I know that not all of you are mathematicians, nor blessed with math degrees from UCLA, as I am. However, the future of your retirement funds relies on a few simple numbers. So, I will try to be gentle.
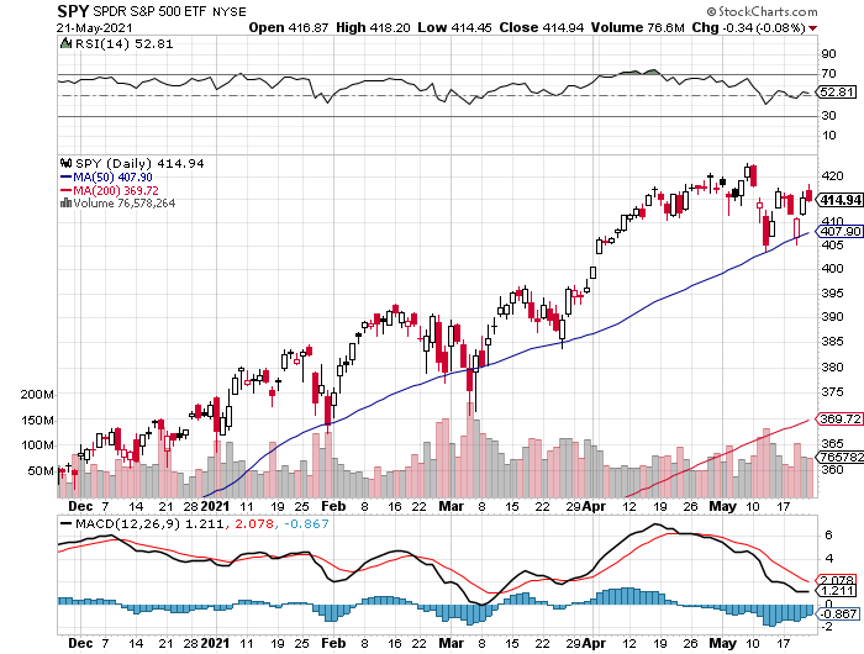
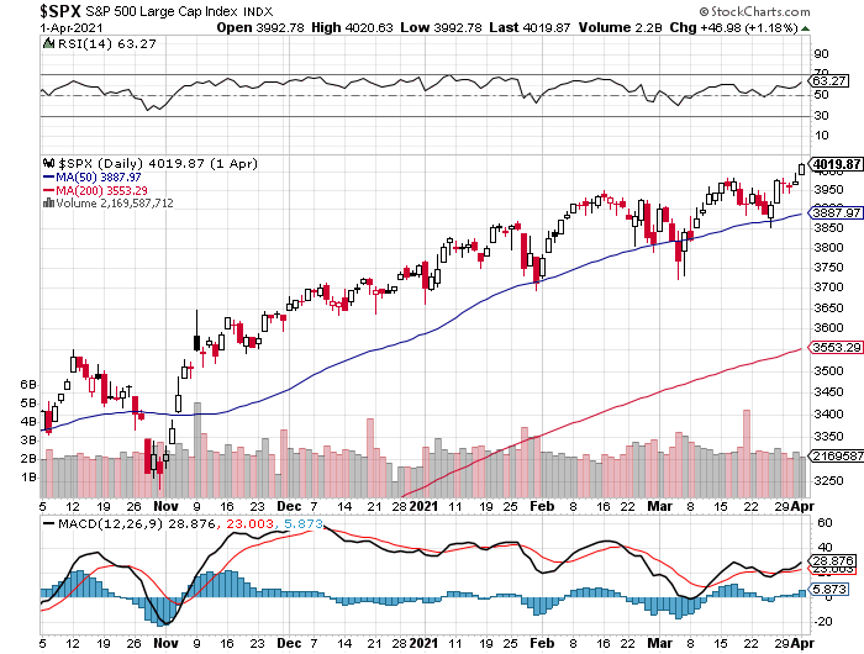
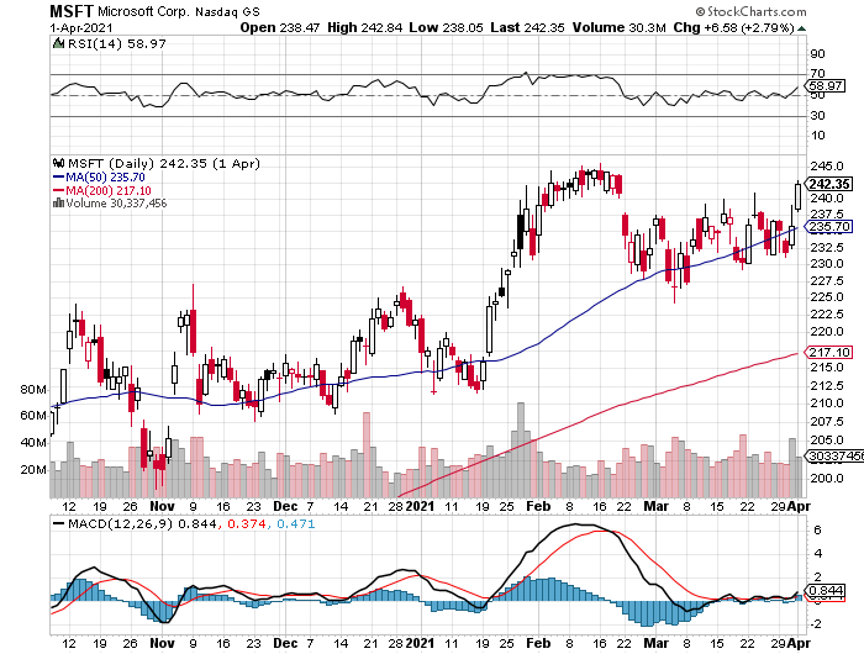
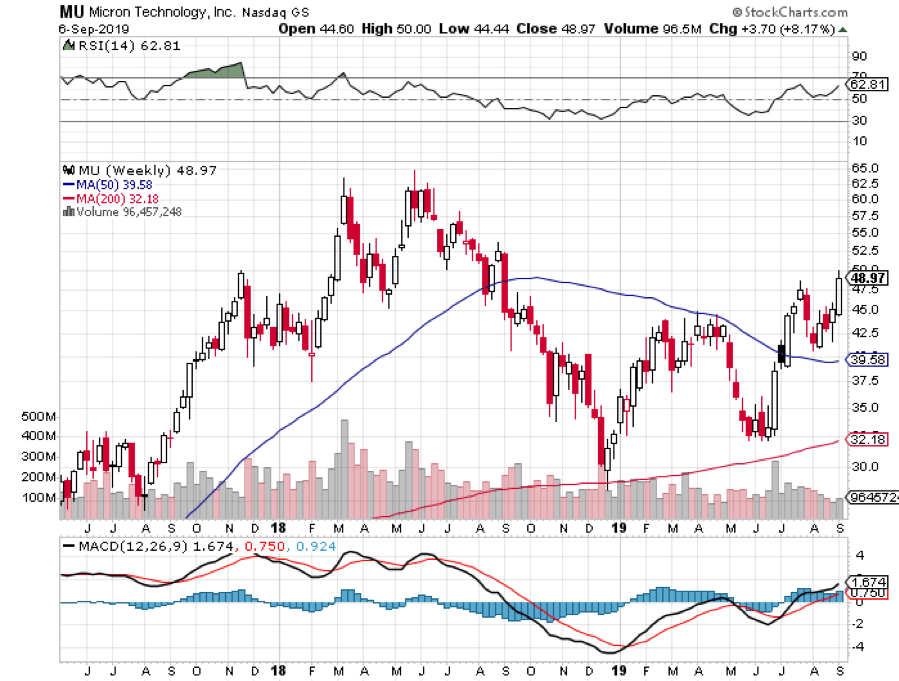
S&P tech stocks are trading at a 27 price earnings multiple. The S&P 500 Index, as a whole, trades at a 21 multiple. S&P value stocks, financials, and old-line recovery stocks like industrials and materials are trading at a 17 multiple.
Historically, companies with double the earnings power of the index trade at a 5-point premium to the main market. As long as this disparity exists, tech stocks will go down and value with go up.
However, we are getting close to a reversal. Allowing for market noise, I don’t see tech dropping more than 10% from here over the coming months. Then we will see the mother of all Q4 rallies taking it to new highs.
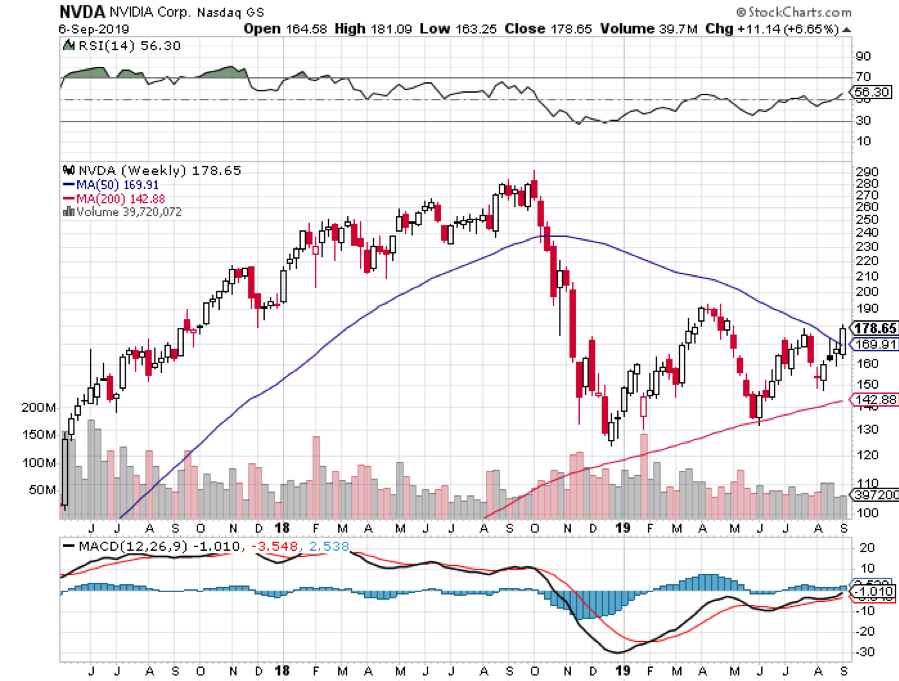
That explains why investors have been nibbling on tech lately, especially the best ones like NVIDIA (NVDA), Applied Materials (AMAT), and Salesforce (CRM). You also want to pick up big cap money machines like Alphabet (GOOG), Amazon (AMZN), Apple (AAPL), and Facebook (FB). Their LEAPS are begging for attention.
That means the downside from here is limited. Sorry Cassandras, no crashes here.
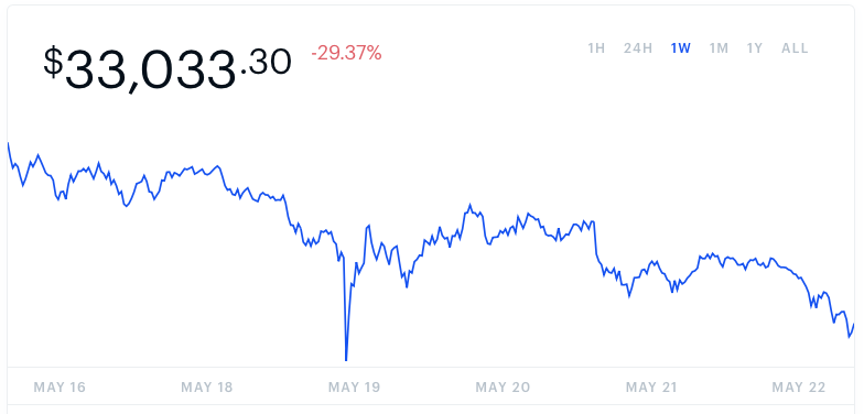
I am more convinced of this outcome than ever, given the substantial number of crashes and disasters, markets have weathered this year. These are truly Teflon markets. Last week, Bitcoin collapsed an amazing 55% in six weeks, wiping $1 trillion off the value of that market.
The fear had been that a crypto crash of this size would ignite a system contagion that would take everything down. A few years ago, it would have. But with massive Fed liquidity and unprecedented deficit spending, all we got was down 600 points one day and 600 up the next.
No crash here.
We’ve also had smaller crashes in sectors that were the most egregiously overpriced in February, like SPACS, meme stocks, and shares trading at 100 times sales with no earnings. Again, no harm no foul. It was a comeuppance that was well earned.
The big tell that I am right came screaming loud and clear last week from the US dollar, which hit a new 2021 low. A cheaper greenback means cheaper US stocks for foreign investors, which means they buy more of them. A weak buck also means that interest rates will stay lower for longer, which is great news for stocks, especially tech.
So, take it easy for the next few months. Keep positions small and rejoin the human race.
It seems odd going out into civilization and seeing live people walking around without masks. All the batteries on my watches are dead, as they have not been used for nearly two years, so they are getting replaced. I walked into my closet, and it was like adventuring into an archeological dig, with dozens of Turnbull & Asser shirts untouched by human hands. I’ve been living in Marine Corps sweats since 2019.
Bitcoin Crashes, down 33% on the day at the lows to $30,000, and off a heart-palpitating 55% from the April high. You wanted volatility, you got volatility! The problem for the rest of us is whether this will cause a real systemic financial crisis, with the Dow already down 560 at today’s low. Was Elon Musk the shoeshine boy giving tips at the market top?
Chip Shortage causes $110 Billion in US Car Industry Sales, in 2021 and will take years to address. Supply chains will need to be rebuilt. My neighbor just had to wait 11 months to take delivery of his Ford F-150.
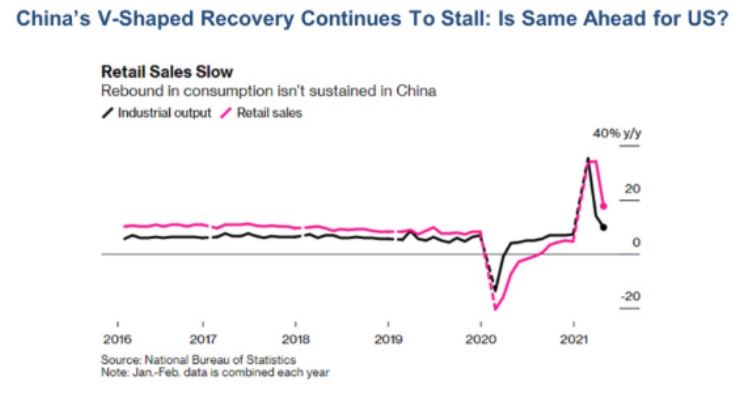
China’s Industrial Production Slows, from 14.1% in March to only 9.8% in April. That gives us a hint to our own future, as the Middle Kingdom emerged from the pandemic a year before we did. Retail sales also disappointed. After rocketing in 2020, the Chinese economy started slowing at the beginning of this year. The dead cat bounce in the economy is over. If this continues, it's bad news for copper prices of which the Middle Kingdom is the largest producer. If (FCX) closes under $40, stop out of all short-term longs immediately.
Housing Starts Dive, as builders run out of materials at reasonable prices. It gave the Dow Average a punch in the nose worth $220. Single family homes took the big hit, down 13.4% to 1.08 million. Permits are still up 70% YOY from when Covid completely shut the industry down. This is the most inflationary sector of the economy right now but barely registers in the CPI numbers. Prices must go even higher for frustrated buyers which are accelerating their rate of increase. Builders are including contingency clauses that allow price rises after the sale, a first. The South has dominated in starts where the population is moving and took the biggest hit. Buy (LEN), (KBH), and (PHM) on dips.
Existing Home Sales Drop 2.7%, in April to 5.85 million units. Inventories are down 20% YOY to only an unimaginable two-month supply. There’s nothing for sale. With the strongest YOY price gains in history, there is nothing for sale. It’s all about high prices, high prices, high prices. Homes over $1 million are up an incredible 214% YOY. The 70-year migration from North to South continues, costing democrats 5 seats in the House. Millennials are entering their peak home-buying years and that $150,000 four-bedroom home in Savannah, GA doesn’t look so bad.
Bitcoin is the Most Crowded State in the World, according to a survey of investment managers. That may explain the 35% plunge in cryptocurrency since April. Is this the end of the Ponzi scheme? Technology and ESG stocks are the second and third most over-owned, which may explain their recent flaccid performance.
Why is the Gold Hedge Working this Time? The Barbarous relic is finally giving investors the insurance and the downside hedge they need, after failing to do so during the last correction in February. That’s because interest rates were spiking in the winter but aren’t now. Interest rates are the enemy of all no-yielding assets, like precious metals.
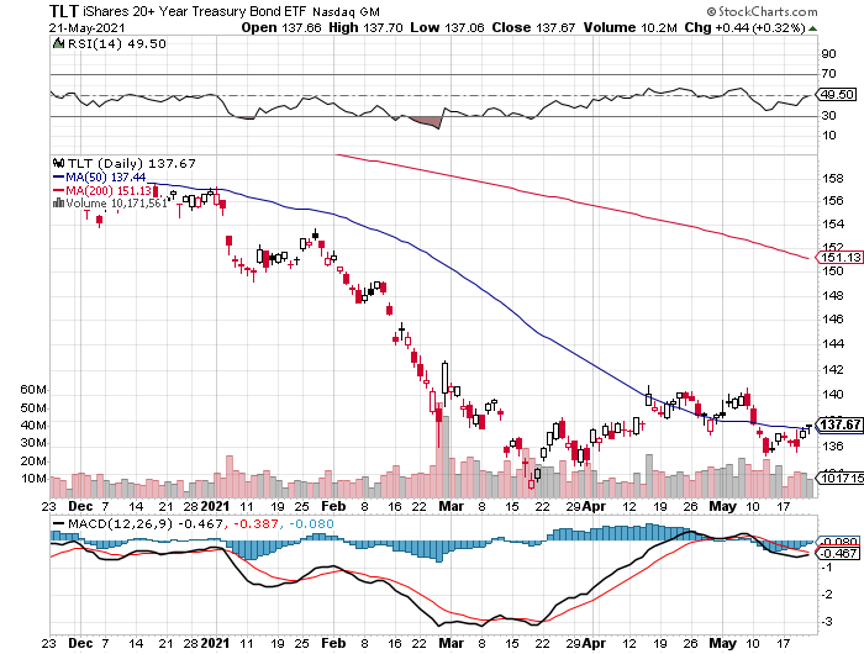
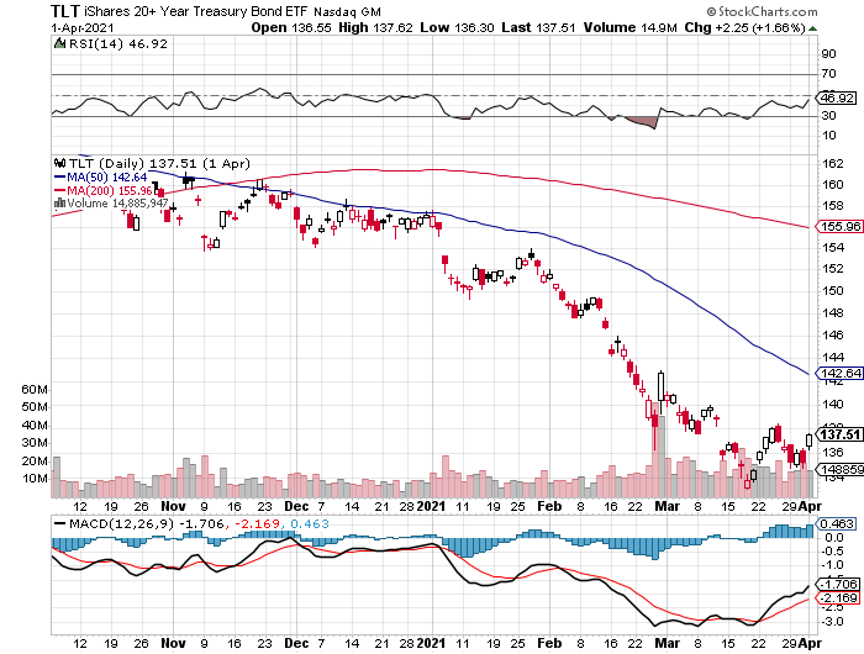
Fed Hints of Early Rate Rise, trashing both stocks and bonds. The big one could be here, a complete collapse of the US Treasury bond market. I’m already running the biggest (TLT) shorts ever. We should fall from the current $135 to $120 by yearend. Sell all (TLT) rallies.
Lumber Futures Collapse by 40%. There goes your inflation. Now if only Biden will end the Trump-era import duty on Canadian lumber. It gives a big boost to the “transitory” camp, arguing that this is just a one or two-month spike spawned by the cover recovery. Soaring lumber prices had been a key factor igniting new home prices.
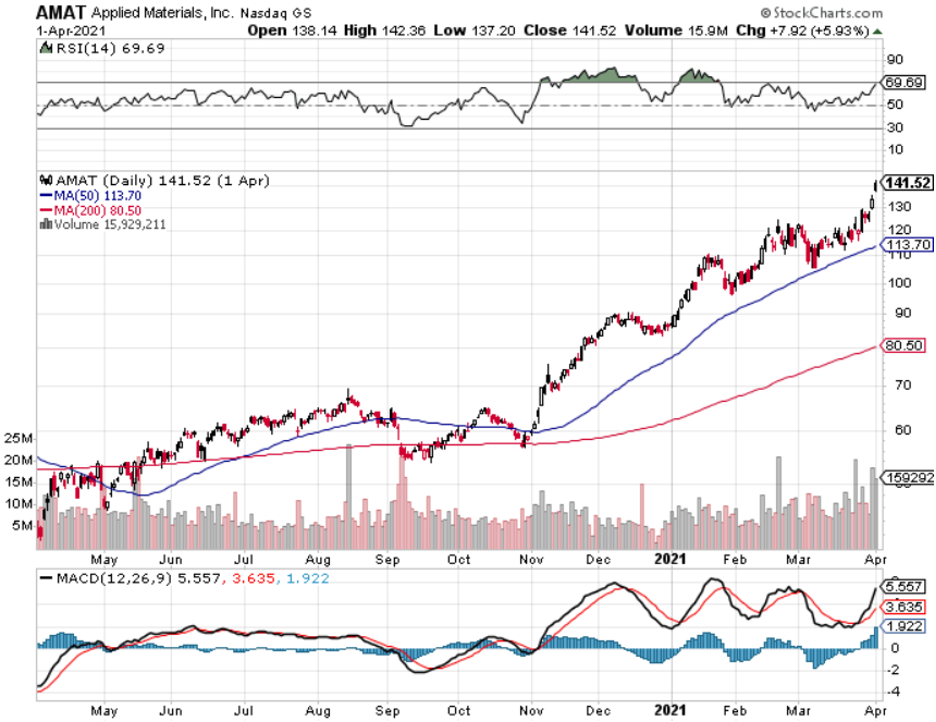
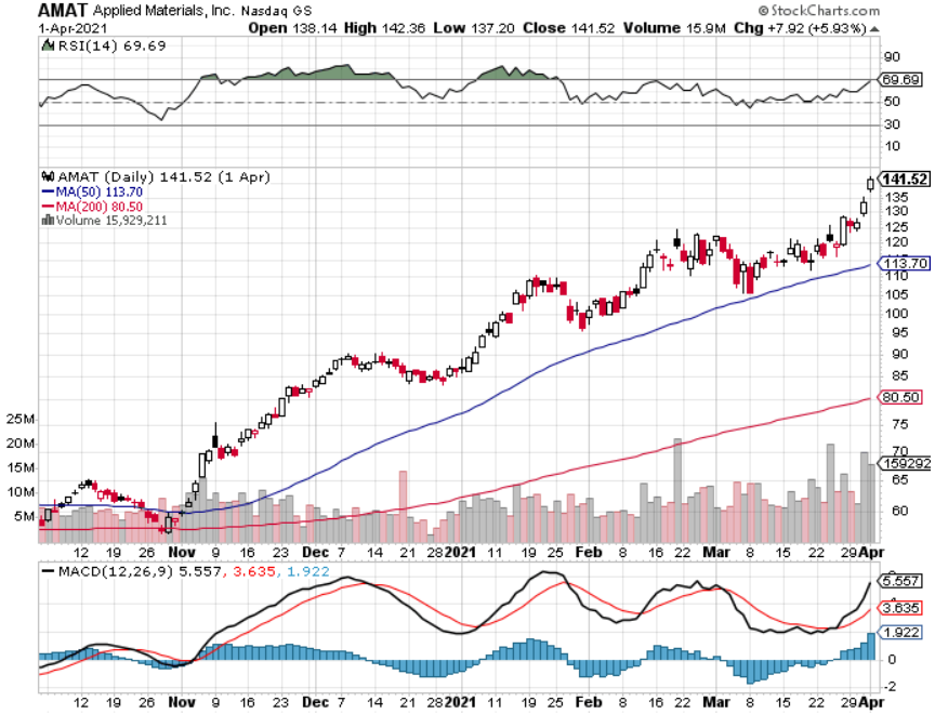
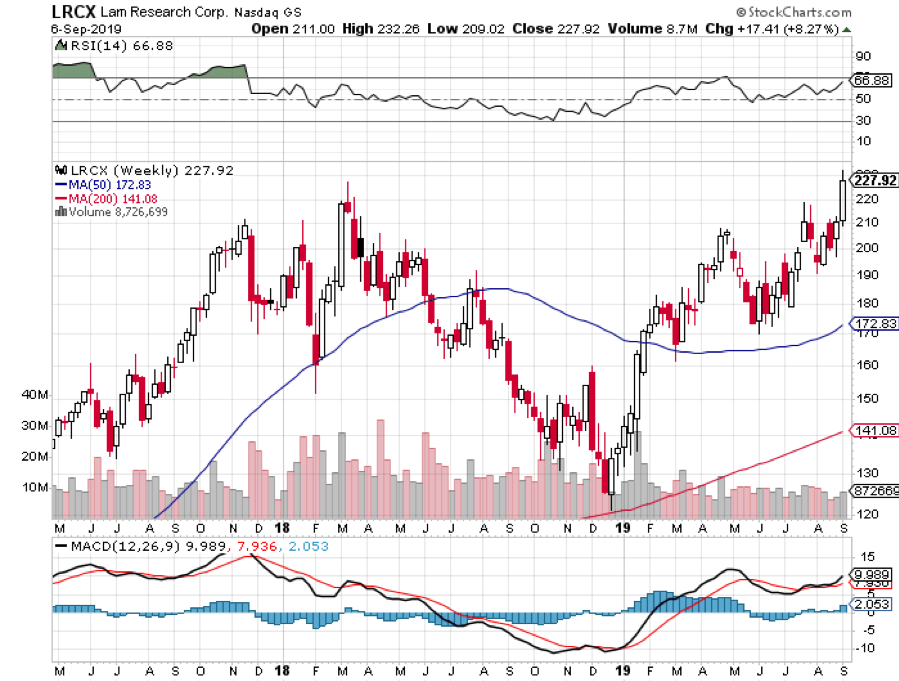
Applied Materials Knocks the Cover off the Ball, reporting blowout earnings. The semiconductors equipment maker has been the best performing chip-related stock of 2021, up 72%. (AMAT) sees a structural chip shortage lasting for years. DRAMs are speeding up, while NAN is slowing down. Customers are placing orders years in advance for the first time ever. A new $7.5 billion stock buyback plan and 9% dividend increase were announced. Buy (AMAT) on the dips.
My Ten-Year View
When we come out the other side of pandemic, we will be perfectly poised to launch into my new American Golden Age, or the next Roaring Twenties. With interest rates still at zero, oil cheap, there will be no reason not to. The Dow Average will rise by 400% to 120,000 or more in the coming decade. The American coming out the other side of the pandemic will be far more efficient and profitable than the old. Dow 120,000 here we come!
My Mad Hedge Global Trading Dispatch profit reached 7.48% gain so far in May on the heels of a spectacular 15.67% profit in April. That leaves me 50% invested and 50% cash. We actually have a shot at reaching a double-digit performance for the seventh month in a row.
My 2021 year-to-date performance soared to 67.24%. The Dow Average is up 11.79% so far in 2021.
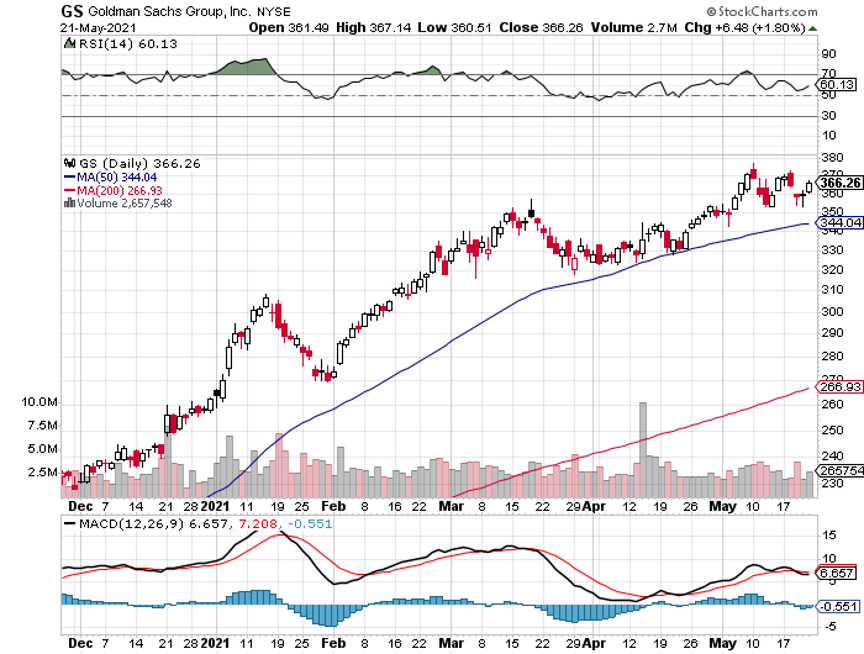
We got another major meltdown last week followed by an immediate recovery. I used the dip to reinitiate new positions in the (TLT), Goldman Sachs (GS), and Berkshire Hathaway (BRKB) to replace ones that expired on the Friday options expiration.
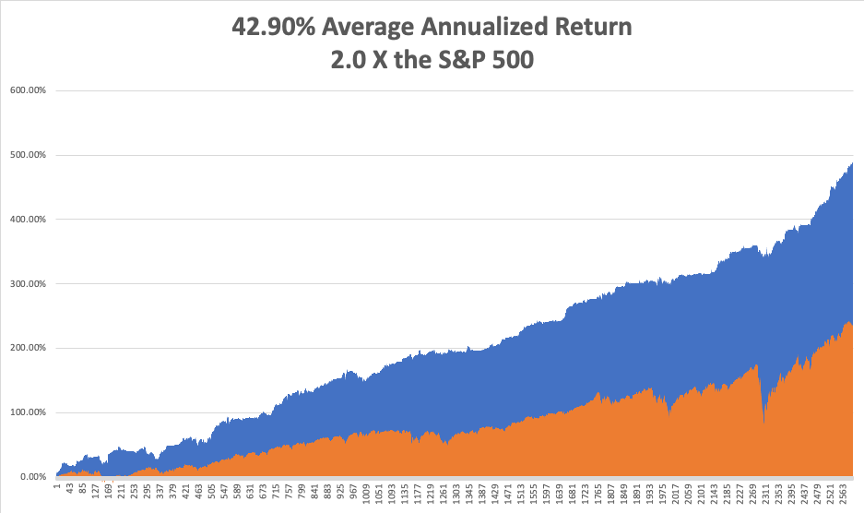
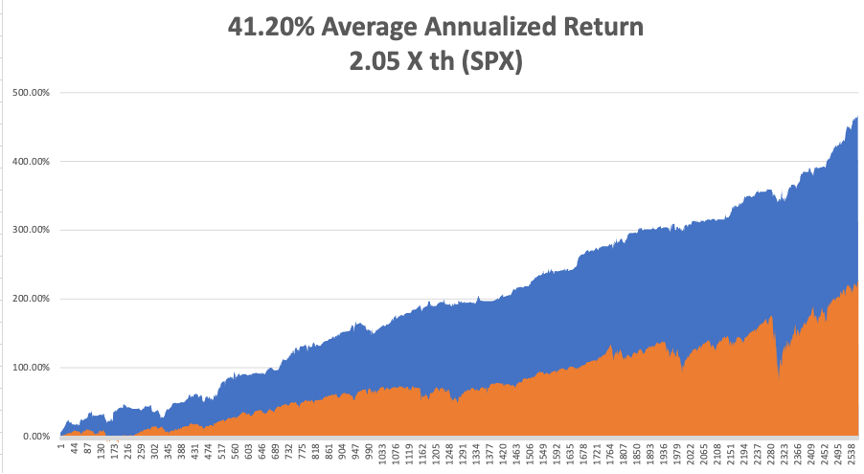
That brings my 11-year total return to 489.79%, some 2.00 times the S&P 500 (SPX) over the same period. My 11-year average annualized return now stands at an unbelievable 42.90%, easily the highest in the industry.
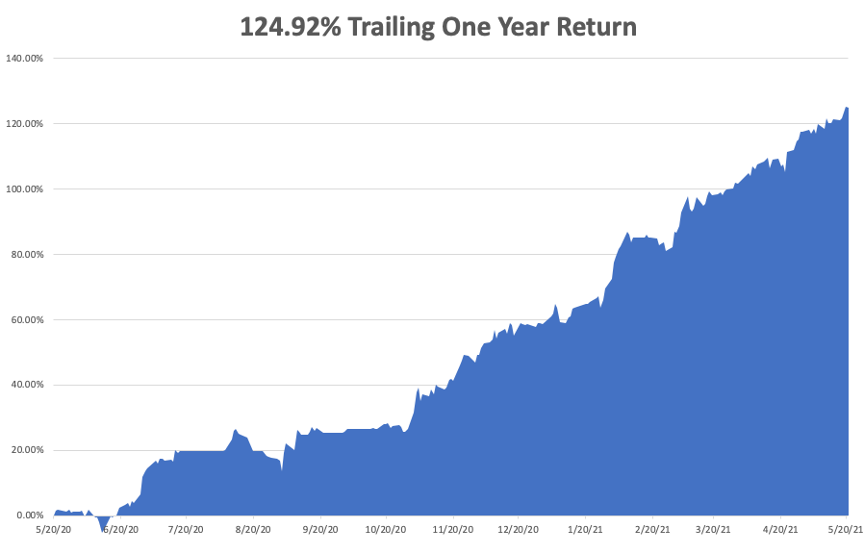
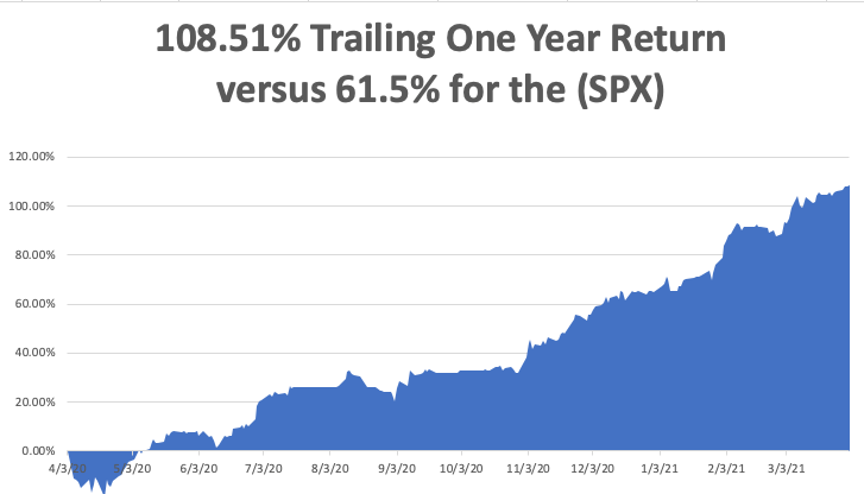
My trailing one-year return exploded to positively eye-popping 124.92%. I truly have to pinch myself when I see numbers like this. I bet many of you are making the biggest money of your long lives.
We need to keep an eye on the number of US Coronavirus cases at 33.1 million and deaths topping 590,000, which you can find here. Some 33.1 million Americans have contracted Covid-19.
The coming week will be a weak one on the data front.
On Monday, May 24, at 8:30 AM, the Chicago Fed National Activity Index is released.
On Tuesday, May 25, at 10:00 AM, the S&P Case Shiller National Home Price Index for March is announced.
On Wednesday, May 26 at 8:30 PM, MBA Mortgage Applications are revealed.
On Thursday, May 27 at 8:30 AM, the Weekly Jobless Claims are Published. We also get a second estimate for the red hot Q2 GDP.
On Friday, May 28 at 8:30 AM, the even hotter Personal Spending for April is disclosed. At 2:00 PM, we learn the Baker-Hughes Rig Count.
As for me, as this pandemic winds down, I am reminded of a previous one in which I played a role in ending.
After a 30-year effort, the World Health organization was on the verge of wiping out smallpox, a scourge that had been ravaging the human race since its beginning. I have seen Egyptian mummies at the Museum of Cairo that showed the scarring that is the telltale evidence of smallpox, which is fatal in 50% of cases.
By the early 1970s, the dread disease was almost gone but still remained in some of the most remote parts of the world. So, they offered a reward to anyone who could find live cases.
To join the American Bicentennial Mt. Everest Expedition in 1976, I took a bus to the eastern edge of Katmandu and started walking. That was the furthest roads went in those days. It was only 150 miles to basecamp and a climb of 14,000 feet.
Some 100 miles in, I was hiking through a remote village, which was a page out of the 14th century, back when families threw buckets of sewage into the street. The trail was lined with mud brick two-story homes with wood shingle roofs, with the second story overhanging the first.
As I entered the town, every child ran to their windows to wave, as visitors were so rare. Every smiling face was covered with healing but still bleeding smallpox sores. I was immune, since I received my childhood vaccination, but I kept walking.
Two months later, I returned to Katmandu and wrote to the WHO headquarters in Geneva about the location of the outbreak. A year later, I received a letter of thanks at my California address and a check for $100 telling me they had sent in a team to my valley in Nepal and vaccinated the entire population.
Some 15 years later, while on customer calls in Geneva for Morgan Stanley, I stopped by the WHO to visit a scientist I went to school with. It turned out I had become quite famous, as my smallpox cases in Nepal were the last ever discovered.
The WHO certified the world free of smallpox in 1980. The US stopped vaccinating children for smallpox in 1972, as the risks outweighed the reward.
Today, smallpox samples only exist at the CDC in Atlanta frozen in liquid nitrogen at minus 346 degrees Fahrenheit in a high-security level 5 biohazard storage facility. China and Russia probably have the same.
That’s because scientists fear that terrorists might dig up the bodies of some British sailors who were known to have died of smallpox in the 19th century and were buried on the north coast of Greenland remaining frozen ever since. If you need a new smallpox vaccine, you have to start from somewhere.
As for me, I am now part of the 34% of Americans who remain immune to the disease. I’m glad I could play my own small part in ending it.
Stay healthy.
John Thomas
CEO & Publisher
The Diary of a Mad Hedge Fund Trader
On Mt. Everest, Smallpox-Free in 1976
Bitcoin