The Golden Era of Cybersecurity Spend
The tech sector and the U.S. government are poised to engage in a more transactional relationship than ever before after the cybersecurity attack on Colonial Pipeline and the U.S. President’s executive order that followed it.
This doesn’t mean just servicing an email account, but this will incorporate broad-based networking cloud infrastructure from the top-down and the bits in between.
Technology is just getting too good, too fast, and applicable to the point that it allows nefarious actors to wield it in a way that could damage and permanently set back sovereign nations and global business.
Don’t get me wrong, this was already in the works, and U.S. President Joe Biden has signaled his intent to ramp up the IT spent, but this cyberattack that is causing gas hoarding in parts of South Eastern United States is just the event to really kick this initiative into overdrive.
Colonial Pipeline paid the almost $5 million ransom payment that will encourage similar type of behavior in the long-term.
The Cyberattack also means that the relationship between U.S. tech and government could swerve from net negative of a relentless anti-monopoly narrative to one in which big tech will be anointed as the saviors to the foreign cyber-criminals and paid handsomely to defend the operations of private and state U.S. business.
The latter sounds much better to Silicon Valley than the former and the bigwigs in Silicon Valley might ostensibly push this marketing dynamic of internet protection to save their bacon and get the regulatory heat off their back.
Polarizing figures such as U.S. Senator Elizabeth Warren have made it a point to bash big tech whenever she sees fit which is more often than not.
CEOs like Facebook’s Mark Zuckerberg have tried a disingenuous approach of blaming China’s marginal data privacy policies as a way to protect its Instagram business and prevent growth monster TikTok, a Chinese app, from cannibalizing its cash cow business.
The origin of the Colonial Attack is purportedly to be Russian which would offer more fuel to the fire and create a ready-made reason for U.S. government to pour incremental billions into Silicon Valley and its array of almost multi-trillion dollar heavy hitters while protecting their business moat.
This event also means Tesla is toast in China.
Officials in China banned Tesla vehicles from military bases and housing compounds amid concerns that potentially sensitive data from its onboard cameras could be collected and stored on Tesla servers.
Once the data privacy genie is out of the bottle, it’s hard to contain the fallout and Tesla will need to adopt a whack-a-mole strategy in China which often proves futile in the long-term.
The United States faces persistent and increasingly sophisticated malicious cyber campaigns that threaten the public sector, the private sector, and ultimately the American people’s security and privacy.
This is all just the beginning, a little taste of what’s on the menu.
Collaborating with U.S tech companies to improve its efforts to identify, deter, protect against, detect, and respond to these actions and actors is now a must.
The Federal Government must also carefully examine what occurred during any major cyber incident and apply lessons learned.
Incremental improvements will not offer the security Americans need; instead, the Federal Government needs to make bold changes and significant investments in order to defend the vital institutions that underpin the American way of life.
It’s the authorities’ job and to offer resources to protect and secure its computer systems, whether they are cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid.
The scope of protection and security must include systems that process data (information technology (IT)) and those that run the vital machinery that ensures our safety (operational technology (OT)).
Contracts will be signed with IT and OT service providers to conduct an array of day-to-day functions on Federal Information Systems. These service providers, including cloud service providers, have unique access to and insight into cyber threat and incident information on Federal Information Systems.
Increasing the sharing of information about such threats, incidents, and risks, and enabling more effective defense of agencies’ systems and of information collected, processed, and maintained by or for the Government are necessary steps to accelerating incident deterrence, prevention, and response efforts.
The executive order signed by Biden shows that within 60 days, the Director of the Office of Management and Budget will hash out “language for contracting with IT and OT service providers and recommend updates.”
The U.S. must take decisive steps to modernize its approach to cybersecurity and must increase the Federal Government’s visibility into threats while protecting privacy and civil liberties.
Money will be spent to accelerate movement to secure cloud services, including Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS); centralize and streamline access to cybersecurity data to drive analytics for identifying and managing cybersecurity risks; and invest in both technology and personnel to match these modernization goals.
Prioritizing money spent on addressing “critical software” will translate into huge paydays to many cloud providers and not just the big guys.
Most recently, The Central Intelligence Agency awarded its long-awaited Commercial Cloud Enterprise, or C2E, contract to five companies—Amazon Web Services (AMZN), Microsoft (MSFT), Google (GOOGL), Oracle (ORCL), and IBM (IBM).
No doubt they will be vying for more government procurement contracts since they already have one hand in the honey jar.
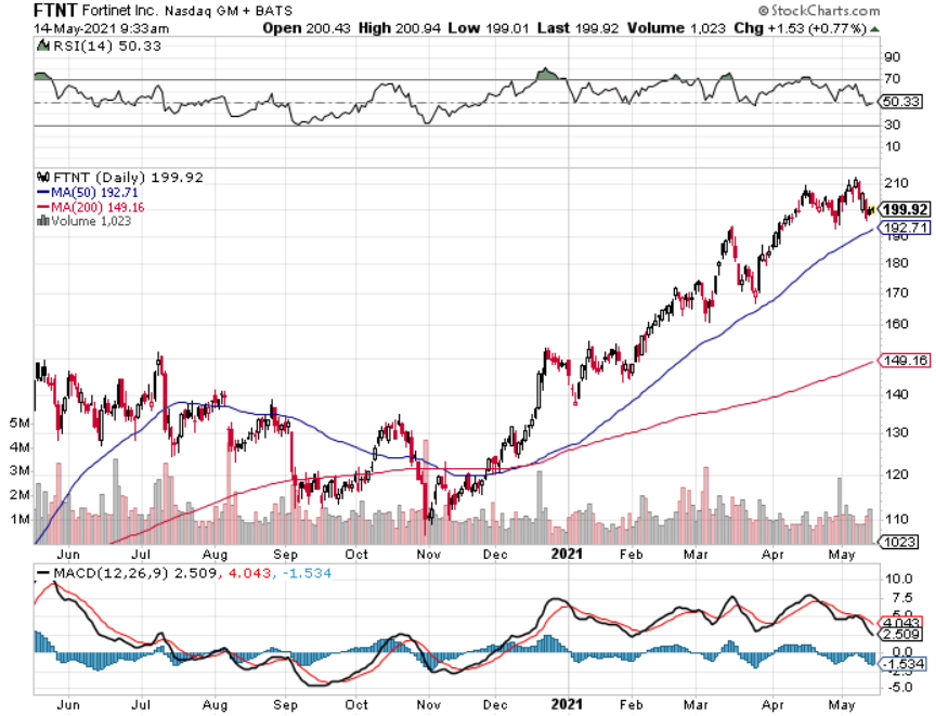
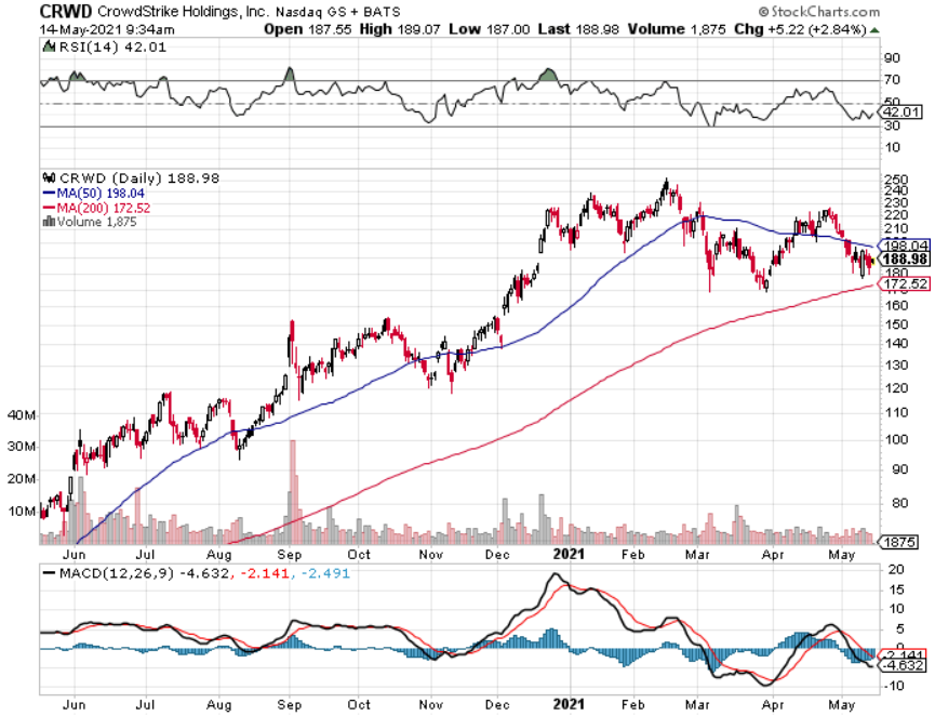
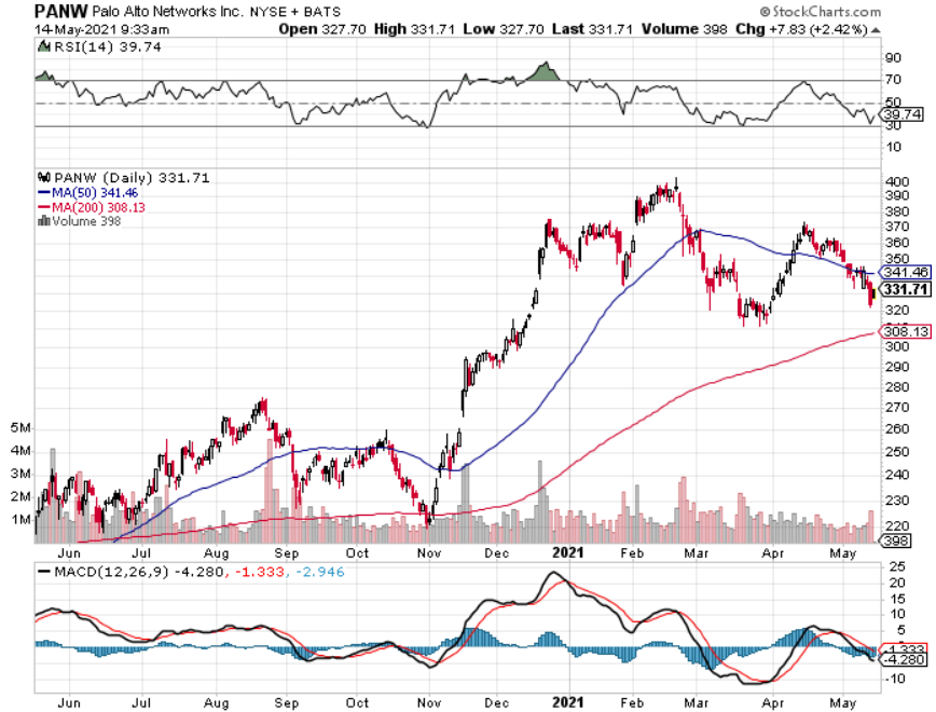
At a lower level, readers should consider buying cybersecurity companies Fortinet (FTNT), Palo Alto Networks, Inc. (PANW), and CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc. (CRWD), but these smaller names come with more volatility.
This event really anoints the impending future as the golden era of IT cybersecurity spend and it will never go back to what it once was.
Paying for IT protection is here for the long haul and this goes for private companies and public institutions.
Nearly 80% of senior IT and IT security leaders believe their organizations lack sufficient protection against cyberattacks despite increased IT security investments made in 2020 to deal with distributed IT and work-from-home challenges, according to a new IDG Research Services survey commissioned by Insight Enterprises.
There will be a huge boom in IT cybersecurity spend because CEOs don’t want to be the idiot that allowed cybercriminals to hijack their whole business.
That’s the fastest way to end a management career.
Last time I checked, it’s a hard slog up the corporate ladder to land a prime CEO gig and it’s not getting any easier.