Why Amazon is the Most Undervalued AI Play Out There
Before I took off for the current trip to Europe, I logged into my Amazon Prime account to buy some lightweight polyester T-shirts, size 4XL. Not only are these ideal for long-distance hiking but they can be washed in a hotel sink and dried quickly when I am traveling too fast to use the house laundry.
The next morning when I logged into my laptop, my email account was flooded with ads for every kind of T-shirt in the world, from heavy-duty sports types FOR $100 to bargain basement $5 ones from China (although the Chinese ones were a little light on the 4X sizes).
That is Amazon’s AI at work. And you know what? It is getting smarter. And while the big fear among investors is that the US government will break up this retail giant for antitrust reasons, Amazon is integrating faster than ever. The impact on profits will be enormous.
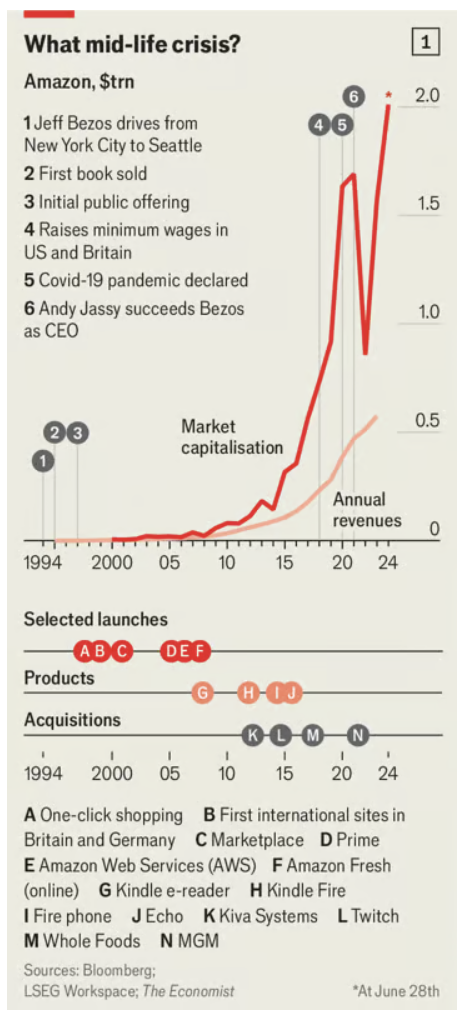
My friend Jeff Bezos’ creation has a lot to work with. Amazon not only pioneered online retail. It subsequently invented the Kindle, an e-reader (click here where the John Thomas autobiography is for sale) Alexa, a smart speaker and, more consequentially, cloud-computing—Amazon Web Services has a 31% share of that $300bn market (full disclosure: Mad Hedge uses their service).
It also runs Prime Video, America’s fourth-most-watched video-streaming service (full disclosure: Mad Hedge is a Prime member). Its newish, high-margin advertising business is already the third largest in the world behind Alphabet (GOOGL) (Google’s parent company) and Meta (META) (Facebook’s).
Amazon also has a few moonshot projects of its own. One subsidiary, Zoox, is building self-driving cars. Another, Kuiper, is developing a fleet of communications satellites in low-Earth orbit, in competition with SpaceX Starlink (full disclosure: Mad Hedge is a Starlink user).
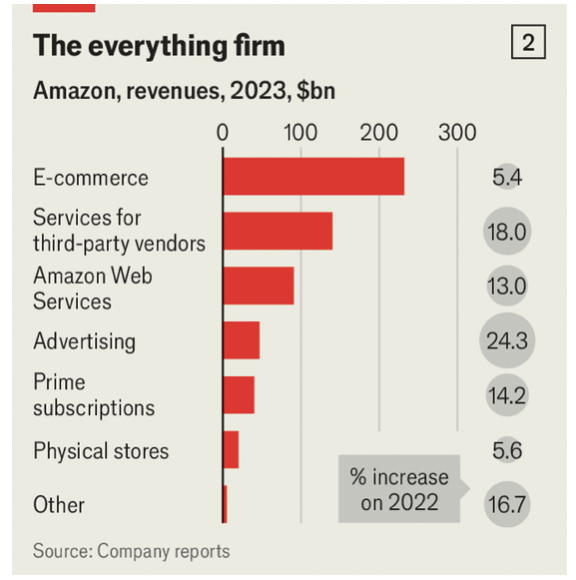
This year, Amazon’s websites will sell a staggering $554bn-worth of goods in America. That gives it a 42% share of American e-commerce, far beyond the 6% captured by Walmart (WMT), its nearest online competitor (and the country’s biggest retailer overall). The reward for all these efforts was a $2 trillion market capitalization in June and an all-time high share price of $203.
Amazon’s fourth decade looks poised to be an era of integration. The company has grown to the size that any needle-moving new investment is costly and high-risk. Andy Jassy, the former boss of AWS whom Bezos appointed as his successor as CEO in 2021, therefore appears keen to generate value by stitching the company’s existing businesses together more tightly.
Jeff, who I knew at Morgan Stanley, still retains a 9% stake after some hefty recent sales and a big say over strategy, seems to approve. This metamorphosis would make Amazon more similar to Apple (AAPL) and Microsoft (MSFT), two older big-tech rivals that have bundled and cross-sold their way to world domination in consumer devices and business software, respectively—and to $3trn valuations.
Retail and advertising appear to be the first to integrate. The thread running through the two businesses is Prime, Amazon’s $139 a-year subscription service, which has 300m-odd members around the world, providing shoppers with free delivery and access to Prime Video. Prime members like me spend twice as much on Amazon’s websites as non-members do and they tend to be logged in more often. Amazon also has intimate knowledge of their shopping behavior, which allows it to target ads more accurately.
Advertising is another great hope at Amazon. Advertisers are willing to pay handsomely for this service: analysts estimate that Amazon’s ads business enjoys operating margins of around a mind-blowing 40%, higher even than those of the cloud operation, not to mention the much less lucrative retail division.
Most of these ads, responsible for four-fifths of the company’s ad sales, are nestled among search results on its app or next to information about products, as with my above-mentioned T-shirts. But a growing share is coming from third-party websites and, most recently, from Prime Video. In January Amazon started showing commercials to viewers in America, Britain, Canada, and Germany.
Analysts reckon that video ads alone will boost Amazon’s ads sales by about 6% this year, adding $3bn to the top line. Given the ad operation’s fat margins, the impact on profit will be considerably larger.
To turn more Prime members into actual ad-watchers, Amazon is splurging on content. It recently signed a contract with Mr. Beast (??), a YouTube superstar, rumored to be worth $100m. It is trying to seal a deal in which it would pay $2bn a year for the rights to show National Basketball Association games on Prime Video. It is already reportedly spending $1bn annually to stream some National Football League (NFL) fixtures.
This hefty price tag is worth it, the company thinks, because popular sporting moments, such as “Thursday Night Football”, have turned out to be among the biggest sign-up days for Prime. Ads aired during sports events are some of the most lucrative in all of the ad business.
Analysts speculate that clever AWS software may also be assisting the retail operation’s 750,000 warehouse robots in sorting shoppers’ packages. And having a business as gigantic as Amazon’s retail arm as a captive customer gives AWS the confidence to scale up, helping spread costs.
The most important thread stitching Amazon’s two main businesses together is generative AI. Most rivals will struggle to match Amazon’s access to specialized AI hardware, which is in short supply but which it has in abundance thanks to long-standing commercial partnerships with companies like Nvidia (NVDA), which makes advanced AI semiconductors.
Amazon’s recent share-price rise was uninterrupted by a Fair Trade Commission lawsuit. But for every cloud customer that AWS loses to rivals such as Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Platform, it could win one that is repelled by Microsoft’s and Google’s new businesses in their own increasingly tightly-knit empires.
It all looks like a giant, super-efficient machine to me which should justify at least a 50% gain in Amazon’s share price in the next year or two.