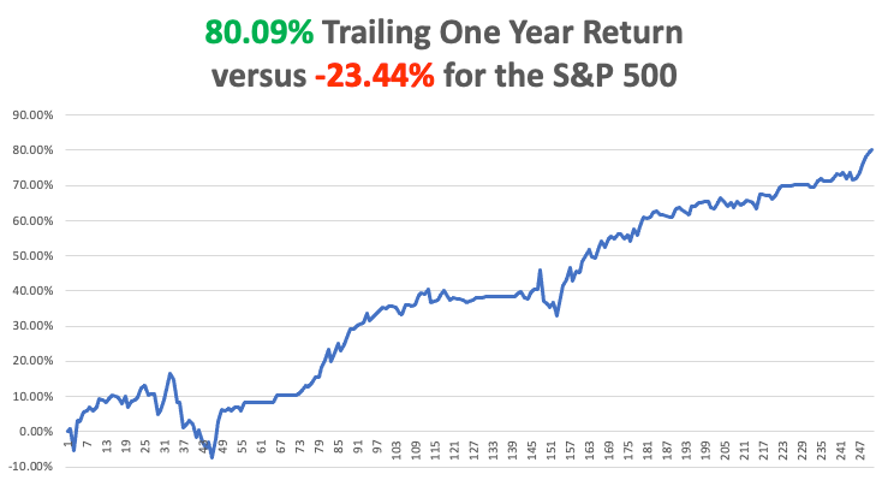
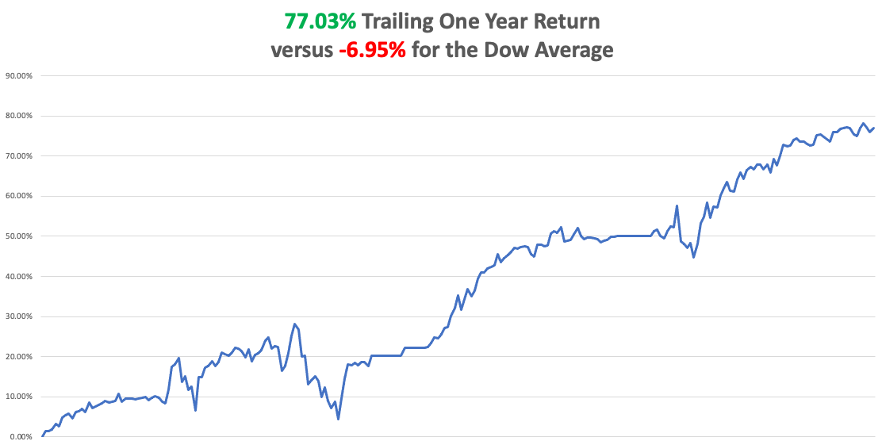
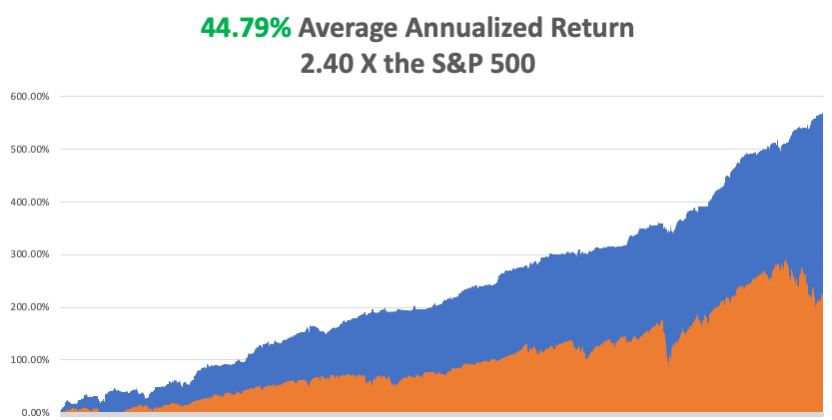
My 2022 year-to-date performance ballooned to +77.57%, a new high. The Dow Average is down -11.85% so far in 2022.
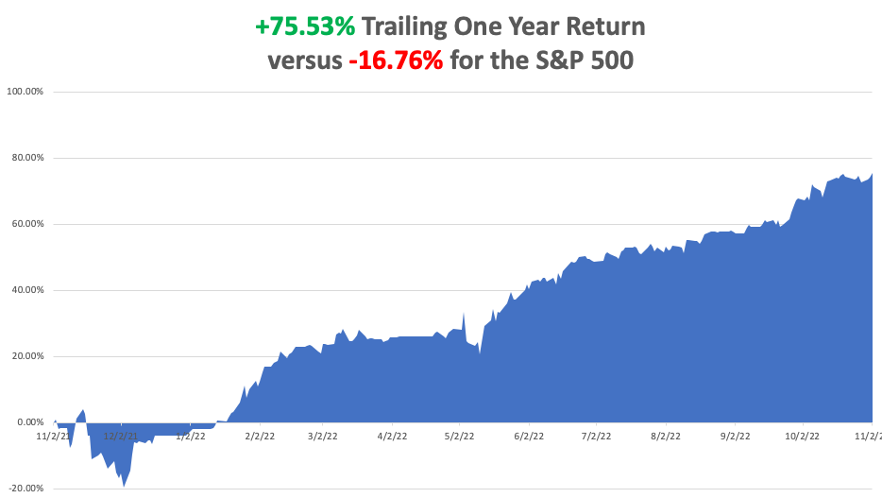
It is the greatest outperformance on an index since Mad Hedge Fund Trader started 14 years ago. My trailing one-year return maintains a sky-high +75.53%.
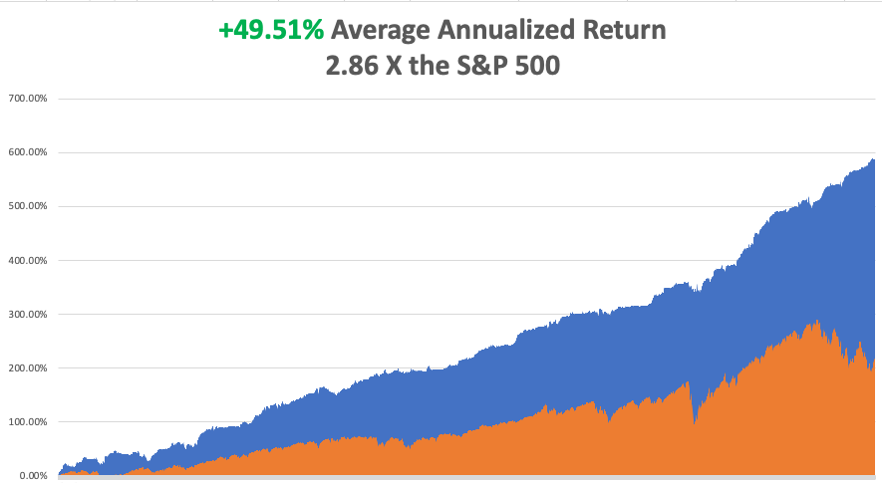
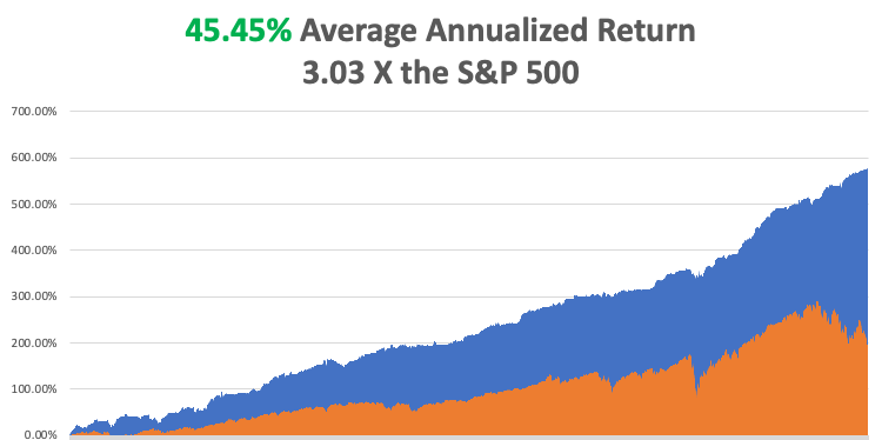
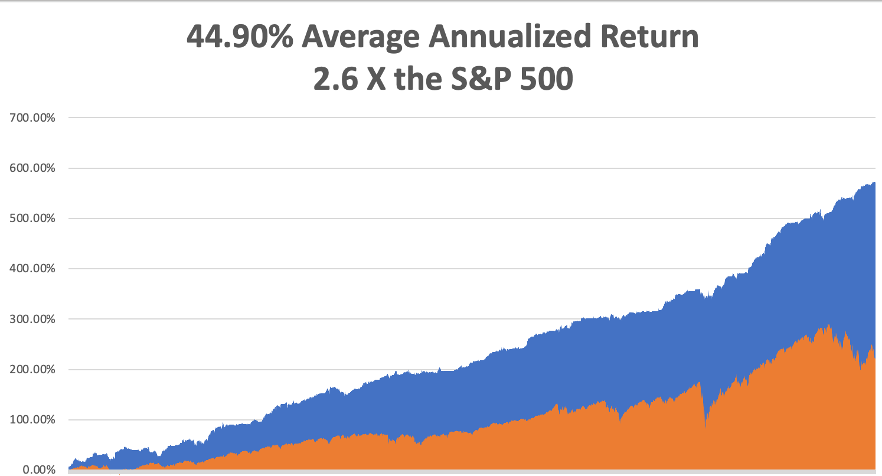
That brings my 14-year total return to +590.13%, some 2.86 times the S&P 500 (SPX) over the same period and a new all-time high. My average annualized return has ratcheted up to +49.51%, easily the highest in the industry.
Bonds Clock Best Day in Years, taking the ten-year US Treasury bond fund up $3.64. All low interest rate plays had monster days. Junk bond ETFs (JNK) and (HYG) were up two points. 30-year fixed rate mortgages dropped 60 basis points to 6.60%, the biggest drop in history. Long bonds will be THE big trade of 2023.
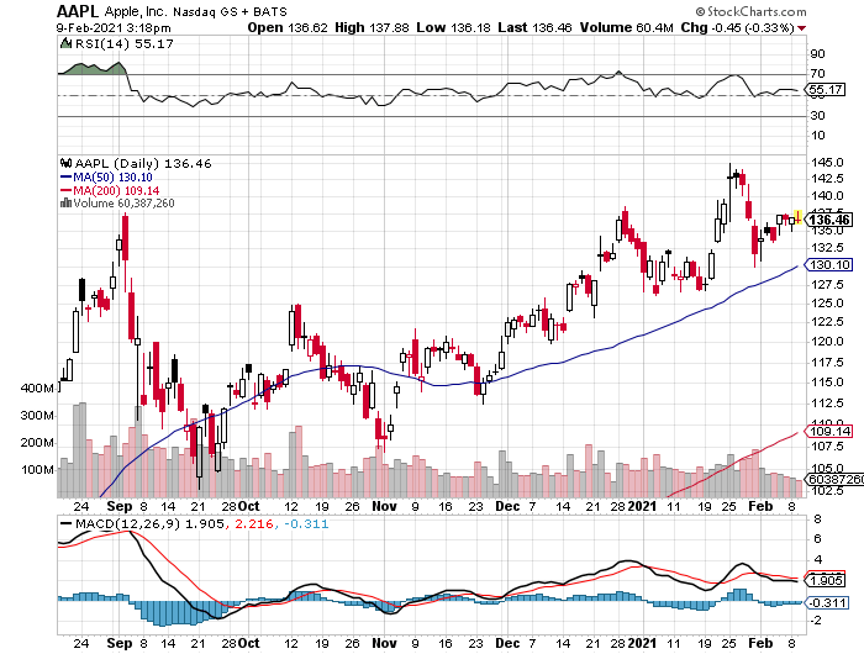
US Dollar has Worst Day in 20 Years, driven by plunging interest rates. Big tech, which gets a major share from overseas sales, rocketed. Apple alone was up $12. Cathy Wood’s Ark Innovation Fund (ARKK) was up an incredible 14%. It vindicates my view that tech will turn when interest rates and the dollar fall.
Oil Companies (USO) Book Record $200 Million Profit this year, using the Ukraine War to double your cost of gasoline. If we have a recession next year, or the war ends, energy share prices should be peaking around here. Even if they don’t, the risk-reward here is terrible. It means we will have to pay a much higher price to decarbonize the economy at a later date.
Wells Fargo Gets Hit with $1 Billion Fine for its many regulatory transgressions over the last decade. Looting of customer accounts with bogus fees has been a recurring problem. Use any selloffs to buy (WFC) on dips.
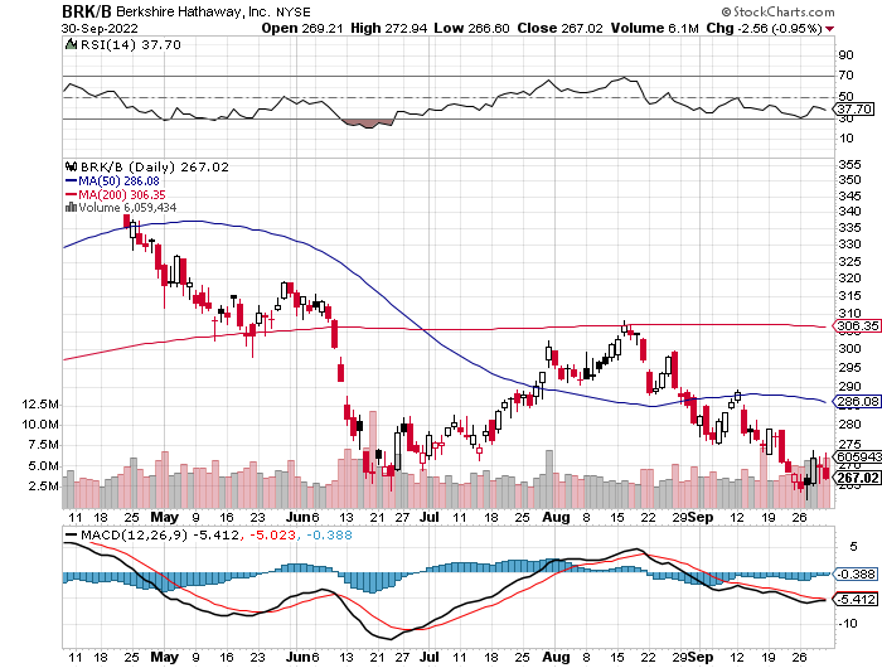
Berkshire Hathaway's 20% Profit Increase YOY and buys back another $1 billion worth of stock. However, they did take a $10 billion loss on stocks in Q3 during the market meltdown. Keep buying (BRKB) stock and LEAPS on dips.
$1.5 trillion in Homeowners Equity Lost Since May, thanks to interest rates at 20-year high and a shrinking money supply. Since July, the median home price has dropped by $11,560. The average borrower has lost $30,000 in equity. It’s not a great time to rent either as prices there are soaring. Residential housing could remain weak for another 12-24 months, compared to the six-year drawdown we had from 2006.
Boeing Orders Rise in October, but deliveries fall. The company is finally out of the penalty box, up 40% since October 1. Don’t buy (BA) up here.
The Red Wave Fails to Show, with control of congress still too close to call. Republican House control has shrunk from an expected 60 seats six months ago to maybe two today. Donald Trump threw the election for his party, picking unelectable extremist candidates and campaigning where he wasn’t wanted. A pro-life Supreme Court brought out millions of women voters across the country. If the Republicans can’t win with inflation at 8.7%, they are toast in 2024 when it drops back down to 2%.
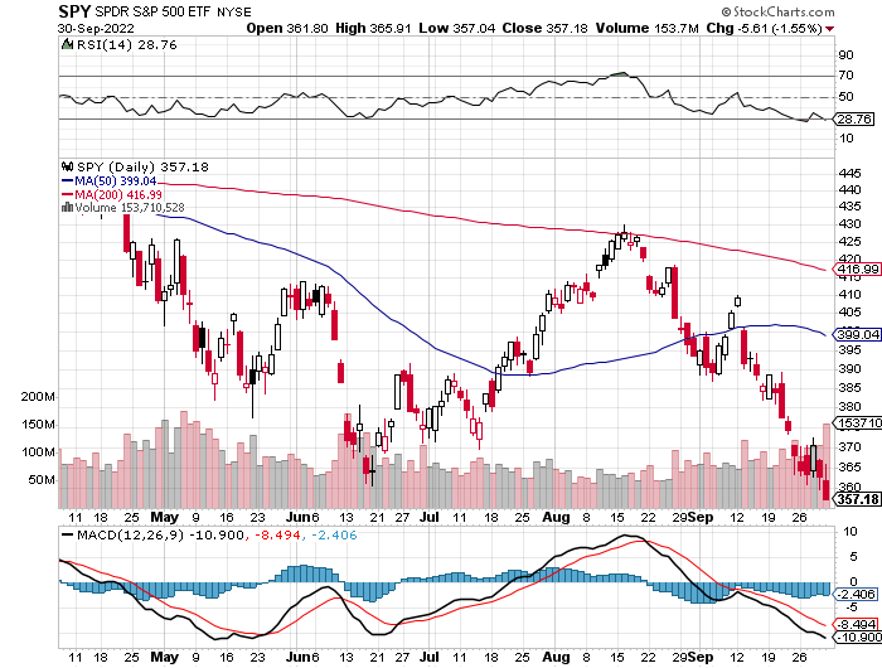
Market Dives 646 Points on Democratic Win, with technology stocks taking the biggest hit. The red wave no-show was a black swan traders were not looking for. Energy was the worst performing sector because they aren’t getting the air cover they paid for with a red wave. The result was much as I expected, which is why I went into November 8 with a rare 100% cash position waiting to buy the next low. It turns out that rights are more important than prices.
Elon Musk Sells More Tesla Shares and Warns of a Twitter Bankruptcy, some $3.9 billion worth, bringing this year’s total to $36 billion. Musk is raising money to head off a bankruptcy of Twitter now that major advertisers are fleeing en masse. This certainly is a distress sale. If Musk was looking to build a real business, re-tweeting fringe conspiracy theories was the worst thing he could have done. Endorsing the Republican party will cost him half of his customers. Is this Musk’s Waterloo, or his Dien Bien Phu?
Facebook to Lay Off 11,000, about 13% of its total employees. Zuckerberg admits the error of pushing the company into the metaverse too far too fast. With the stock down 77%, there are not a lot of happy campers at One Hacker Way. Avoid (META) for now, but it may be a 2023 play when we get closer to a new final product.
FTX Becomes an Epic Bankruptcy, with $9.5 billion missing from its balance sheet, in one of the biggest blowups of the crypto age. Losses are expected to reach $50-$60 billion, with the bankruptcy of 130 affiliated companies. It is also a potential Dept of Justice target. All affiliated tokens and coins have gone to zero. So, placing your money with a fresh-faced kid in the Bahamas wearing baggy shorts and with no financial background was not such a great idea after all. It’s amazing how many serious people were sucked in on this one. At least Sam Bankman-Fried said he was sorry.
My Ten-Year View
When we come out the other side of the recession, we will be perfectly poised to launch into my new American Golden Age, or the next Roaring Twenties. With the economy decarbonizing and technology hyper-accelerating, there will be no reason not to. The Dow Average will rise by 800% to 240,000 or more in the coming decade. The America coming out the other side will be far more efficient and profitable than the old. Dow 240,000 here we come!
On Monday, November 14 at 8:00 AM, the Consumer Inflation Expectations for October are released.
On Tuesday, November 15 at 8:30 AM, the Producer Price Index for October is released.
On Wednesday, November 16 at 8:30 AM, Retail Sales for October are published.
On Thursday, November 17 at 8:30 AM, Weekly Jobless Claims are announced. Housing Starts and Permits for October are also out.
On Friday, November 18 at 10:00 AM, the Housing Starts for October are printed. At 2:00 the Baker Hughes Oil Rig Count is out.
As for me, I am often told that I am the most interesting man people ever met, sometimes daily. I had the good fortune to know someone far more interesting than myself.
When I was 14, I decided to start earning merit badges if I was ever going to become an Eagle Scout. I decided to start with an easy one, Reading Merit Badge, where you only had to read four books and write one review.
I was directed to Kent Cullers, a high school kid who had been blind since birth. During the late 1940s, the medical community thought it would be a great idea to give newborns pure oxygen. It was months before it was discovered that the procedure caused the clouding of corneas and total blindness. Kent was one of these kids.
It turned out that everyone in the troop already had Reading Merit Badge and that Kent had exhausted our supply of readers. Fresh meat was needed.
So, I rode my bicycle over to Kent’s house and started reading. It was all science fiction. America’s Space Program had ignited a science fiction boom and writers like Isaac Asimov, Jules Verne, Arthur C. Clark, and H.G. Welles were in huge demand. Star Trek came out the following year, in 1966. That was the year I became an Eagle Scout.
It only took a week for me to blow through the first four books. In the end, I read hundreds to Kent. Kent didn’t just listen to me read. He explained the implications of what I was reading (got to watch out for those non-carbon-based life forms).
Having listened to thousands of books on the subject, Kent gave me a first class education and I credit him with moving me towards a career in science. Kent is also the reason why I got an 800 SAT score in math.
When we got tired of reading, we played around with Kent’s radio. His dad was a physicist and had bought him a state-of-the-art high-powered short-wave radio. I always found Kent’s house from the 50-foot-tall radio antenna.
That led to another merit badge, one for Radio, where I had to transmit in Morse Code at five words a minute. Kent could do 50. On the badge below the Morse Code says “BSA.” In those days, when you made a new contact, you traded addresses and sent each other postcards.
Kent had postcards with colorful call signs from more than 100 countries plastered all over his wall. One of our regular correspondents was the president of the Palo Alto High School Radio Club, Steve Wozniak, who later went on to co-found Apple (AAPL) with Steve Jobs.
It was a sad day in 1999 when the US Navy retired Morse Code and replaced it with satellites. However, it is still used as beacon identifiers at US airfields.
Kent’s great ambition was to become an astronomer. I asked how he would become an astronomer when he couldn’t see anything. He responded that Galileo, the inventor of the telescope, was blind in his later years.
I replied, “good point”.
Kent went on to get a PhD in Physics from UC Berkely, no mean accomplishment. He lobbied heavily for the creation of SETI, or the Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence, once an arm of NASA. He became its first director in 1985 and worked there for 20 years.
In the 1987 movie Contact written by Carl Sagan and starring Jodie Foster, Kent’s character is played by Matthew McConaughey. The movie was filmed at the Very Large Array in western New Mexico. The algorithms Kent developed there are still in widespread use today.
Out here in the west aliens are a big deal, ever since that weather balloon crashed in Roswell, New Mexico in 1947. In fact, it was a spy balloon meant to overfly and photograph Russia, but it blew back on the US, thus its top secret status.
When people learn I used to work at Area 51, I am constantly asked if I have seen any spaceships. The road there, Nevada State Route 375, is called the Extra Terrestrial Highway. Who says we don’t have a sense of humor in Nevada?
After devoting his entire life to searching, Kent gave me the inside story on searching for aliens. We will never meet them but we will talk to them. That’s because the acceleration needed to get to a high enough speed to reach outer space would tear apart a human body. On the other hand, radio waves travel effortlessly at the speed of light.
Sadly, Kent passed away in 2021 at the age of 72. Kent, ever the optimist, had his body cryogenically frozen in Hawaii where he will remain until the technology evolves to wake him up. Minor planet 35056 Cullers is named in his honor.
There are no movies being made about my life…. yet. But there are a couple of scripts out there under development.
Watch this space.
Stay healthy,
John Thomas
CEO & Publisher
The Diary of a Mad Hedge Fund Trader