The Market Outlook for the Week Ahead, or The Big Pull Forward
Somehow, the summer got moved this year.
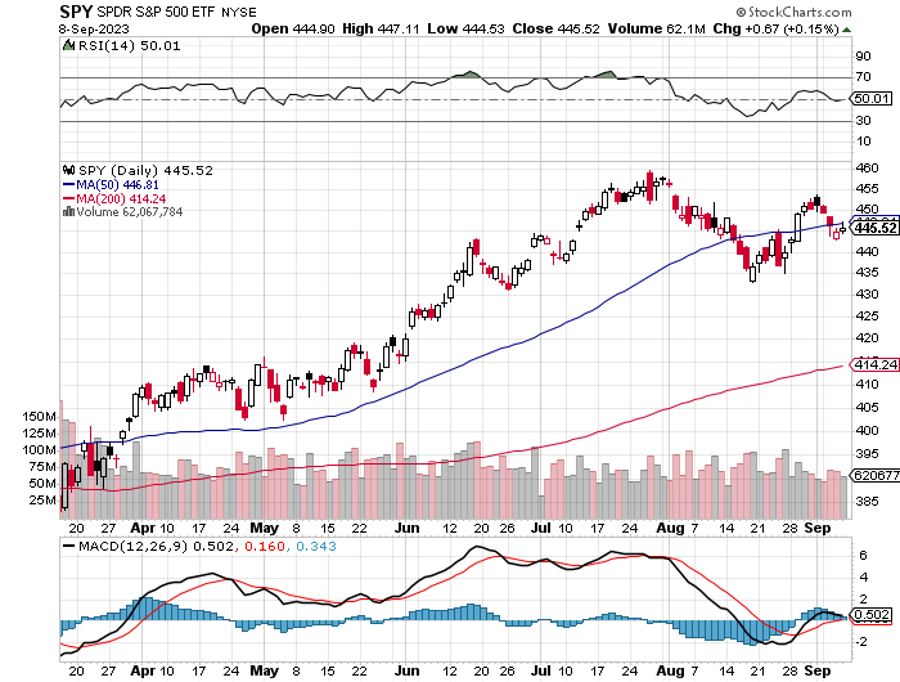
For here it is September, and the stock market is behaving like it is only July. July was different from normal as well, going straight up almost every day when it is usually asleep. This year, July acted like May, when you’re supposed to sell and go away.
If you’re thoroughly confused by all of this, so am I. The historic cyclicality of the markets, the ebb and flow of share prices according to the calendar, has gone out the window. But then, what isn’t confusing these days?
I went to buy a green drink from Whole Foods on Friday and the counter was closed because of staff shortages. Whole Foods unable to sell a green drink?
I tried to climb the Matterhorn this summer but was told that the guides weren’t taking anyone up because of the extreme heat. The mountain was literally melting, dropping rocks on the heads of climbers. No climbing the Matterhorn in Switzerland? I went to the Dolomites instead where you climb ice-free shear rock faces.
I tried to get into the Pantheon in Rome this summer and was met with a five-hour line. The Sistine Chapel in the Vatican was worse. When I first went there in the 1960’s the place was empty. The fact is that Italy now has more tourists than Italians. Oh, and the pope is from Argentina.
Has the world gone mad?
What has happened is that there has been a great pull forward that took place in financial markets during the first half of the year. I’ve seen this before. When a conclusion becomes obvious, everyone jumps on the bandwagon and brings everything forward.
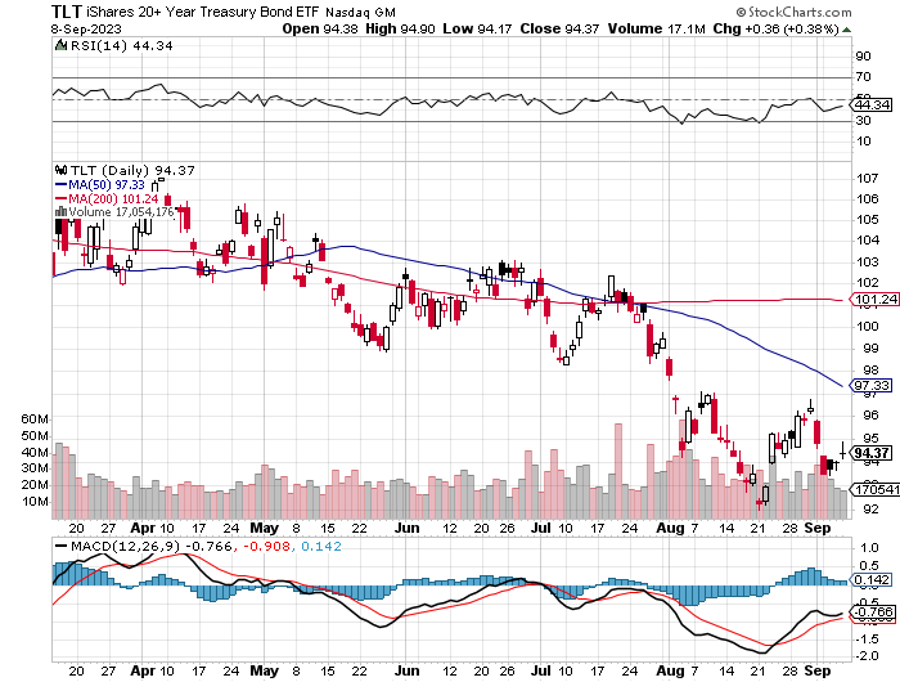
So from January to July stock markets saw the blatantly obvious future that inflation would fall, interest rates decline, the US dollar weaken, and commodities and precious metals would rise. That’s why the “Magnificent Seven” led.
What happens next?
Now shares have to wait until these predictions actually happen before they can move any further. Markets have moved as far as they can on faith alone. Next, we need facts. This could take weeks or even months.
I knew this was going to happen. That’s why I went pedal to the metal, full speed ahead, damn the torpedoes aggressive during the first half of the year and clocked a 60% profit. I expected that if you didn’t make a profit in the first half of the year, you wouldn’t have any profits in 2023 at all.
And the trade alert drought continues.
There isn’t a day that goes by when I am not asked if America’s $33 trillion national debt will destroy the economy, cause the stock market to crash, and bring the end of Western Civilization. The answer is no, never, not in our lifetimes.
The reason is very simple. Any dollar the government borrows today sees its purchasing power go to zero in 30 years. That’s where the massive Civil War debt went, that's where the WWI debt went, and that’s where the gigantic WWII debt went, some 105% of GDP. Today’s debt will similarly vaporize over time.
Who pays for this cataclysmic decline in value? US government debt holders, who similarly see their purchasing power disappear over time. It turns out that the ultimate avoiders of risk, investors in US government debt, not only don’t get paid for their cowardice, they lose their entire principal as well, at least in terms of purchasing power.
There is a wonderful article in Barron’s this week entitled “Government Debt Needs to Be Repaid, And Other Myths About the Federal Deficit” by Paul Sheard which explains how all this works, which I quote below in its entirety.
“The U.S. national debt currently stands at $32.91 trillion, and 10 months into this fiscal year, the U.S. government has spent $1.6 trillion more than it has collected in revenue. Those intimidating figures animate political battles that can shut down the government and even bring it to the brink of default. But the meaning of this money isn’t as simple as it seems. Five myths in particular deserve straightening out.
The first is that the government has to borrow in order to spend and run deficits. It’s the other way around. The government creates money (injects it into the economy) when it spends and destroys money (withdraws it from the economy) when it taxes. The government taxes variously to correct for negative externalities, to redistribute income, and to modulate aggregate demand; “raising revenue” is just a cover story.
A related myth is that the government needs to repay its debt. “Debt” is a misnomer; government debt is just money (or purchasing power) in another form. A $20 bill is a liability of the Fed, which makes it a liability of the federal government. A $20 bill never has to be repaid; it just is. Fundamentally, Treasuries aren’t much different.
That government debt never needs to be repaid doesn’t mean the government can or should create as much of it as it likes.
Too big a pile of debt because of prior and ongoing budget deficits may be inflationary, as too much money chases insufficient goods and services. That will require some combination of monetary and fiscal tightening. A mountain of debt may indicate a government that is too big and intrusive in the economy for many people’s liking, an issue that can be fought out at the ballot box.
A third myth is that the Fed prints money when it does quantitative easing. The money-printing happens when the government runs a budget deficit; QE just changes the form of that money.
QE is really just a debt refinancing operation of the consolidated government—that is, the government including the Fed—whereby it refinances one form of debt (government bonds or guarantees) into another (reserves). QE changes the composition of the (consolidated) government debt in the hands of the private sector, but it doesn’t directly add one iota of new purchasing power. For every dollar the Fed “pumps into” the economy by doing QE, it “sucks out” a dollar of assets. Conversely, quantitative tightening just returns assets to private sector portfolios, expunging reserves in the process.
Reserves are like banknotes: The Fed can withdraw them, but it never has to repay them as such. It looks like the government has to repay Treasuries, but this is an institutional artifact. In extremis, the Fed could convert all outstanding Treasuries into reserves, and it could maintain monetary control by it, rather than the fiscal authorities, paying interest on reserves.
Japan is the poster child for a miserable-looking fiscal picture. Yet, the Bank of Japan, the pioneer of QE, owns almost half of the stock of outstanding Japanese government securities and, at the same time, since 2016 has managed the 10-year yield, with some leeway, to be “around zero percent.”
It is precisely because the government can create money at will that the modern monetary and fiscal architecture has been designed to put shackles on its ability to do so: The creation of an “independent” central bank within the government, the central bank not allowing the government’s account with it to go into overdraft, the central bank not buying bonds directly from the government, and governments issuing debt securities rather than leaving their deficits in the form of reserves all serve that purpose. But what the government taketh away, it can give back. Faced with the need, it could loosen those shackles.
A fourth, and related, myth is that banks could, if so moved, “lend out” the excess reserves created by QE. Banks can lend these reserves to one another but they cannot turn them into lending to companies and households in the broader economy.
It isn’t just the government that creates money. Banks do, too. A fifth myth is that banks are just financial intermediaries “taking in” deposits and “lending them out.” Not so. Banks create money when they lend. For an individual bank making a new loan, it may not feel like this, because the first thing borrowers do is spend their money. If none of that money flows back into the same bank, its reserves at the central bank will decline by the amount of the loan. It will then probably want to attract deposits to “fund” the loan, but doing so will just top up its lost reserves. Bank lending for the system is entirely self-funding (so long as none of the money created leaks into bank notes).
The U.S. economy currently produces about $27 trillion of goods and services annually, a little more than the amount of federal debt held by the public and the QE-embracing Fed. The money needed to sustain this giant prosperity-generating machine comes from the government running deficits and from banks extending credit, with the Fed’s activities linking the two. Political debates and decisions currently are based on a befuddled grasp of how this monetary system works. The stakes for society are too high for that.”
So far in August, we are down -4.70%. My 2023 year-to-date performance is still at an eye-popping +60.80%. The S&P 500 (SPY) is up +17.10% so far in 2023. My trailing one-year return reached +92.45% versus +8.45% for the S&P 500.
That brings my 15-year total return to +657.99%. My average annualized return has fallen back to +48.15%, another new high, some 2.50 times the S&P 500 over the same period.
Some 41 of my 46 trades this year have been profitable.
Beige Book Shows Consumer Spending Slowing, long a pillar of this recovery, as the last of the pandemic bonuses work their way for the system. It’s putting a dent in corporate profits and hints at a shrinking economy, contrary to recent economic data.
The US Dollar (UUP) is Soaring, thanks to “higher interest rates for longer” and a strengthening US economy. Asian currencies are at ten-month lows and central bank intervention is looking. The dollar shorting selling opportunity of the decade is setting up.
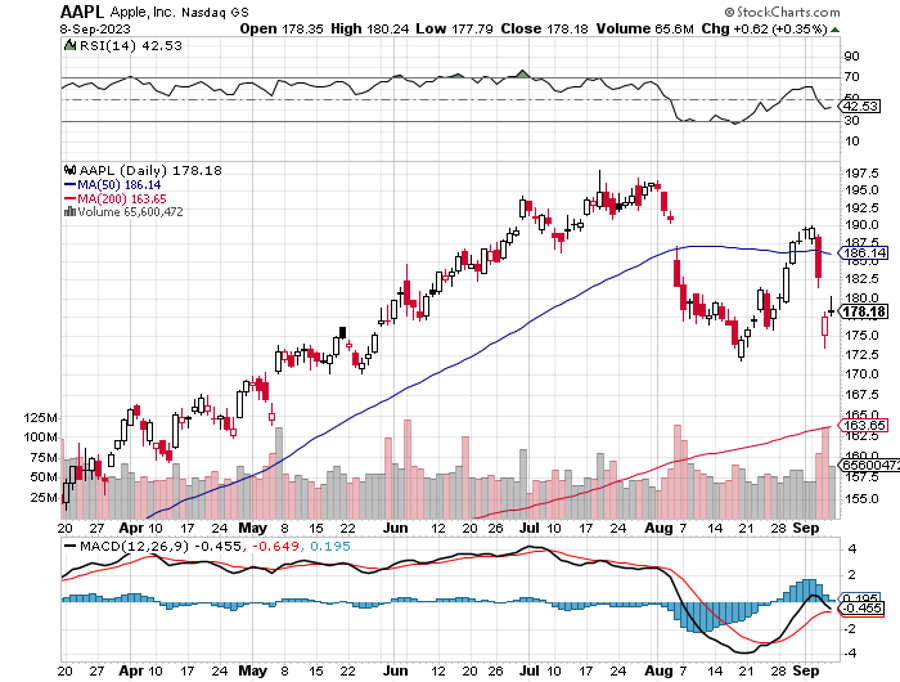
China Restricts Sales of iPhones (AAPL), barring sales to government agencies. It’s only a small nick in overall sales, but certainly casts of cloud over doing business in the Middle Kingdom. Some $200 billion, (AAPL)’s market cap has been vaporized.
Weekly Jobless Claims Dive, down 13,000 to 216,000, a seven-month low. It’s the fourth consecutive decline and not what the Fed wanted to hear.
Rate Hikes Will Drag on the Economy for at Least a Decade, as the Fed's $8.24 trillion balance sheet unwinds, according to the San Francisco Fed. The balance sheet was only at $800 million before the 2008 Great Recession.
Saudi Arabia and Russia Engineer Short Squeeze on Oil (USO), taking the price over $90 a barrel this year. Large production cuts announced in June will be maintained until yearend. Will Biden counter with a release from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, or SPR?
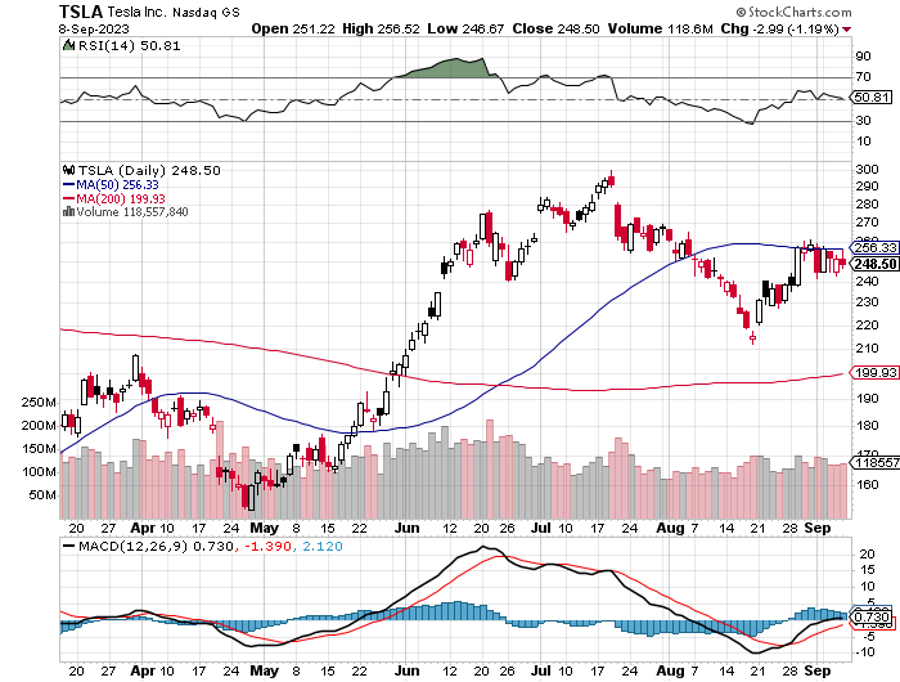
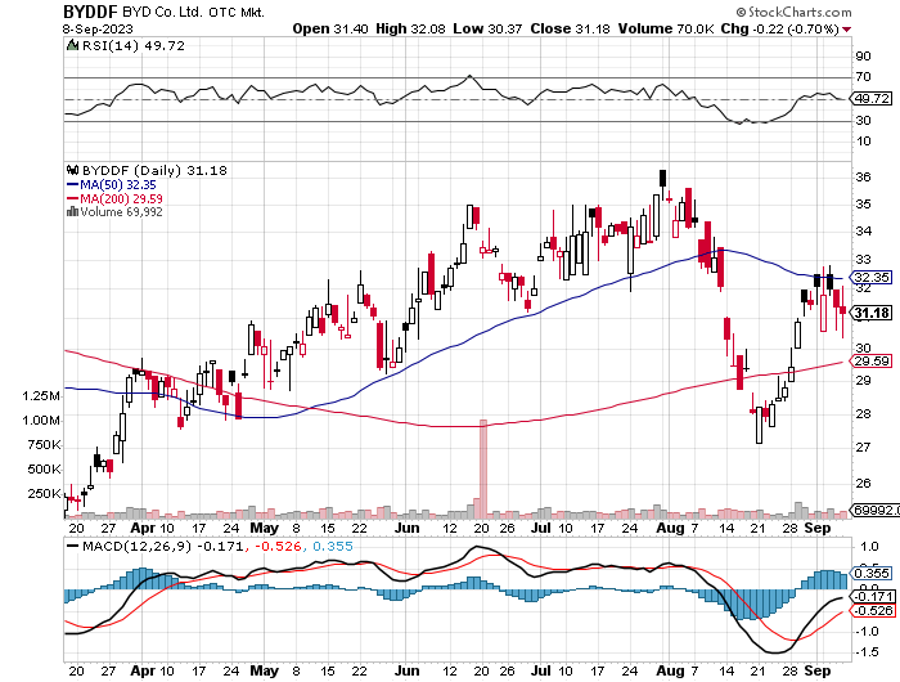
Tesla’s Chinese EV Deliveries Rise 9.3% in August, thanks to aggressive price cuts. There is a two-month wait for the Model Y. Chinese rival BYD (BYD), with its Dynasty and Ocean series of EVs and petrol-electric hybrid models, recorded deliveries of 274,086 passenger vehicles in August, a jump of 57.5% year-on-year. China has the world’s largest car market.
My Ten-Year View
When we come out the other side of the recession, we will be perfectly poised to launch into my new American Golden Age, or the next Roaring Twenties. The economy decarbonizing and technology hyper-accelerating, creating enormous investment opportunities. The Dow Average will rise by 800% to 240,000 or more in the coming decade. The new America will be far more efficient and profitable than the old.
Dow 240,000 here we come!
On Monday, September 11, US Consumer Inflation Expectations are announced.
On Tuesday, September 12 at 8:30 PM EST, NFIB Business Optimism Index is released. Apple announced the new iPhone 15.
On Wednesday, September 13 at 8:30 AM, the Core Inflation Rate for August is published.
On Thursday, September 14 at 8:30 AM, the Weekly Jobless Claims are announced. ARM started trading after its IPO, which was five times oversubscribed. NVIDIA tried but failed to take over the chip maker.
On Friday, September 15 at 2:30 PM, the Producer Price Index for August is published. At 2:00 PM the Baker Hughes Rig Count is printed.
As for me, not just anybody is allowed to fly an aircraft in Hawaii. You have to undergo special training and obtain a license endorsement to cope with the Aloha State’s many aviation challenges.
You must learn how to fly around an erupting volcano, as it can swing your compass by 30 degrees. You must master the fine art of not getting hit by a wave on takeoff since it will bend your wingtips forward. And you’re not allowed to harass pods of migrating humpback whales at a low level, a sight I will never forget.
Traveling interisland can be highly embarrassing when pronouncing reporting points that have 16 vowels. And better make sure your navigation is good. Once a plane ditched interisland and the crew was found six months later off the coast of Australia. Many are never heard from again.
And when landing on the Navy base at Ford Island you were told to do so lightly, as they still hadn’t found all the bombs the Japanese had dropped during their Pearl Harbor attack in 1941.
You are also informed that there is one airfield on the north shore of Molokai you can never land at unless you have the written permission from the Hawaii Department of Public Health. I asked why and was told that it was the last leper colony operating in the United States.
My interest piqued, the next day found me at the Hawaiian state agency with an application in hand. I still carried my UCLA ID which described me as a DNA researcher, which did the trick.
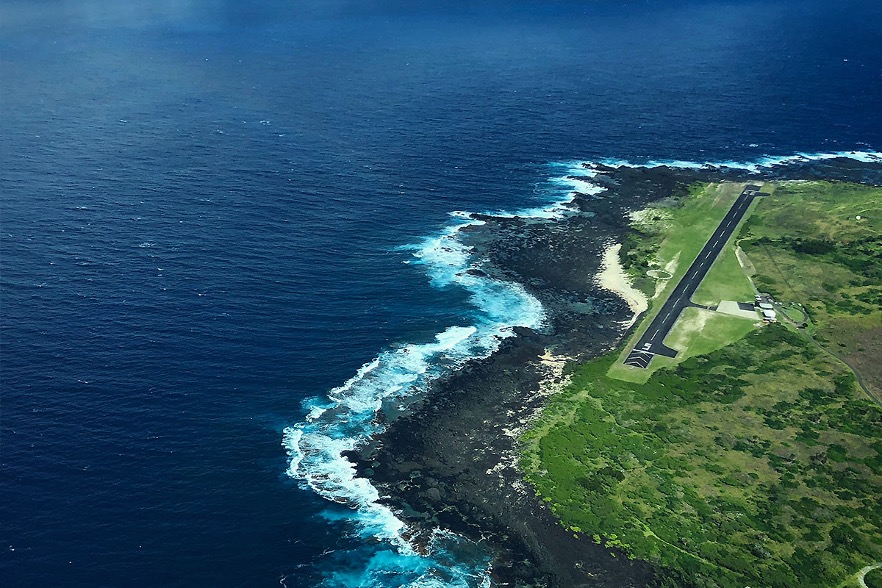
When I read my flight clearance to the controller at Honolulu International Airport, he blanched, asking if I had authorization because he’d never seen one before. I answered that yes, I did, I really was headed to the dreaded Kalaupapa Airport, the Airport of no Return.
Getting into Kalaupapa is no mean feat. You have to follow the north coast of Molokai, a 3,000-foot-high series of vertical cliffs punctuated by spectacular waterfalls. Then you have to cut your engine and dive for the runway in order to land into the wind. You can only do this on clear days, as the airport has no navigational aids. The crosswind is horrific.
If you don’t have a plane it is a 20-mile hike down a slippery trail to get into the leper colony. It wasn’t always so easy.
During the 19th century, Hawaiians were terrified of leprosy, believing it caused the horrifying loss of appendages, like fingers, toes, and noses, leaving bloody open wounds. So, King Kamehameha I exiled lepers to Kalaupapa, the most isolated place in the Pacific.
Sailing ships were too scared to dock. They simply threw their passengers overboard and forced them to swim for it. Once on the beach, they were beaten a clubbed for their possessions. Many starved.
Leprosy was once thought to be a result of sinfulness or infidelity. In 1873, Dr. Gerhard Henrik Armauer Hansen of Norway was the first person to identify the germ that causes leprosy, the Mycobacterium leprae.
Thereafter, it became known as Hanson’s Disease. A multidrug treatment that arrested the disease, but never cured it, did not become available until 1981.
Leprosy doesn’t actually cause appendages to drop off as once feared. Instead, it deadens the nerves, and then rats eat the fingers, toes, and noses of the sufferers when they are sleeping. It can only be contracted through eating or drinking live bacteria.
When I taxied to the modest one-hut airport, I noticed a huge sign warning “Closed by the Department of Health.” As they so rarely get visitors the mayor came out to greet me. I shook his hand but there was nothing there. He was missing three fingers.
He looked at me, smiled, and asked, “How did you know?”
I answered, “I studied it in college.” Even today, most are terrified of shaking hands with lepers.
Not me.
He then proceeded to give me a personal tour of the colony. The first thing you notice is that there are cemeteries everywhere filled with thousands of wooden crosses. Death is the town’s main industry.
There are no jobs. Everyone lives on food stamps. A boat comes once from Oahu a week to resupply the commissary. The government stopped sending new lepers to the colony in 1969 and is just waiting for the existing population to die off before they close it down.
Needless to say, it is one of the most beautiful places on the planet.
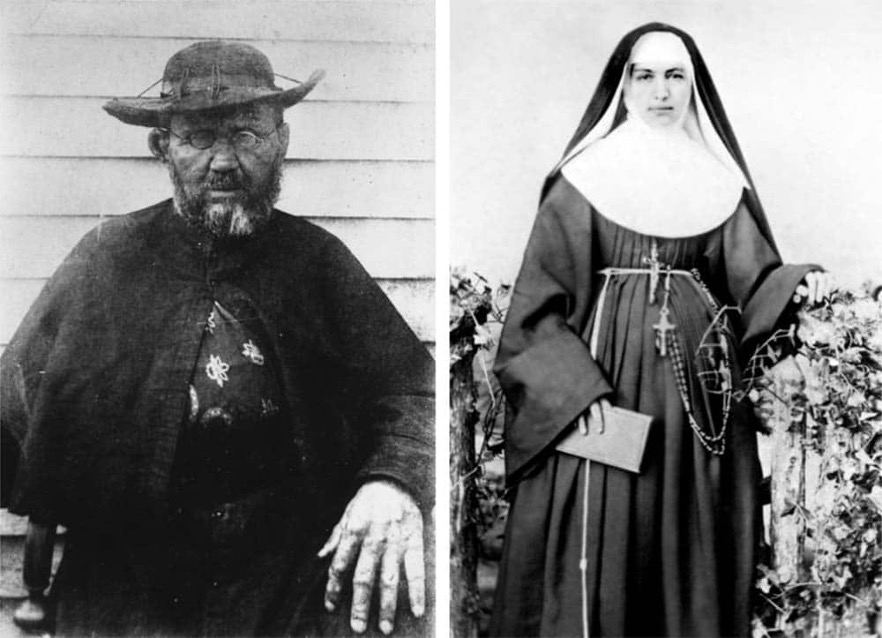
The highlight of the day was a stop at Father Damien’s church, the 19th century Belgian catholic missionary who came to care for the lepers. He stayed until the disease claimed him and was later sainted. My late friend Robin Williams made a movie about him, but it was never released to the public.
The mayor invited me to stay for lunch, but I said I would pass. I had to take off from Kalaupapa before the winds shifted.
It was an experience I will never forget.
Stay Healthy,
John Thomas
CEO & Publisher
The Diary of a Mad Hedge Fund Trader
The Airport of No Return
Father Damien