Spinoff Stocks Poised for Long-Term Growth
Spinoffs have historically been known to deliver healthy returns for their investors.
A good example is PayPal (PYPL), which grew sevenfold since 2015 following its spinoff from eBay (EBAY).
A more recent example is Carrier Global (CARR), which tripled its shares amid the pandemic after its spinoff from United Technologies (UTC) last year.
Basically, spinoffs allow smaller segments of companies to thrive on their own or push high-growth divisions to expand faster.
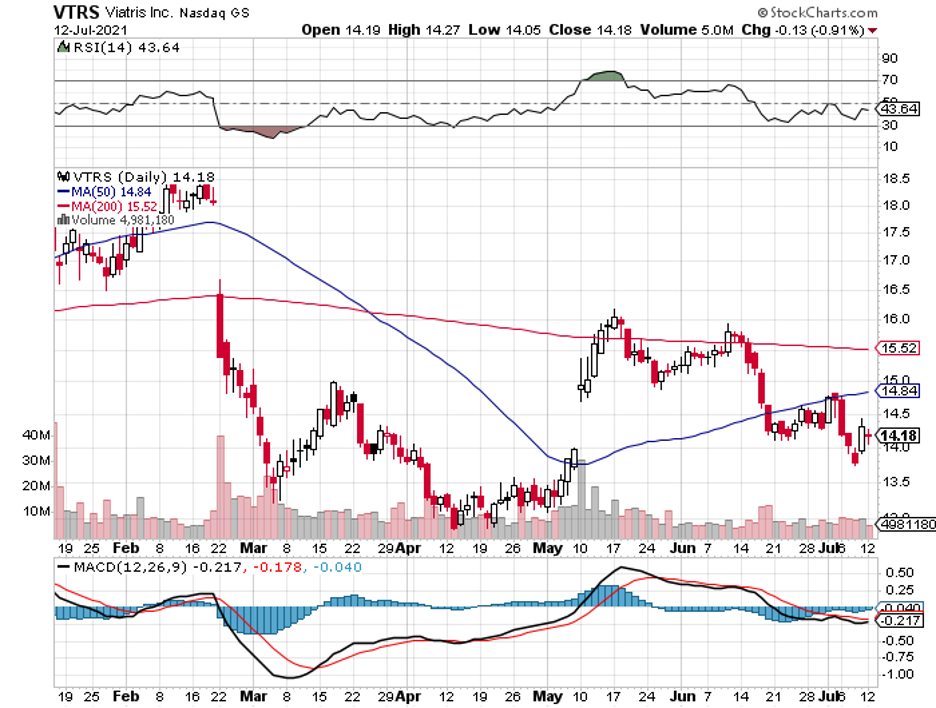
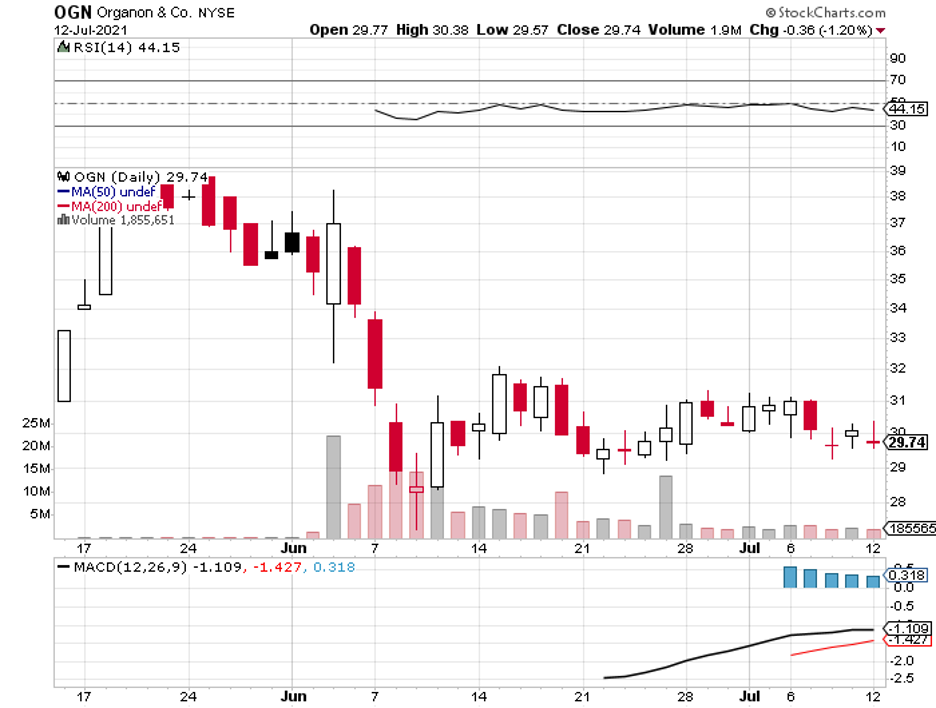
Over the past months, the cheapest stocks found in the S&P 500 have recently spun off pharmaceutical companies: Viatris (VTRS) and Organon (OGN).
Viatris is a spinoff of Pfizer (PFE), which merged with Mylan, while Merck (MRK) jettisoned Organon (OGN) just last month.
Both are brand new and still under the radar, particularly among investors who don’t follow healthcare updates.
While these two have yet to impress the market, both exhibit potential that could make them promising long-term prospects.
Viatris holds an extensive portfolio of drugs courtesy of Pfizer’s Upjohn unit and Mylan’s pipeline.
The list includes the previously top-selling Lipitor, Viagra, Lyrica, and even Norvasc from Pfizer. It also has Mylan’s income-generating EpiPen along with the company’s HIV/AIDS therapies and 7,500 marketed products across the globe.
To date, Viatris has fallen roughly 30% from its average price target. It’s not for the subpar performance of its products though. This is mostly attributed to the lack of attention from investors and possibly a bit of skepticism from some analysts.
However, Viatris has a really good value proposition.
The main goal of the biggest names in the biopharmaceutical sector, such as Johnson & Johnson (JNJ), Eli Lilly (LLY), AbbVie (ABBV), AstraZeneca (AZN), GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMY), and Gilead Sciences (GILD), is to develop and launch the best-in-class treatments to market.
To achieve that, these industry giants are granted a set period to exclusively sell and market each new drug that gains approval.
This would allow them to command a premium price, which in turn would give them the money to fund the next round of research and development needed to come with the next generation of newer and improved versions of the treatment.
However, not everyone can afford those premium prices.
So when the periods of exclusivity end, there are companies like Mylan—now Viatris—that are allowed to manufacture generic versions of those branded drugs and sell them at lower prices.
The list of drugs with soon-to-expire patents for which Viatris has been working on creating biosimilars or generic versions include Humira from AbbVie, which recorded peak sales at $20 billion; Eylea from Regeneron (REGN), which peaked at $7.5 billion; and even Allergan’s Botox, which peaked at $5 billion.
Viatris is also working on biosimilars for Roche’s (RHHBY) cancer treatments Avastin, which had peak sales of $7 billion, and Perjeta, which peaked at $5 billion.
Obviously, Viatris will not reach the same height of success as the companies that created those branded drugs.
But, if it manages to achieve even only 10% of those numbers, then it can generate roughly $4 to $5 billion in sales—and that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
So far, Viatris owns at least 1,400 approved molecules applicable in roughly 10 therapeutic segments.
It has roughly 350 products in its pipeline at the moment, with each item estimated to generate approximately $100 million to $500 million in sales.
With its current performance and access to 165 countries and territories, Viatris is expected to generate roughly $224 billion in global sales annually.
With all these in mind, Viatris’ value proposition looks impressively strong to me.
More importantly, this Pfizer spinoff has the capacity to become the world’s first dominant generic and biosimilar drug manufacturer, with its revenues potentially becoming comparable to major pharmaceutical companies at some point.
The same value proposition could be behind Organon, as this newly spun-off company markets Merck’s off-patent drugs.
While the move to separate from its parent company has yet to show tangible results, Organon is projected to rake $6.1 billion to $6.4 billion in revenue for 2021, with annual sales expected to rise in mid-single digits and dividends anticipated to be about 3%.
The biosimilars market is still relatively young, with only 60 biosimilars approved in the EU and 29 in the US thus far. In total, those represent a market worth approximately $17 billion.
Conservative estimates project that the global biosimilars market will be worth $692 billion by 2027, considerably outpacing the mainstream pharmaceutical sector.
Given their potential and prospect for future gains, the low prices for companies like Viatris and Organon present rare opportunities to grab long-term investments.