Global Market Comments
April 24, 2019
Fiat Lux
Featured Trade:
(WHY ARE BOND YIELDS SO LOW?)
(TLT), (TBT), (LQD), (MUB), (LINE), (ELD),
(QQQ), (UUP), (EEM), (DBA)
(BRING BACK THE UPTICK RULE!)

Global Market Comments
April 24, 2019
Fiat Lux
Featured Trade:
(WHY ARE BOND YIELDS SO LOW?)
(TLT), (TBT), (LQD), (MUB), (LINE), (ELD),
(QQQ), (UUP), (EEM), (DBA)
(BRING BACK THE UPTICK RULE!)

Investors around the world have been confused, befuddled, and surprised by the persistent, ultra-low level of long-term interest rates in the United States.
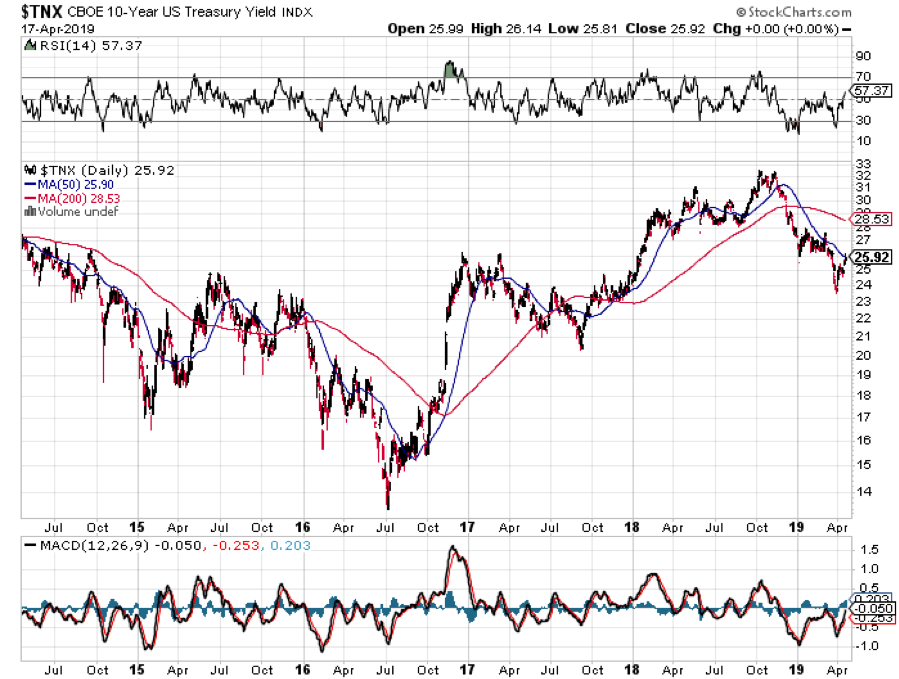
At today’s close, the 30-year Treasury bond yielded a parsimonious 2.99%, the ten years 2.59%, and the five years only 2.40%. The ten-year was threatening its all-time low yield of 1.33% only three years ago, a return as rare as a dodo bird, last seen in the 19th century.
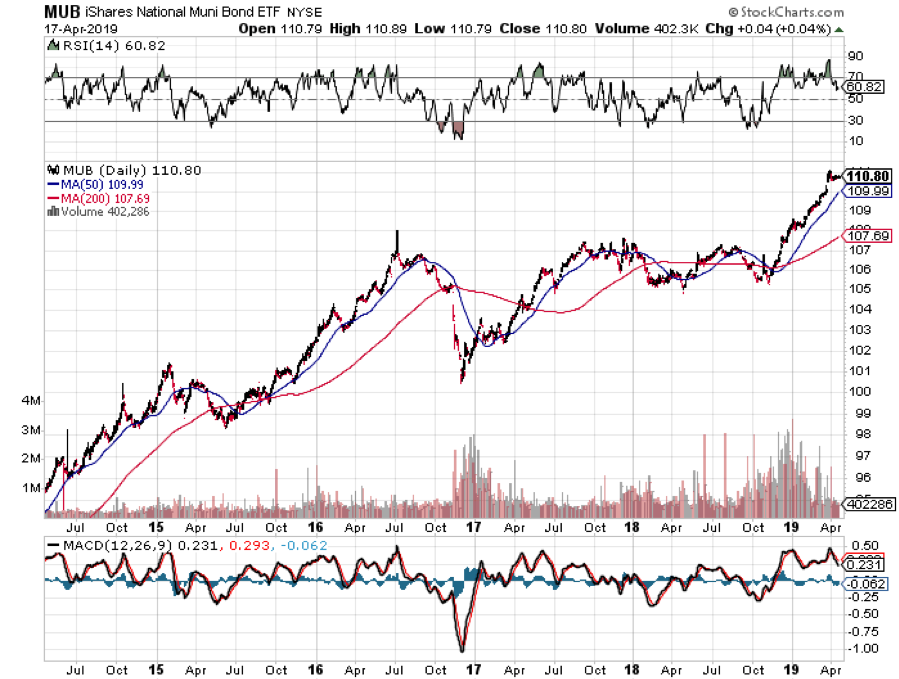
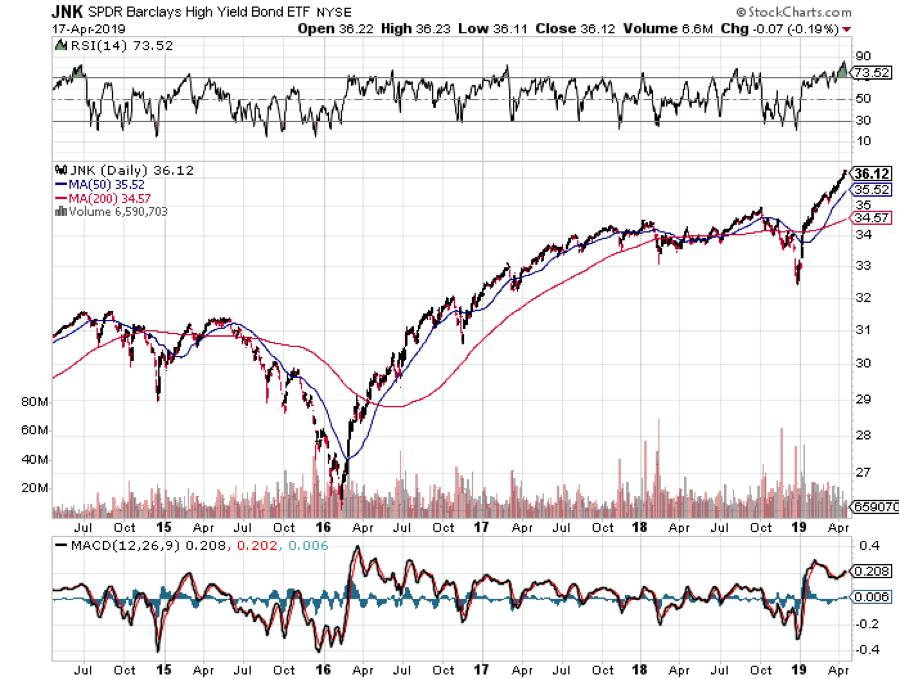
What’s more, yields across the entire fixed income spectrum have been plumbing new lows. Corporate bonds (LQD) have been fetching only 3.72%, tax-free municipal bonds (MUB) 2.19%, and junk (JNK) a pittance at 5.57%.
Spreads over Treasuries are approaching new all-time lows. The spread for junk over of ten-year Treasuries is now below an amazing 3.00%, a heady number not seen since the 2007 bubble top. “Covenant light” in borrower terms is making a big comeback.
Are investors being rewarded for taking on the debt of companies that are on the edge of bankruptcy, a tiny 3.3% premium? Or that the State of Illinois at 3.1%? I think not.
It is a global trend.
German bunds are now paying holders 0.05%, and JGBs are at an eye-popping -0.05%. The worst quality southern European paper has delivered the biggest rallies this year.
Yikes!
These numbers indicate that there is a massive global capital glut. There is too much money chasing too few low-risk investments everywhere. Has the world suddenly become risk averse? Is inflation gone forever? Will deflation become a permanent aspect of our investing lives? Does the reach for yield know no bounds?
It wasn’t supposed to be like this.
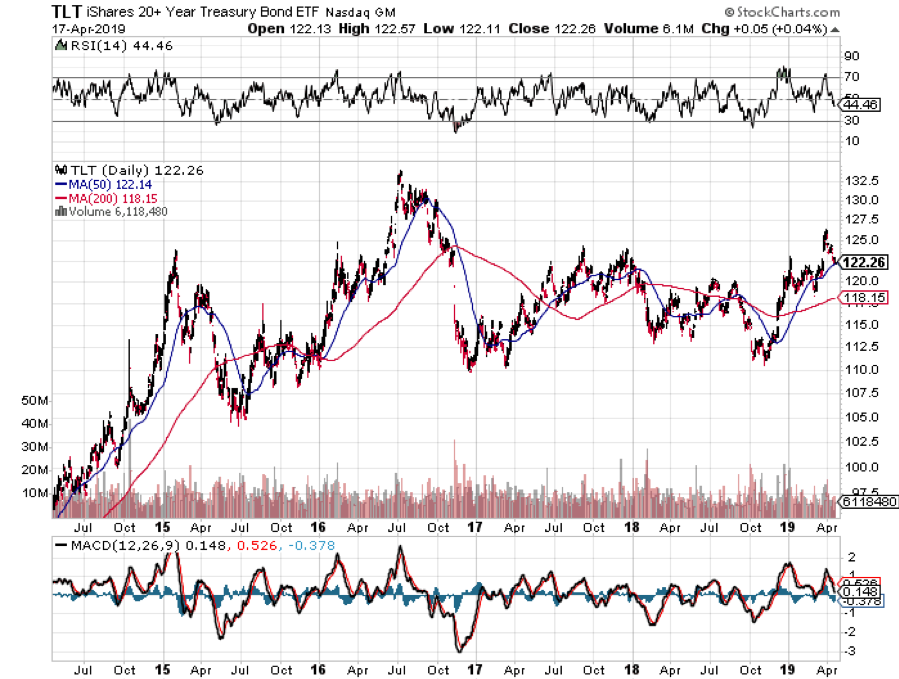
Almost to a man, hedge fund managers everywhere were unloading debt instruments last year when ten-year yields peaked at 3.25%. They were looking for a year of rising interest rates (TLT), accelerating stock prices (QQQ), falling commodities (DBA), and dying emerging markets (EEM). Surging capital inflows were supposed to prompt the dollar (UUP) to take off like a rocket.
It all ended up being almost a perfect mirror image portfolio of what actually transpired since then. As a result, almost all mutual funds were down in 2018. Many hedge fund managers are tearing their hair out, suffering their worst year in recent memory.
What is wrong with this picture?
Interest rates like these are hinting that the global economy is about to endure a serious nosedive, possibly even re-entering recession territory….or it isn’t.
To understand why not, we have to delve into deep structural issues which are changing the nature of the debt markets beyond all recognition. This is not your father’s bond market.
I’ll start with what I call the “1% effect.”
Rich people are different than you and I. Once they finally make their billions, they quickly evolve from being risk takers into wealth preservers. They don’t invest in start-ups, take fliers on stock tips, invest in the flavor of the day, or create jobs. In fact, many abandon shares completely, retreating to the safety of coupon clipping.
The problem for the rest of us is that this capital stagnates. It goes into the bond market where it stays forever. These people never sell, thus avoiding capital gains taxes and capturing a future step up in the cost basis whenever a spouse dies. Only the interest payments are taxable, and that at a lowly 2.59% rate.
This is the lesson I learned from servicing generations of Rothschilds, Du Ponts, Rockefellers, and Gettys. Extremely wealthy families stay that way by becoming extremely conservative investors. Those that don’t, you’ve never heard of because they all eventually went broke.
This didn’t use to mean much before 1980, back when the wealthy only owned less than 10% of the bond market, except to financial historians and private wealth specialists, of which I am one. Now they own a whopping 25%, and their behavior affects everyone.
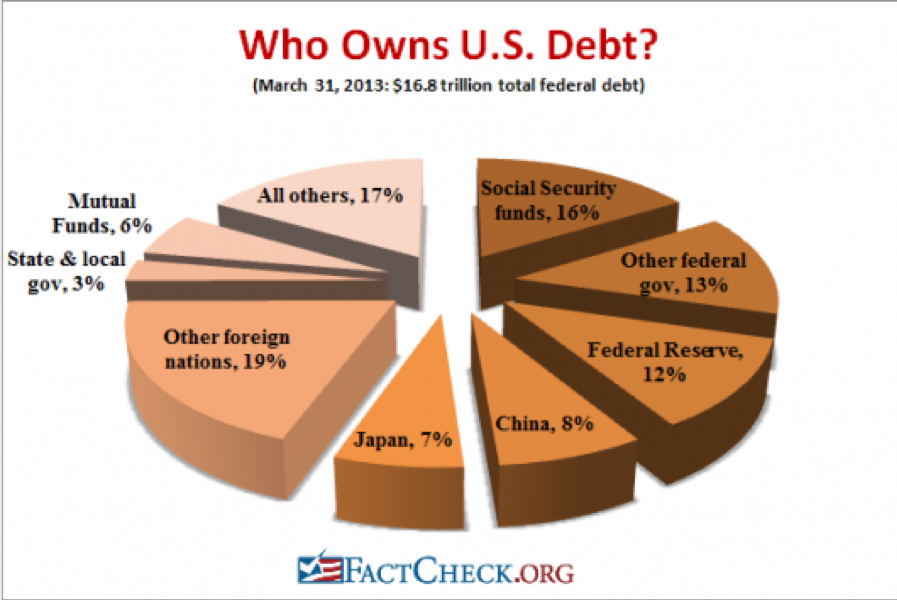
Who has been the largest buyer of Treasury bonds for the last 30 years? Foreign central banks and other governmental entities which count them among their country’s foreign exchange reserves. They own 36% of our national debt with China in the lead at 8% (the Bush tax cut that was borrowed), and Japan close behind with 7% (the Reagan tax cut that was borrowed). These days they purchase about 50% of every Treasury auction.
They never sell either, unless there is some kind of foreign exchange or balance of payments crisis which is rare. If anything, these holdings are still growing.
Who else has been soaking up bonds, deaf to repeated cries that prices are about to plunge? The Federal Reserve which, thanks to QE1, 2, 3, and 4, now owns 13.63% of our $22 trillion debt.
An assortment of other government entities possesses a further 29% of US government bonds, first and foremost the Social Security Administration with a 16% holding. And they ain’t selling either, baby.
So what you have here is the overwhelming majority of Treasury bond owners with no intention to sell. Ever. Only hedge funds have been selling this year, and they have already done so, in spades.
Which sets up a frightening possibility for them, now that we have broken through the bottom of the past year’s trading range in yields. What happens if bond yields fall further? It will set off the mother of all short-covering squeezes and could take ten-year yield down to match 2012, 1.33% low, or lower.
Fasten your seat belts, batten the hatches, and down the Dramamine!
There are a few other reasons why rates will stay at subterranean levels for some time. If hyper accelerating technology keeps cutting costs for the rest of the century, deflation basically never goes away (click here for “Peeking Into the Future With Ray Kurzweil” ).
Hyper accelerating corporate profits will also create a global cash glut, further levitating bond prices. Companies are becoming so profitable they are throwing off more cash than they can reasonably use or pay out.
This is why these gigantic corporate cash hoards are piling up in Europe in tax-free jurisdictions, now over $2 trillion. Is the US heading for Japanese style yields, of zero for 10-year Treasuries?
If so, bonds are a steal here at 2.59%. If we really do enter a period of long term -2% a year deflation, that means the purchasing power of a dollar increases by 35% every decade in real terms.
The threat of a second Cold War is keeping the flight to safety bid alive, and keeping the bull market for bonds percolating. You can count on that if the current president wins a second term.

A reader emailed me yesterday to tell me that while visiting his daughter at a college in North Carolina, he refilled his rental car with gas for $1.39 a gallon.
So I got the idea that something really big is going on here that no one is yet seeing. I processed the possibilities in my snowshoe up to the 10,000-foot level above Lake Tahoe last night.
By the way, the view of the snow covered High Sierras under the moonlight was incredible.
For decades, I have dismissed the hopes of my environmentalist friends that alternatives will soon replace oil (USO) as our principal source of energy.
I have long agreed with the views of my fracking buddies in the Texas Barnett Shale that it will be decades before wind, solar, and biodiesel make any appreciable dent in our energy makeup.
It took 150 years to build our energy infrastructure, and you don?t replace that overnight. The current weakness in oil prices is a simple repeat of a predictable cycle that has continued for a century and a half. In a couple years, Texas tea will be posting triple digits once again.
I always thought that oil had one more super spike left in it. After that, it will fade into history, reduced to limited applications, like making plastics and asphalt, probably sometime in the 2030?s.
The price for a barrel of oil should then vaporize to $5.
But given the price action for energy and all other commodities I?m starting to wonder if this time I?m wrong.
I have watched with utter amazement while Freeport McMoRan (FCX) plunged from $38 to $3. I was gob smacked to see Linn Energy (LINE), admittedly a leveraged play, crater from $32 to 30 cents.
And I was totally befuddled to see gas major Chesapeake Energy (CHK) implode from $65 to $1.
Has the world gone mad?
When the data don?t match your view, it?s time to change your view.
Maybe there won?t be another spike in oil prices. Could its disappearance from the modern industrialized economy have already begun?
That would certainly explain a lot of the recent eye-popping price action in the markets. In five short years oil has dropped 82%. It did this while global GDP grew by 20% and auto sales, and therefore gasoline demand, has been booming.
Of course, you could just call all of this a big giant reversion to the mean.
Over the past 150 years, the average, inflation adjusted price of oil has been $35 a barrel. The price for gasoline has been $2.25 a gallon, exactly where it was in 1932, and where it now is in much of the country.
I know all of these numbers because I once did a study to see if oil prices are rigged (conclusion: they are). How can the price of a commodity stay the same for 150 years?
Wait, the naysayers announce. Things don?t happen that fast.
But they do, my friends, they do, especially in energy.
Until 1849, my ancestors were the largest producers of whale oil on Nantucket Island. (Our family name,? Coffin, was mentioned in ?Moby Dick? seven times, and was a focus of the just released film, ?In the Heart of the Sea.?)
Then this stuff called petroleum came along, wrested from the ground with new technology by men like Drake and Rockefeller. The whale oil market crashed, dropping in price by 90%, and virtually disappeared in two years.
My relatives were wiped out and moved to San Francisco, which they already knew from their whaling days, and where gold had just been found.
A half-century later, this thing called an ?automobile? came along meant to replace the ubiquitous horse and buggy. People laughed. It was loud, noisy, smelly, inefficient, and expensive. Only the rich could afford them.
You had to go to a drug store to buy high priced fuel in one-gallon tins. And it scared the horses. England passed a national automobile speed limit of 5 miles per hour, as cars were considered dangerous.
Then huge oil discoveries were made in Texas and California (watch ?There Will Be Blood?), the Hughes drill bit came along, and gasoline prices fell sharply. Suddenly cars were everywhere. The horse population declined from 100 million to only 1 million today.
All of this is a long-winded, history packed way of saving ?This time it may be different?.
I have on my desktop a Trade Alert already written up to buy the (USO) May, 2016 $9 calls. Today, they traded at $1.00. I?m just waiting for another melt down in oil to take a low risk punt on the long side.
If we rocket back up to $100, as many are predicting, these calls will be worth a fortune. But you know what, oil may only peak out at $44 this time. The trade will still make money, but not as much as in past cycles.
So, you better think hard about loading up on too many oil stocks at these distressed levels. Look what has already happened to the coal industry (KOL), which has essentially gone bankrupt.
You could well be buying into the buggy whip industry circa 1900.
I am sitting here at the Lone Eagle Grill in Incline Village, Nevada, enjoying a rare solo lunch. No one is asking me about the future of interest rates, if there is any gold inside Fort Knox or if the aliens really landed at Roswell, New Mexico.
My table overlooks majestic Lake Tahoe, and a brace of mallard ducks has just skidded across the smooth surface for a landing.
My big score last night was coming across a wild bobcat, the first I had ever seen in the Sierras. After cautiously studying me for a minute with his bright yellow glowing eyes, he scampered up the mountain.
My pastrami sandwich is cooked to perfection, and would give Manhattan?s best culinary effort a run for its money. In fact, I have enough food here for two entire meals. Bring on the doggie bag!
After surviving a meat grinder of a January, putting the pedal to the metal in February, and dodging the raindrops of March, the model-trading portfolio of the Mad Hedge Fund Trader has posted a year-to-date gain of 10%.
We have generated profits for followers every month this year, and are now a mere 4.75% short of a new all time performance high.
Mad Day Trader, Jim Parker, and myself have performed like tag team wrestlers, delivering winners for our paid subscribers one right after the other. Some 12 out of my last 14 Trade Alerts have been profitable.
I managed to nail the collapse in the euro (FXE), (EUO) big time, backing that up with profitable long positions in the S&P 500 (SPY), the Russell 2000, and Gilead Sciences (GILD).
When the markets turned jittery, I coined it with short positions in Alcoa (AA), QUALCOM (QCOM) and AT&T (T).
Only a premature long in oil (LINE) and a short in Treasuries (TBT) have scarred my numbers so far this year.
Jim has been on an absolute hot streak in 2015, shaking the Bull Run in biotechs for all it is worth (ZIOP), (THRX), (ZTS) and executing some perfectly times shorts in oil (USO).
This is compared to the miserable performance of the Dow Average, which is up a pitiful +2% during the same period.
The nearly four and a half year return of my Trade Alert service is now at an amazing 162.4%, compared to a far more modest increase for the Dow Average during the same period of only 51%.
That brings my averaged annualized return up to 38.2%. Not bad in this zero interest rate world. It appears better to take on some risk and reach for capital gains and trading profits, than surrender to the paltry fixed income yields out there.
This has been the profit since my groundbreaking trade mentoring service was first launched in 2010. Thousands of followers now earn a full time living solely from my Trade Alerts, a development of which I am immensely proud.
What saved my bacon this month was my instant and accurate decoding of Fed chairman Janet Yellen?s cryptic comments on the future of possible interest rate hikes, or the lack thereof.
We got to eat our ?patience? and have it too.
Wall Street gets so greedy, and takes out so much money for itself, there is now nothing left for the individual investor any more. They literally kill the goose that lays the golden egg.
The Mad Hedge Fund Trader seeks to address this imbalance and level the playing field for the average Joe. Looking at the testimonials that come in every day, I?d say we?ve accomplished that goal.
It has all been a vindication of the trading and investment strategy that I have been preaching to followers for the past seven years.
Quite a few followers were able to move fast enough to cash in on my trading recommendations. To read the plaudits yourself, please go to my testimonials page by clicking here.
Watch this space, because the crack team at Mad Hedge Fund Trader has more new products and services cooking in the oven. You?ll hear about them as soon as they are out of beta testing.
Our business is booming, so I am plowing profits back in to enhance our added value for you.
The coming year promises to deliver a harvest of new trading opportunities. The big driver will be a global synchronized recovery that promises to drive markets into the stratosphere by the end of 2015.
Global Trading Dispatch, my highly innovative and successful trade-mentoring program, earned a net return for readers of 40.17% in 2011, 14.87% in 2012, and 67.45% in 2013, and 30.3% in 2014.
Our flagship product,?Mad Hedge Fund Trader PRO, costs $4,500 a year. It includes?Global Trading Dispatch(my trade alert service and daily newsletter). You get a real-time trading portfolio, an enormous research database and live biweekly strategy webinars. You also get Jim Parker?s?Mad Day Trader?service and?The Opening Bell with Jim Parker.
To subscribe, please go to my website, ?www.madhedgefundtrader.com, click on the ?Memberships? located on the second row of tabs.
By the way, those of you who ran up huge profits with your euro shorts in January and February, and the overnight killing I scored with the Russell 2000 (IWM) this week, you all owe me new testimonials.
Ship em in!
Oh, and buy the way, there is no gold in Fort Knox. That is why Nixon took us off the gold standard in 1973. And the aliens did land at Roswell. Where do you think my iPhone and Tesla came from?
Investors around the world have been confused, befuddled and surprised by the persistent, ultra low level of long term interest rates in the United States.
At today?s close, the 30 year Treasury bond yielded a parsimonious 2.01%, the ten year, 2.62%, and the five year only 1.51%. The ten-year was threatening its all time low yield of 1.37% only two weeks ago, a return as rare as a dodo bird, last seen in August, 2012.
What?s more, yields across the entire fixed income spectrum have been plumbing new lows. Corporate bonds (LQD) have been fetching only 3.29%, tax-free municipal bonds (MUB) 2.89%, and junk (JNK) a pittance at 5.96%.
Spreads over Treasuries are approaching new all time lows. The spread for junk over of ten year Treasuries is now below an amazing 3.00%, a heady number not seen since the 2007 bubble top. ?Covenant light? in borrower terms is making a big comeback.
Are investors being rewarded for taking on the debt of companies that are on the edge of bankruptcy, a tiny 3.3% premium? I think not.
It is a global trend.
German bunds are now paying holders 0.35%, and JGB?s are at an eye popping 0.30%. The worst quality southern European paper has delivered the biggest rallies this year. Portuguese government paper is paying only 2.40%, and is rapidly closing in on US government yields.
Yikes!
These numbers indicate that there is a massive global capital glut. There is too much money chasing too few low risk investments everywhere. Has the world suddenly become risk averse? Is inflation gone forever? Will deflation become a permanent aspect of our investing lives? Does the reach for yield know no bounds?
It wasn?t supposed to be like this.
Almost to a man, hedge fund managers everywhere were unloading debt instruments in January. They were looking for a year of rising interest rates (TLT), accelerating stock prices (QQQ), falling commodities (DBA), and dying emerging markets (EEM). Surging capital inflows were supposed to prompt the dollar (UUP) to take off like a rocket.
It all ended up being almost a perfect mirror image portfolio of what actually transpired since then. As a result, almost all mutual funds are down so far in 2014. Many hedge fund managers are tearing their hair out, suffering their worst year in recent memory.
What is wrong with this picture?
Interest rates like these are hinting that the global economy is about to endure a serious nose dive, possibly even re-entering recession territory?or it isn?t.
To understand why not, we have to delve into deep structural issues, which are changing the nature of the debt markets beyond all recognition. This is not your father?s bond market.
I?ll start with what I call the ?1% effect.?
Rich people are different than you and I. Once they finally make their billions, they quickly evolve from being risk takers into wealth preservers. They don?t invest in start-ups, take fliers on stock tips, invest in the flavor of the day, or create jobs. In fact, many abandon shares completely, retreating to the safety of coupon clipping.
The problem for the rest of us is that this capital stagnates. It goes into the bond market where it stays forever. These people never sell, thus avoiding capital gains taxes and capturing a future step up in the cost basis whenever a spouse dies. Only the interest payments are taxable and that at a lowly 20% rate.
This is the lesson I learned from servicing generations of Rothschild?s, Du Ponts, Rockefellers, and Getty. Extremely wealthy families stay that way by becoming extremely conservative investors. Those that don?t, you?ve never heard of, because they all eventually went broke.
This didn?t used to mean much before 1980, back when the wealthy only owned 10% of the bond market, except to financial historians and private wealth specialists, of which I am one. Now they own a whopping 23%, and their behavior affects everyone.
Who has bee the largest buyer of Treasury bonds for the last 30 years? Foreign central banks and other governmental entities, which count them among their country?s foreign exchange reserves. They own 36% of our national debt, with China in the lead at 8% (the Bush tax cut that was borrowed), and Japan close behind with 7% (the Reagan tax cut that was borrowed). These days they purchase about 50% of every Treasury auction.
They never sell either, unless there is some kind of foreign exchange or balance of payments crisis, which is rare. If anything, these holdings are still growing.
Who else has been soaking up bonds, deaf to repeated cries that prices are about to plunge? The Federal Reserve, which thanks to QE1, 2, and 3, now owns 22% of our $17 trillion debt. Both the former Federal Reserve governor Ben Bernanke, and the present one, Janet Yellen, have made clear they have no plans to sell these bonds. They will run them to maturity instead, minimizing the market impact.
An assortment of other government entities possess a further 29% of US government bonds, first and foremost the Social Security Administration, with a 16% holding. And they ain?t selling either, baby.
So what you have here is the overwhelming majority of Treasury bond owners with no intention to sell. Only hedge funds have been selling this year, and they have already done so, in spades.
Which sets up a frightening possibility for them, now that we are at the very bottom of the past year?s range in yields. What happens if bond yields fall further? It will set off the mother of all short covering squeezes and could take ten-year yield down to match the 2012, 2.38% low.
Fasten your seat belts, batten the hatches, and down the Dramamine!
There are a few other reasons why rates will stay at subterranean levels for some time. If hyper accelerating technology keeps cutting costs for the rest of the century, deflation basically never goes away (click here?for ?Peeking into the Future with Ray Kurzweil?).
Hyper accelerating corporate profits will also create a global cash glut, further levitating bond prices. Companies are becoming so profitable they are throwing off more cash then they can reasonably use or pay out.
This is why these gigantic corporate cash hoards are piling up in Europe in tax free jurisdictions, now over $2 trillion. Is the US heading for Japanese style yields, or 0.39% for 10 year Treasuries?
If so, bonds are a steal here at 2.55%. If we really do enter a period of long term -2% a year deflation, that means the purchasing power of a dollar increases by 35% every decade in real terms.
The threat of a second Cold War is keeping the flight to safety bid alive, and keeping the bull market for bonds percolating. This could put a floor under bond prices for another decade, and Vladimir Putin?s current presidential run could last all the way under 2014.
All of this is why I?m out of the bond market for now, and will remain so for a while.
I?m really glad I watched the Super Bowl yesterday. Not only was it a great warm-up for next year?s championship game, which will be in my hometown of San Francisco. I also witnessed the worst coaching call in football history.
The Seattle Seahawks had the game in the bag. All they had to do was move the ball one foot over two tries at the goal line. Instead, they passed? Too bad I wasn?t able to find a bookie to take a last minute six-figure bet. I expected New England to win.
I have to tell you that I sympathize with Seahawks Coach Peter Carroll. For I sent out one of the worst recommendations in trading history with my BUY of master limited partnership Linn Energy (LINE) on December 1.
I then proceeded to break every rule in the trader?s handbook on how to manage this position. The errors were so many that I have to list them:
1) I scored the instant profit I was looking for, making 80 basis points within two days. I didn?t take it. Instead I got greedy, hanging on for more. It never showed.
2) I then ignored my own stop loss at $15, even though most of you bailed out then and there.
3) I then committed anther sin, waiting for the units to get back to my cost to get out, even though I constantly admonish followers never to do this. The market doesn?t care what your cost is. The market is the market. It has zero memory, and could care less who you are.
4) There were several substantial rallies that I could have sold into for a much smaller loss, to $14.80, $11.90 and $11.70. I didn?t. The ?getting out for even? syndrome strikes again.
5) I expected oil to bottom out in the low $60?s, which was much lower than most people?s targets. It didn?t. Instead, it dropped another $20 to the $43 handle. Once there is a glut of oil, there is no place to put it, as all storage is full, so it always plunges lower than you expect. With more oil industry experience than most traders, I already knew this. But I ignored the writing on the wall.
6) I waited for a yearend short covering rally to take me out of the position. It never showed. Instead, it went down faster, hitting a new five year low of $9.30.
7) I waited for a New Year rally to take me out. Ditto.
At this point, (LINN) is acting like a classic busted stock. Even though oil has bounced back by a hefty 15% in recent days, (LINN) has barely moved. If you throw good news on a stock and it doesn?t move, it is time to say hasta la vista baby.
For more depth on the grim outlook for Texas tea, please read my recent piece, ?More Pain to Come in Oil? by clicking here. Now is not the time to maintain an aggressive long in energy.
I?m sure (LINN) will come back some day, as it is well managed. In fact, it might even be the big trade of the year. But this could happen in months, or even years. And if you haven?t noticed, the name of this service is the Diary of a Mad Hedge Fund Trader, not the Diary of a Mad Long Term Investor.
Where I live, long-term is a long-winded way of saying "wrong".
When the Trade Alerts quit working. I stop sending them out. That?s my trading strategy right now. It?s as simple as that.
So when I received a dozen emails this morning asking if it is time to double up on Linn Energy (LINE), I shot back ?Not yet!? There is no point until oil puts in a convincing bottom, and that may be 2015 business.
Traders have been watching in complete awe the rapid decent the price of Linn Energy, which is emerging as the most despised asset of 2014, after commodity producer Russia (RSX).
But it is becoming increasingly apparent that the collapse of prices for the many commodities is part of a much larger, longer-term macro trend.
(LINN) is doing the best impersonation of a company going chapter 11 I have ever seen, without actually going through with it. Only last Thursday, it paid out a dividend, which at today?s low, works out to a mind numbing 30% yield.
I tried calling the company, but they aren?t picking up, as they are inundated with inquires from investors. Search the Internet, and you find absolutely nothing. What you do find are the following reasons not to buy Linn Energy today:
1) Falling oil revenue is causing Venezuela to go bankrupt.
2) Large layoffs have started in the US oil industry.
3) The Houston real estate industry has gone zero bid.
4) Midwestern banks are either calling in oil patch loans, or not renewing them.
5) Hedge Funds have gone catatonic, their hands tied until new investor funds come in during the New Year.
6) Every oil storage facility in the world is now filled to the brim, including many of the largest tankers.
Let me tell you how insanely cheap (LINN) has gotten. In 2009, when the financial system was imploding and the global economy was thought to be entering a prolonged Great Depression, oil dropped to $30, and (LINN) to $7.50. Today, the US economy is booming, interest rates are scraping the bottom, employment is at an eight year high, and (LINE) hit $9.70, down $70 in six months.
Go figure.
My colleague, Mad Day Trader, Jim Parker, says this could all end on Thursday, when the front month oil futures contract expires. It could.
It isn?t just the oil that is hurting. So are the rest of the precious and semi precious metals (SLV), (PPLT), (PALL), base metals (CU), (BHP), oil (USO), and food (CORN), (WEAT), (SOYB), (DBA).
Many senior hedge fund managers are now implementing strategies assuming that the commodity super cycle, which ran like a horse with the bit between its teeth for ten years, is over, done, and kaput.
Former George Soros partner, hedge fund legend Paul Tudor Jones, has been leading the intellectual charge since last year for this concept. Many major funds have joined him.
Launching at the end of 2001, when gold, silver, copper, iron ore, and other base metals, hit bottom after a 21 year bear market, it is looking like the sector reached a multi decade peak in 2011.
Commodities have long been a leading source of profits for investors of every persuasion. During the 1970?s, when president Richard Nixon took the US off of the gold standard and inflation soared into double digits, commodities were everybody?s best friend. Then, Federal Reserve governor, Paul Volker, killed them off en masse by raising the federal funds rate up to a nosebleed 18.5%.
Commodities died a long slow and painful death. I joined Morgan Stanley about that time with the mandate to build an international equities business from scratch. In those days, the most commonly traded foreign securities were gold stocks. For years, I watched long-suffering clients buy every dip until they no longer ceased to exist.
The managing director responsible for covering the copper industry was steadily moved to ever smaller offices, first near the elevators, then the men?s room, and finally out of the building completely. He retired early when the industry consolidated into just two companies, and there was no one left to cover. It was heartbreaking to watch. Warning: we could be in for a repeat.
After two decades of downsizing, rationalization, and bankruptcies, the supply of most commodities shrank to a shadow of its former self by 2000. Then, China suddenly showed up as a voracious consumer of everything. It was off to the races, and hedge fund managers were sent scurrying to look up long forgotten ticker symbols and futures contracts.
By then commodities promoters, especially the gold bugs, had become a pretty scruffy lot. They would show up at conferences with dirt under their fingernails, wearing threadbare shirts and suits that looked like they came from the Salvation Army. As prices steadily rose, the Brioni suits started making appearances, followed by Turnbull & Asser shirts and Gucci loafers.
There was a crucial aspect of the bull case for commodities that made it particularly compelling. While you can simply create more stocks and bonds by running a printing press, or these days, creating digital entries on excel spreadsheets, that is definitely not the case with commodities. To discover deposits, raise the capital, get permits and licenses, pay the bribes, build the infrastructure, and dig the mines and pits for most commodities, takes 5-15 years.
So while demand may soar, supply comes on at a snail pace. Because these markets were so illiquid, a 1% rise in demand would easily crease price hikes of 50%, 100%, and more. That is exactly what happened. Gold soared from $250 to $1,922. This is what a hedge fund manager will tell us is the perfect asymmetric trade. Silver rocketed from $2 to $50. Copper leapt from 80 cents a pound to $4.50. Everyone instantly became commodities experts. An underweight position in the sector left most managers in the dust.
Some 14 years later and now what are we seeing? Many of the gigantic projects that started showing up on drawing boards in 2001 are coming on stream. In the meantime, slowing economic growth in China means their appetite has become less than endless.
Supply and demand fell out of balance. The infinitesimal change in demand that delivered red-hot price gains in the 2000?s is now producing equally impressive price declines. And therein lies the problem. Click here for my piece on the mothballing of brand new Australian iron ore projects, ?BHP Cuts Bode Ill for the Global Economy?.
But this time it may be different. In my discussions with the senior Chinese leadership over the years, there has been one recurring theme. They would love to have America?s service economy.
I always tell them that they have a real beef with their ancient ancestors. When they migrated out of Africa 50,000 years ago, they stopped moving the people exactly where the natural resources aren?t. If they had only continued a little farther across the Bering Straights to North America, they would be drowning in resources, as we are in the US.
By upgrading their economy from a manufacturing, to a services based economy, the Chinese will substantially change the makeup of their GDP growth. Added value will come in the form of intellectual capital, which creates patents, trademarks, copyrights, and brands. The raw material is brainpower, which China already has plenty of.
There will no longer be any need to import massive amounts of commodities from abroad. If I am right, this would explain why prices for many commodities have fallen further that a Middle Kingdom economy growing at a 7.5% annual rate would suggest. This is the heart of the argument that the commodities super cycle is over.
If so, the implications for global assets prices are huge. It is great news for equities, especially for big commod
ity importing countries like the US, Japan, and Europe. This may be why we are seeing such straight line, one way moves up in global equity markets this year.
It is very bad news for commodity exporting countries, like Australia, South America, and the Middle East. This is why a large short position in the Australian dollar is a core position in Tudor-Jones? portfolio. Take a look at the chart for Aussie against the US dollar (FXA) since 2013, and it looks like it has come down with a severe case of Montezuma?s revenge.
The Aussie could hit 80 cents, and eventually 75 cents to the greenback before the crying ends. Australians better pay for their foreign vacations fast before prices go through the roof. It also explains why the route has carried on across such a broad, seemingly unconnected range of commodities.
In the end, my friend at Morgan Stanley had the last laugh.
When the commodity super cycle began, there was almost no one around still working who knew the industry as he did. He was hired by a big hedge fund and earned a $25 million performance bonus in the first year out. And he ended up with the biggest damn office in the whole company, a corner one with a spectacular view of midtown Manhattan.
He is now retired for good, working on his short game at Pebble Beach.
Good for you, John.
After the catastrophic 25% fall in the units of Linn Energy (LINE) over the past three days, I thought I?d better take another look at the company. The company?s units have now crashed by an eye popping 55% since the May $31 high.
The units have been trading as if the company is imminently going bankrupt. The contradiction is that it clearly isn?t. This is basically a healthy company that is undergoing some volatility typical for the sector.
Is this logical or rational?
No, not at all. But when a real panic hits, you sell first, and ask questions later. That has clearly been happening in the oil patch for the past month.
At the $14 low on Monday, the units were yielding a spectacular 20.7% annualized. This is not some imaginary pie in the sky estimate. This is what the actual $0.24 monthly cash payout announced by the company as recently as December 1 works out to for holders of record as of Thursday, December 11.
Nor are these spectacular yields based on some wild leveraged bets in the financial markets. (LINE) is predominantly a natural gas company, a commodity which has seen its price go largely unchanged for the past two years, hovering above $3.50. And much of its production has already been hedged against any downside risk with offsetting positions in the futures market.
I always try to use every loss as a learning opportunity, or the lesson goes wasted, and is doomed to repetition.
The reasons above were why I shot out a quick Trade Alert last week to buy (LINN) at $16.67. It was an uncharacteristically cautious position for me. But calling bottoms in major trends is always a risky enterprise, so I went small, very small. I bought the underlying units, not the options, and then in unleveraged form.
Initially things went great, rocketing 13% right out the door. Short term, smart traders, like Mad Day Trader Jim Parker, then put in tight stop losses below. That way, he was playing with the house?s money in any further upside, and is assured against loss during any rapid reversal.
I, unfortunately was too slow to do so, and had to bear the cost of the sudden 25% drop. Remember, being right 80% of the time means that I am wrong 20% of the time. But with only a 10% position, my loss never exceeded 1.60% of my total portfolio, something I can live with, and ride out until any recovery.
My guess is that many (LINE) holders violated my ?Sleep at night rule,? lured by the hefty dividend payout into owning too many units.
Once burned, twice forewarned.
My advice to you now is ?Hang on.? You?ve already taken the hit. Don?t bail here and miss the recovery, which will probably begin in earnest next year.
You can pay up to $17 a unit for (LINN) and have a good chance of making a quick, snapback profit.
All of a sudden, everyone I know in Texas, and there are quite a few of them, called to tell me to buy Linn Energy, all within the space of one hour. I summarize their diverse comments below.
We have reached a margin call induced capitulation sell off in Linn Energy this morning, when oil was trading as low as $64 a barrel at the European opening.
There were obviously also a couple of leveraged energy and commodity funds that blew up and are undergoing forced liquidation at the market.
Add to that all the individuals who bought (LINN) on margin when the yield was only 8% so they would take 16% home to the bank.
This has taken the price of the units down to an artificial, and hopefully temporary, low of $15.90. At that price, the yield was a mind blowing 17% (after all, this is California).
It was a classic ?Throwing out the baby with the bathwater? moment. (LINN) gets 54% of its $1.6 billion in revenues from natural gas, which has held up remarkably well in the energy melt down, thanks to the early arrival of the polar vortex this winter.
Only 22% of its income derives from oil related projects, and half of this is hedged in the futures market from any downside exposure in the price of oil, according to the company?s recent pronouncements. Linn has actually plunged more than oil from its recent peak.
Does a loss on 10% of its revenues justify a gut wrenching 50% drop in the units? I think not.
But then, I am being rational and analytical, and I can assure you that the energy markets are now anything but rational and analytical.
Its not like oil is going to stay this low forever. Try to buy oil for delivery in the futures market two years out, and it has already recovered to $75/barrel, and there is very little available at that price.
What happens when the price of something goes down? Demand increases, and that will be good for Linn Energy, which is inherently more of a volume play on gas and oil, not a price play.
Keep also in mind that the absurd salaries the company was paying for workers in the Midwest has also vaporized. Roustabouts can now be had for as little as $75,000 a year compared to $200,000 only six months ago. This will cut (LINN)?s costs quickly and flow straight to the bottom line.
Falling costs and rising volumes sound like a winning formula to me.
And if you have the courage to buy the units here on margin, the yield rockets to a breathtaking 34%. It therefore can?t stay this low for long.
Linn Energy, LLC is an independent oil and natural gas company based in Houston, Texas. It holds oil and gas producing assets in many parts of the United States: Mid-Continent, including properties in Texas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma; the Hugoton Basin in Kansas; the Green River Basin in Wyoming; East Texas; California, including the Brea-Olinda Oil Field in Los Angeles and Orange Counties; the Williston/Powder River Basin, which includes a position in the Bakken Formation; Michigan/Illinois; and the Permian Basin in Texas.
At the end of 2012, the firm reported proved reserves of 4,796 bcfe (billion cubic feet equivalent) of oil and gas combined. Of this total, 24% was crude oil, 54% natural gas, and 22% natural gas liquids.
Structured as a master limited partnership for tax purposes, the firm is required to pay out most of its cash reserve to unitholders (stockholders) each quarter as distributions, thereby ducking the double taxation of corporate taxation.
However Linn retains some attributes of a limited liability corporation, including giving voting rights to its unitholders. Linn Energy also operates a subsidiary, LinnCo, a C Corporation, which is subject to different tax rules from its parent company.
All we have to do is survive the near term volatility and Linn Energy will be a winner.
Boy, that was one hell of a recommendation I made back in 2012, getting readers to buy Master Limited Partnerships (MLP?s).
The share price for my favorite, Linn Energy (LINN), is unchanged from when I urged readers to pick it up. However, they have taken home nearly 25% in dividend payoffs during the same period. Not a bad return in this zero interest rate world.
The origins of the special tax breaks that led to the creation of these most complex of securities are lost in the sands of time. As I recall, they date back to a period when the US was chronically short of oil, and industry desperately needed the big ticket infrastructure to produce and deliver it.
They worked like a charm. Never underestimate the desire of the American investor to avoid paying taxes.
An MLP is a ?pass through? instrument that allows profits to move directly to end investors, thus bypassing corporate double taxation. That set up generates enormous yields that are particularly attractive to individual investors. Some 114 MLP?s now exist, and most can be bought on public exchanges as easily as stocks or exchange traded funds (ETF?s).
It is an old Wall Street nostrum to feed the geese while they are quacking, and investment bankers have done so in spades (see chart below). The number of initial public offering for MLP?s has soared in recent years, from just two in 1985 to a prolific 21 last year.
New issue volumes have become so prodigious that they are disrupting the dynamics of the secondary market. Investors are now unloading their existing MLP?s to make room for the new ones, setting back prices on existing issues. The same disease is also afflicting biotech stocks, where an overly ambitious new issue calendar triggered dramatic falls in the sector.
Will Wall Street kill the gold goose yet again?
MLP?s have benefited enormously from the fracking and horizontal drilling boom now unfolding across the United States. As a result, US energy demand is at a 30 year high, and so is the demand for energy infrastructure.
As I often tell my guests at my Global Strategy Luncheons, the smart play in natural gas, where supplies are burgeoning, is a volume play, and not a price play. MLP?s achieve exactly that.
To qualify for MLP status, a partnership must generate at least 90 percent of its income from what the Internal Revenue Service deems ?qualifying? sources. For many MLPs, these include all manner of activities related to the production, processing or transportation of oil, natural gas, and coal.
Energy MLPs are defined as owning energy infrastructure in the U.S., including pipelines, natural gas, gasoline, oil, storage, terminals, and processing plants. These are all special tax subsidies put into place when oil companies suffered from extremely low oil prices. Once on the books, they lived on forever.
In practice, MLPs pay their investors through quarterly distributions. Typically, the higher the quarterly distributions paid to LP unit holders, the higher the management fee paid to the general partner. The idea is that the GP has an incentive to try to boost distributions through pursuing income-accretive acquisitions and organic growth projects.
Because MLPs are partnerships, they avoid the corporate income tax, on both a state and federal basis. Instead of getting a form 1099-DIV and the end of the year, you receive a form K-1, which your accountant should know how to handle.
Additionally, the limited partner (investor) may also record a pro-rated share of the MLP?s depreciation on his or her own tax forms to reduce liability. This is the primary benefit of MLPs and gives MLPs relatively cheap funding costs.
The tax implications of MLPs for individual investors are complex. The distributions are taxed at the marginal rate of the partner, unlike dividends from qualified stock corporations. On the other hand, there is no advantage to claiming the pro-rated share of the MLP?s depreciation (see above) when held in a tax-deferred account, like an IRA or 401k. To encourage tax-deferred investors, many MLP?s set up corporation holding companies of LP claims which can issue common equity.
The popularity of MLP?s has caused a huge inflow of capital, which has caused yields to crash, from 25% during the dark days of 2009, to an average of 6.7% today. Still, yield starved investors threw money at MLP?s with both hands last year, an eye popping $11.9 billion, according to figures from the tracking firm, Morningstar.
As yields have plunged, risks have risen. In February, Houston based Boardwalk Pipeline Partners (BWP), out of the blue, dramatically cut its payout to investors. A panic ensued, chopping 62% off the value of the shares in the following weeks. No doubt, increased competition for pipelines from railroads was a factor.
To protect yourself you must go to the website and read the prospectus before sending a check to an MLP. Unfortunately, these are so complex that even degrees in securities and tax law might not be enough to help you. What do you do instead? Pray, as seems to be the strategy of most individual investors.
At the end of the day, oil has a big influence on MLP prices. So the antics of Vladimir Putin in the Ukraine are probably a welcome development for MLP holders, as it has helped boost the price of Texas tea from $91 to $105 since the beginning of 2014.
However, get a real recession, and one will be overdue in a couple of years, and the price of oil will collapse once again, causing MLP?s to revisit those subterranean 2009 lows. Mothballed drilling rigs and rusting pipelines don?t produce lease payments or pay dividends. These are the risks you are being paid to take with a double-digit yield.
The lesson here is ?be nimble, or die".
Legal Disclaimer
There is a very high degree of risk involved in trading. Past results are not indicative of future returns. MadHedgeFundTrader.com and all individuals affiliated with this site assume no responsibilities for your trading and investment results. The indicators, strategies, columns, articles and all other features are for educational purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice. Information for futures trading observations are obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but we do not warrant its completeness or accuracy, or warrant any results from the use of the information. Your use of the trading observations is entirely at your own risk and it is your sole responsibility to evaluate the accuracy, completeness and usefulness of the information. You must assess the risk of any trade with your broker and make your own independent decisions regarding any securities mentioned herein. Affiliates of MadHedgeFundTrader.com may have a position or effect transactions in the securities described herein (or options thereon) and/or otherwise employ trading strategies that may be consistent or inconsistent with the provided strategies.
